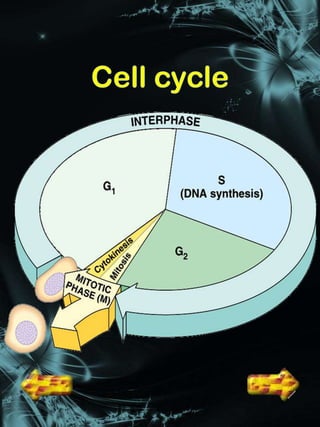
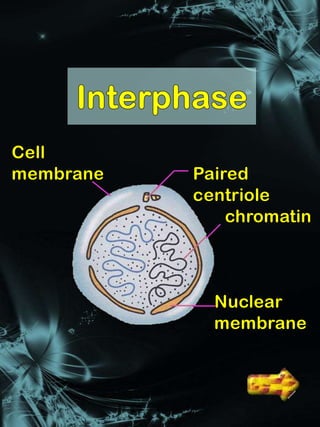
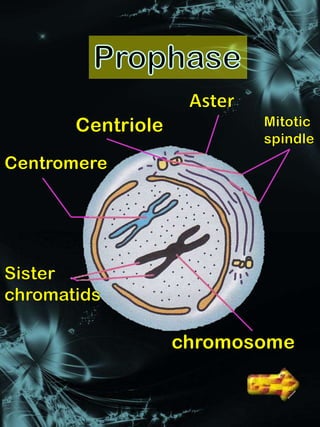
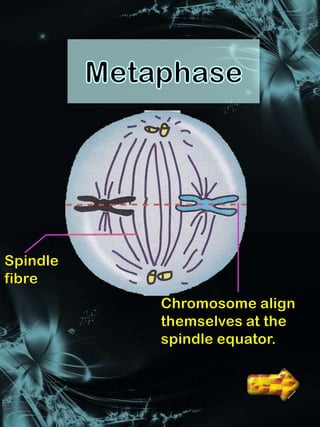
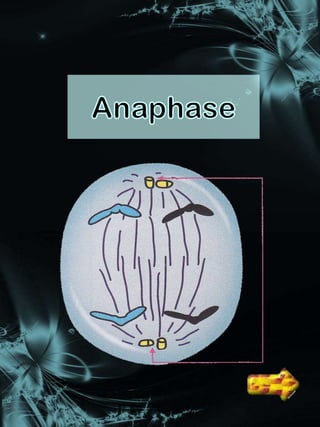
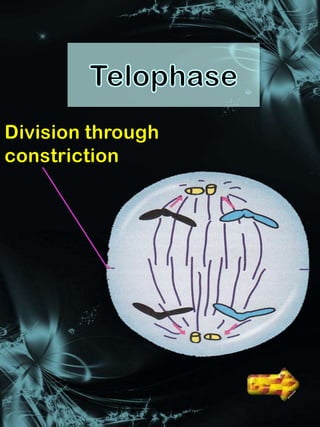
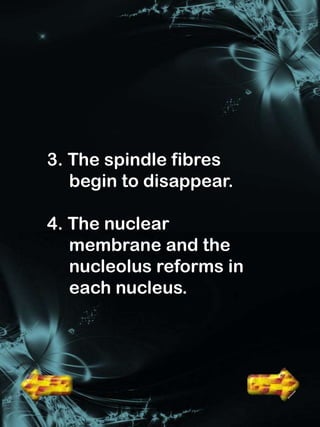
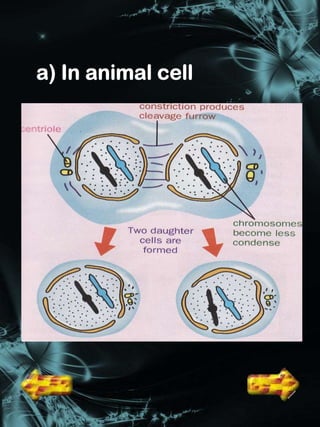
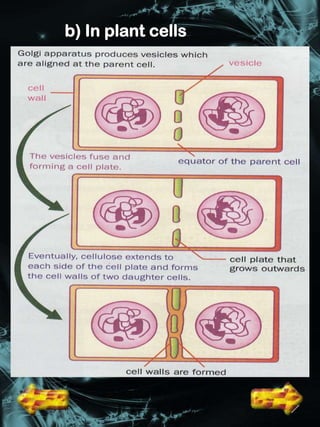
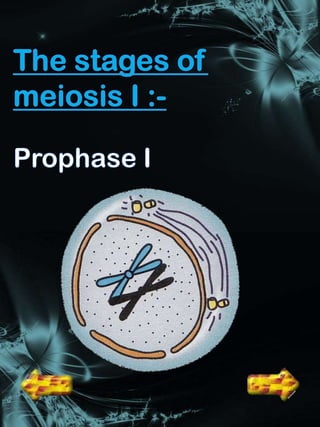
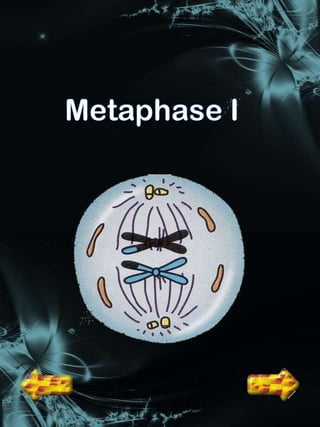
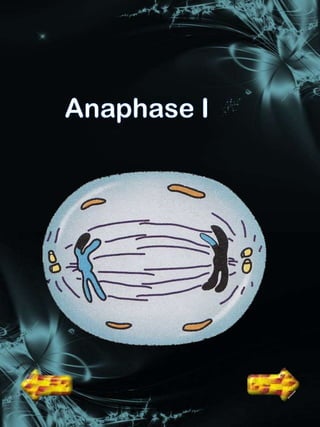
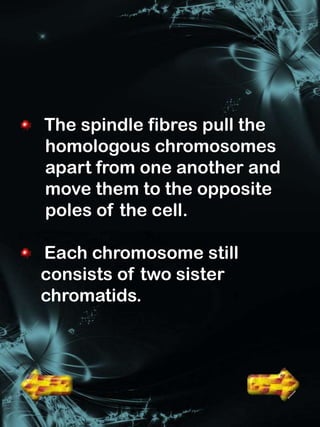
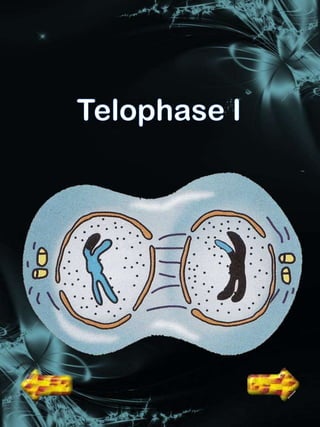
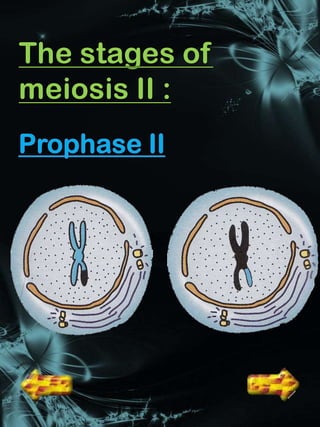
