1) The document discusses the process of writing materials for English for Specific Purposes (ESP) courses. ESP teachers spend most of their time writing materials because commercially available materials may not be suitable or available.
2) Good ESP materials help organize the learning process by providing a clear path through the language, activities, and a sense of progress. Materials should reflect the nature of language learning and the learning task.
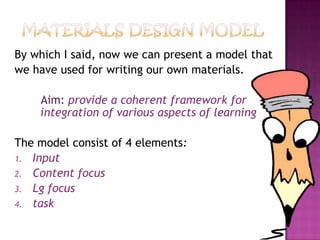
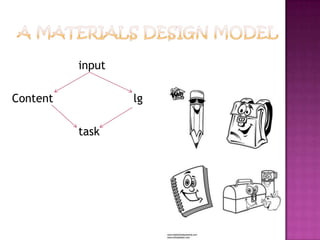
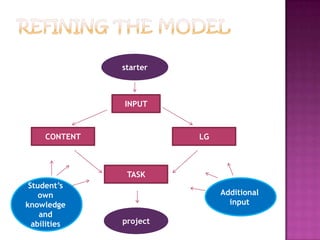
3) The document presents a model for writing ESP materials that includes input, content focus, language focus, and tasks. It provides a framework to integrate various aspects of language learning and ensure coverage of syllabus items.