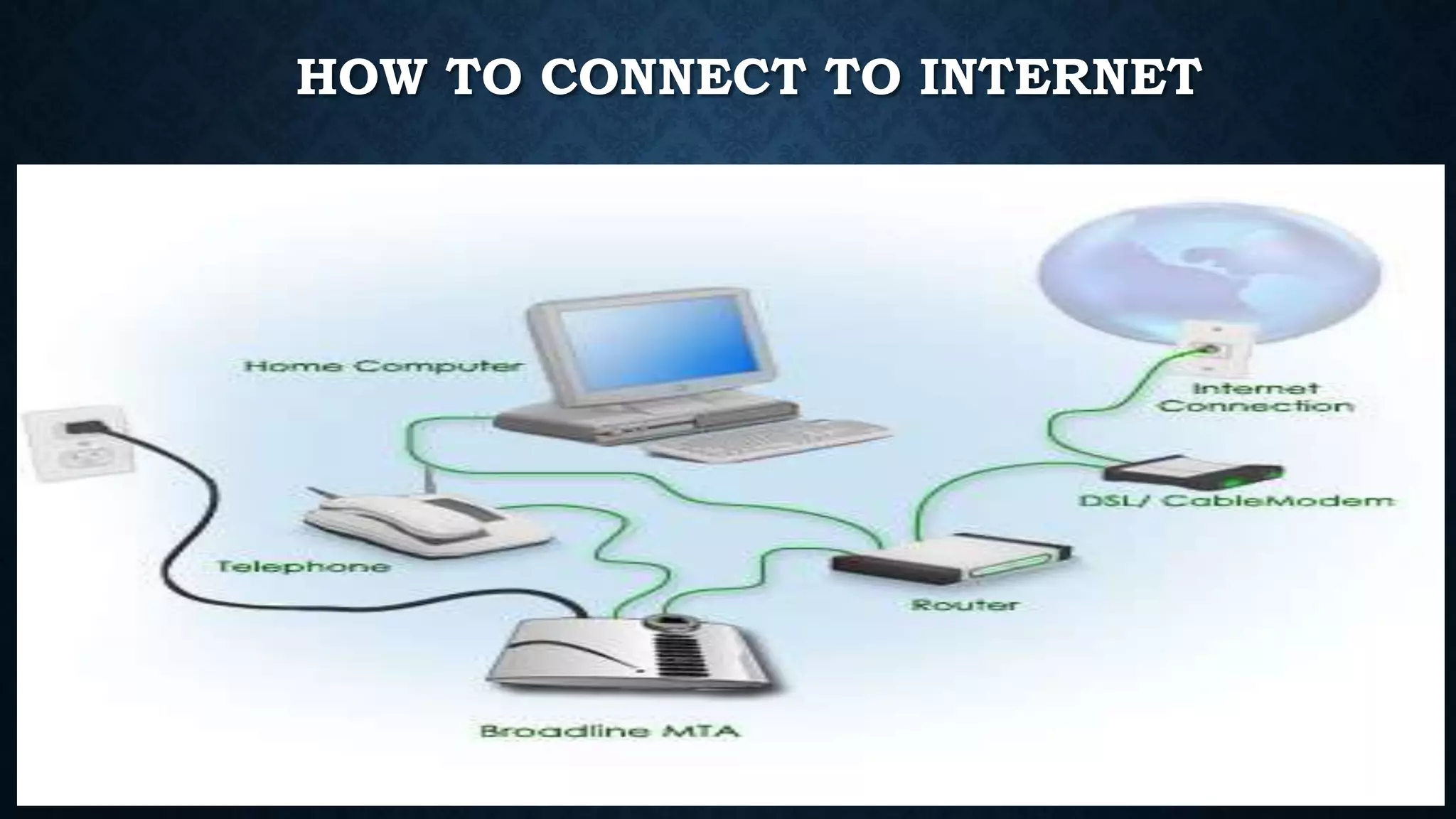
