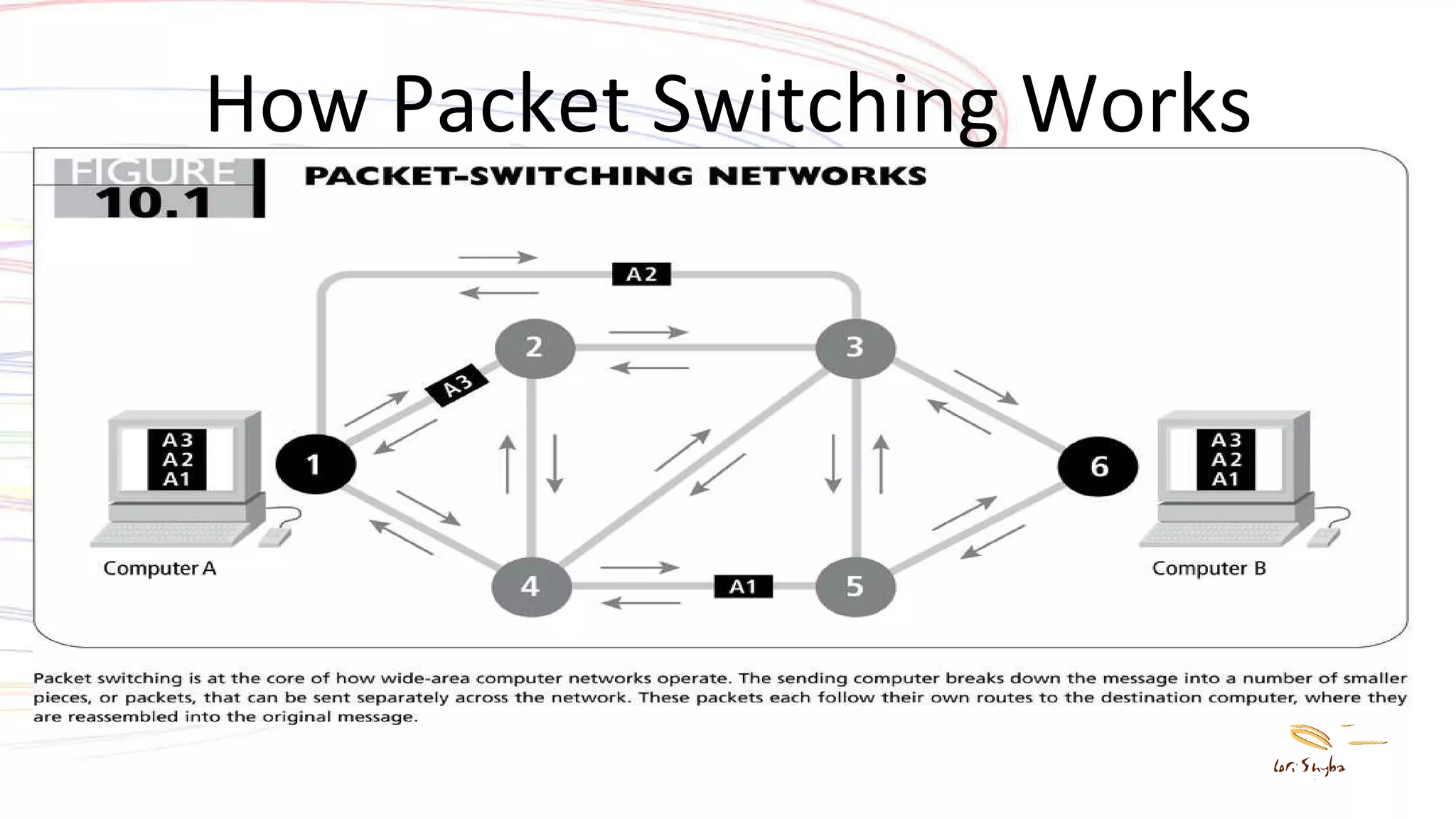
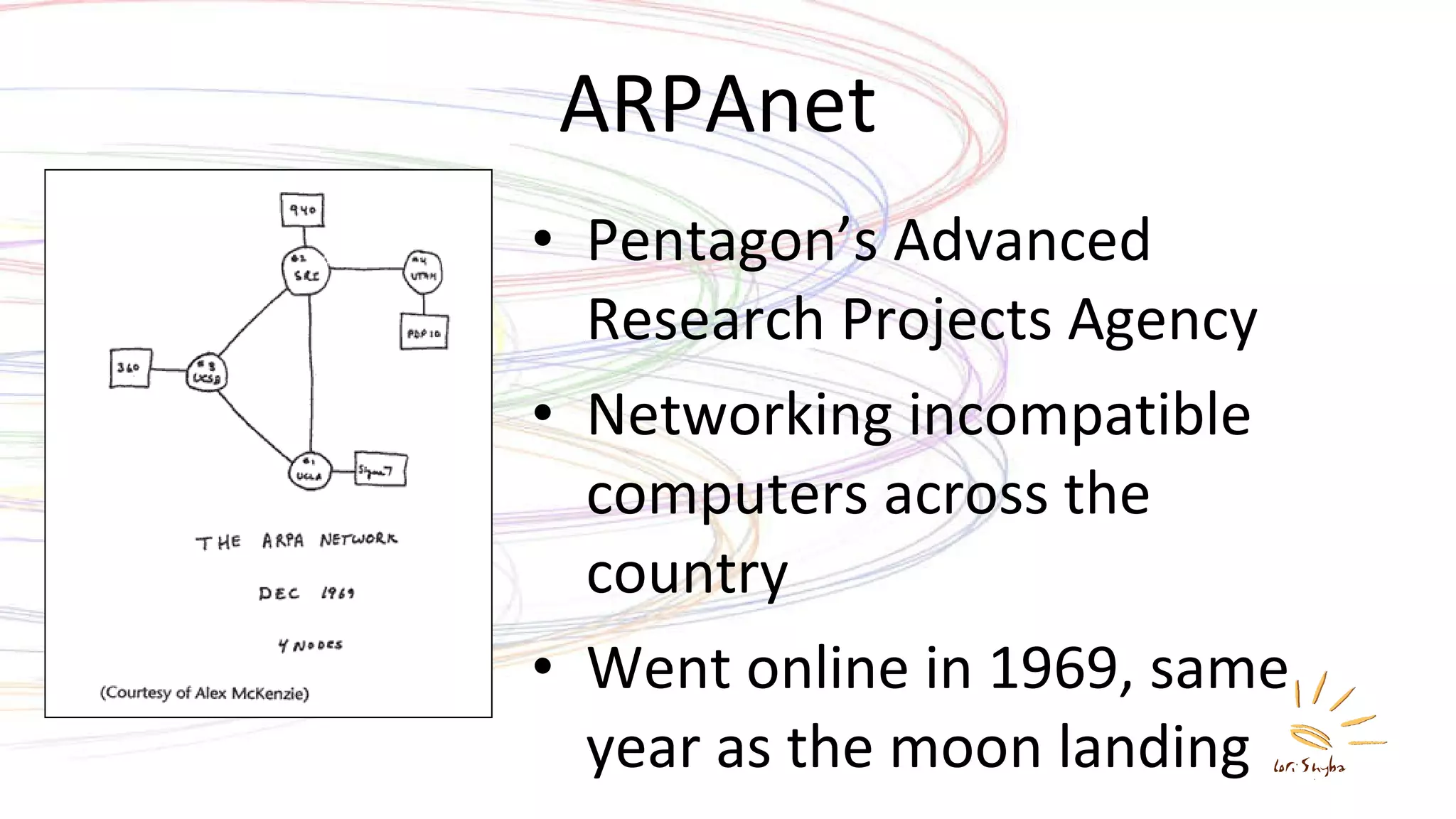
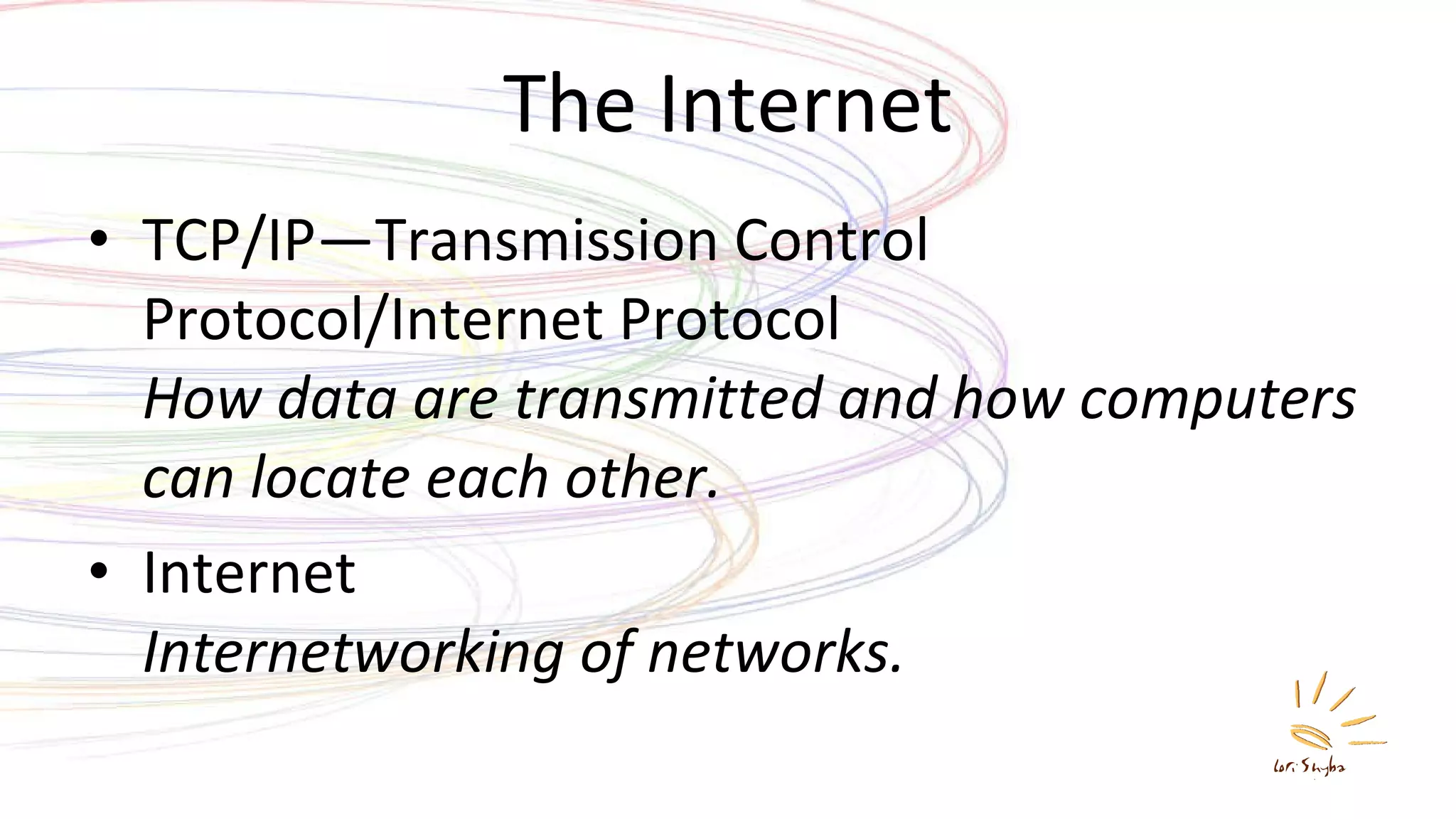
The document discusses the development of the Internet and the World Wide Web. It describes how packet switching networks were developed in the 1960s to allow communication between incompatible computers. This led to the creation of ARPANET and the development of TCP/IP protocols to allow internetworking. The World Wide Web was created by Tim Berners-Lee in the late 1980s and early 1990s, introducing HTML, URLs, and HTTP to allow sharing of documents over the Internet. Today the Internet and Web incorporate elements of interpersonal, group, and mass communication and are major platforms for entertainment, news, and social interaction.