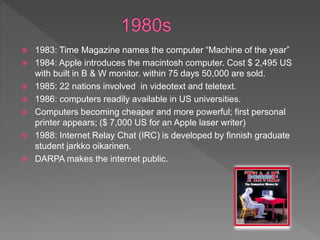
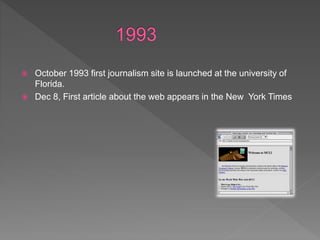
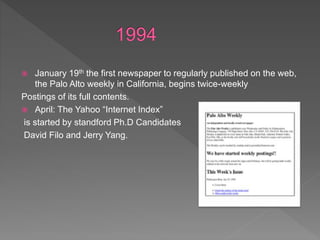
Online journalism allows for global distribution of information through the internet. It provides unlimited space, interactivity through user participation and comments, and immediacy of publishing. However, it also faces weaknesses like issues of credibility due to a lack of gatekeeping and verification, accuracy versus speed of publishing, and the digital divide.