This document provides guidance on writing the introduction and defining the problem for a thesis. It discusses including background information, the problem statement, objectives, significance and delimitations in the introduction. For the problem, it recommends stating it in question form and defining key terms. Variables should also be identified, including independent, dependent, intervening and moderator variables. The problem scope can be focused by delimiting aspects like purpose, time period, location, variables studied, and respondent types and size.




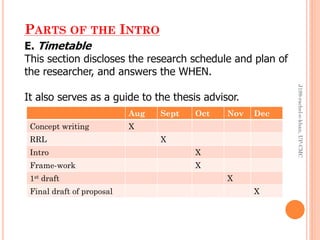
![PARTS OF THE INTRO
A. Background of the Study.
This section must contain the following:
1. An introduction of the communication or media concern that the
work seeks to discuss using historical and baseline data (e.g.,
timelines, statistical trends,
population data, media facts and figures), and qualitative insights
(e.g., quotations, anecdotes, reviews);
2. An introduction and explanation of the chosen cases (e.g., a
media organization, the population of young adults, a specific
geographical area) that are going to be used to study the
communication or media concern.
[For example, the introduction first introduces corruption in media
outlets by explaining envelopmental and checkbook journalism. It
then explains why beat reporters are the best people to study for
this type of corruption in media.]
J199-rachel-e-khan,UP-CMC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/writingthethesis-150922062940-lva1-app6891/85/Writing-the-thesis-5-320.jpg)