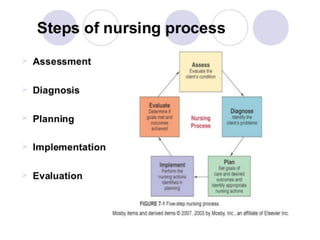
The document discusses the key concepts and steps of the nursing process, including assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. Assessment involves collecting, organizing, validating, and documenting data about the client's health concerns. Nursing diagnosis identifies actual, risk, wellness, possible, or syndrome diagnoses by analyzing data and formulating diagnostic statements. Planning determines how to prevent, reduce, or resolve identified client problems by developing an individualized care plan with goals and nursing interventions.