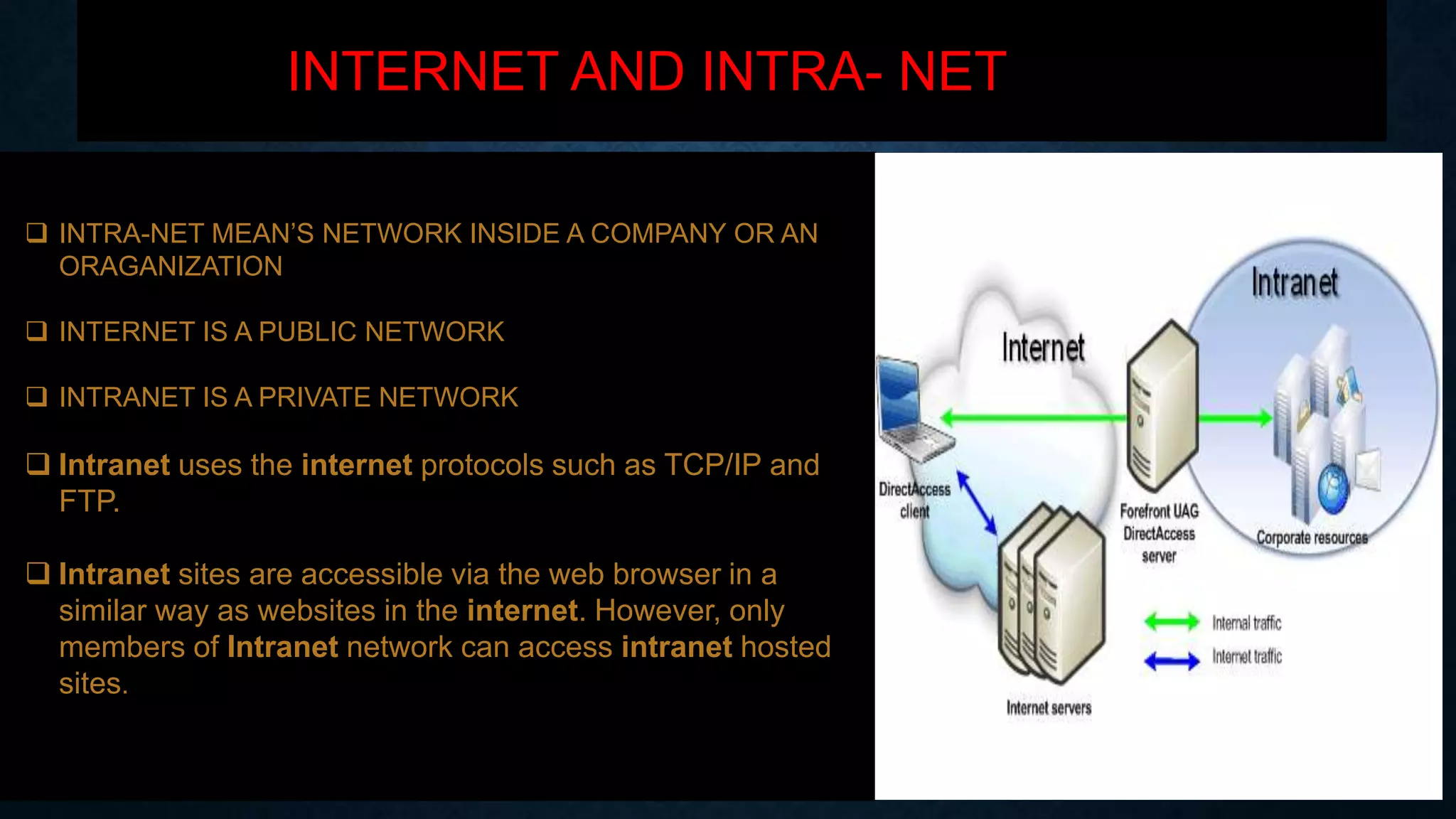