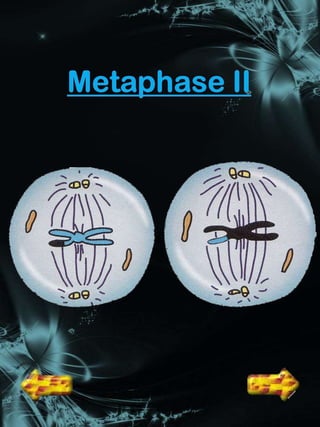
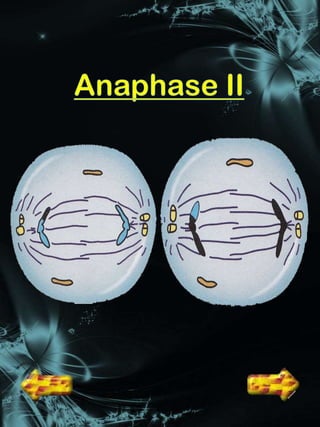
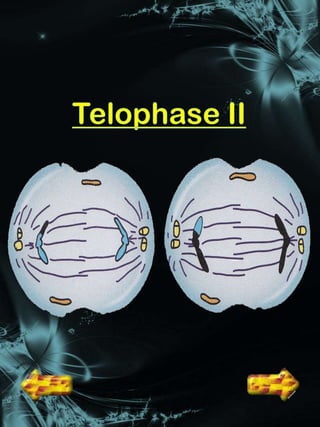
Cell division is a process where a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. It begins with interphase, where the cell grows and duplicates its DNA. Interphase is followed by mitosis, where the nucleus divides into two identical daughter nuclei. Cytokinesis then separates the cytoplasm, forming two or more identical daughter cells each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Meiosis produces gametes with half the normal number of chromosomes through two rounds of nuclear division followed by cytokinesis.