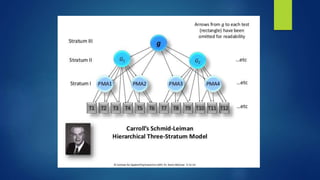
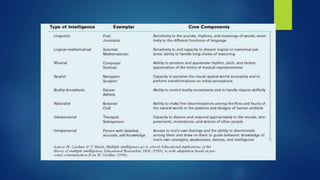
The document discusses various theories of intelligence, highlighting historical perspectives from early tests by Sir Francis Galton to contemporary theories by figures like Gardner and Sternberg. It emphasizes the evolution from factor theories, such as Spearman's g factor, to multifactor, hierarchical, and cognitive process-oriented theories, addressing intelligence's diverse nature and contextual influences. Additionally, it introduces concepts of emotional intelligence and cognitive development through Piaget's stages, as well as distinctions between aptitude and achievement.