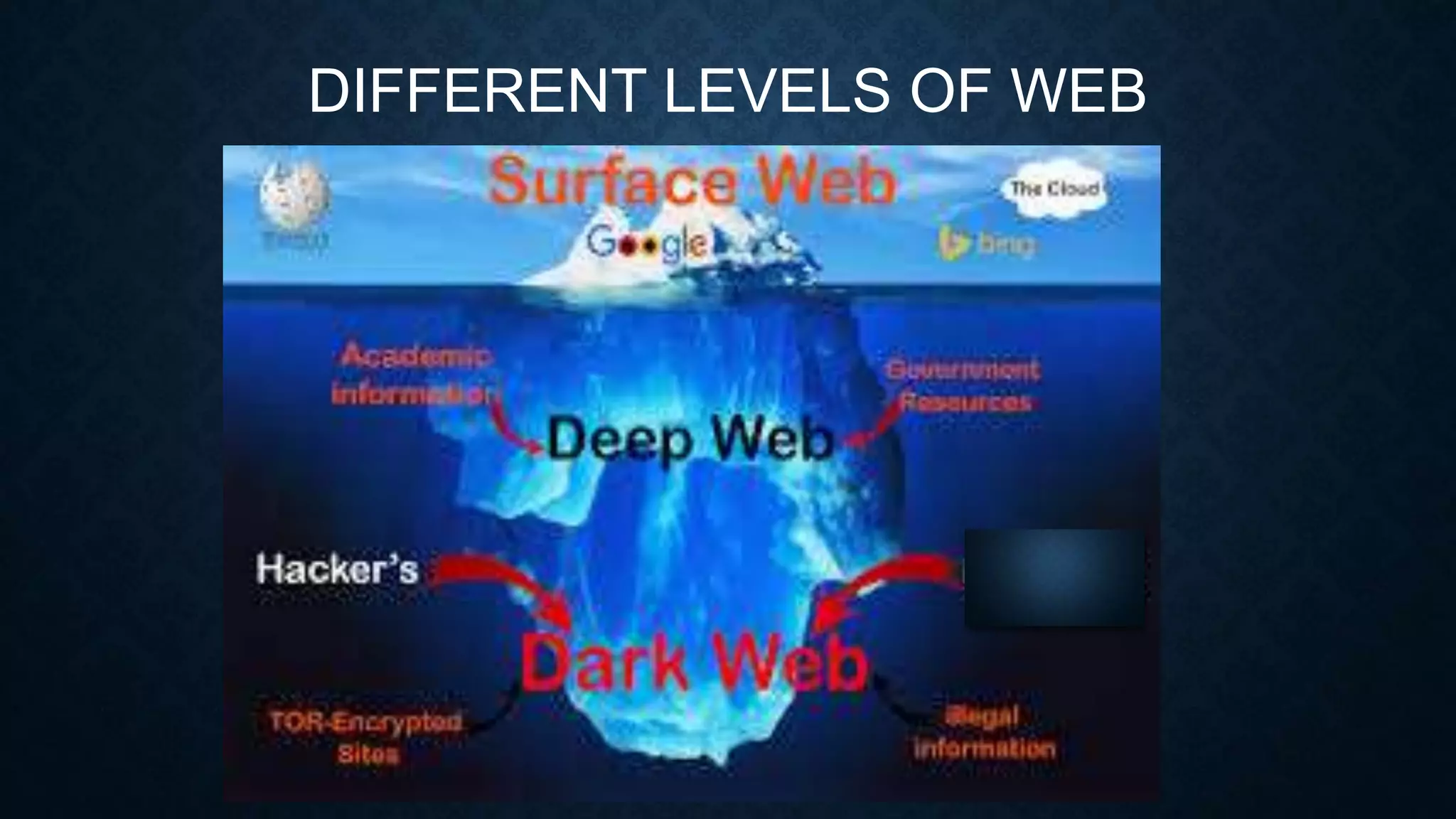
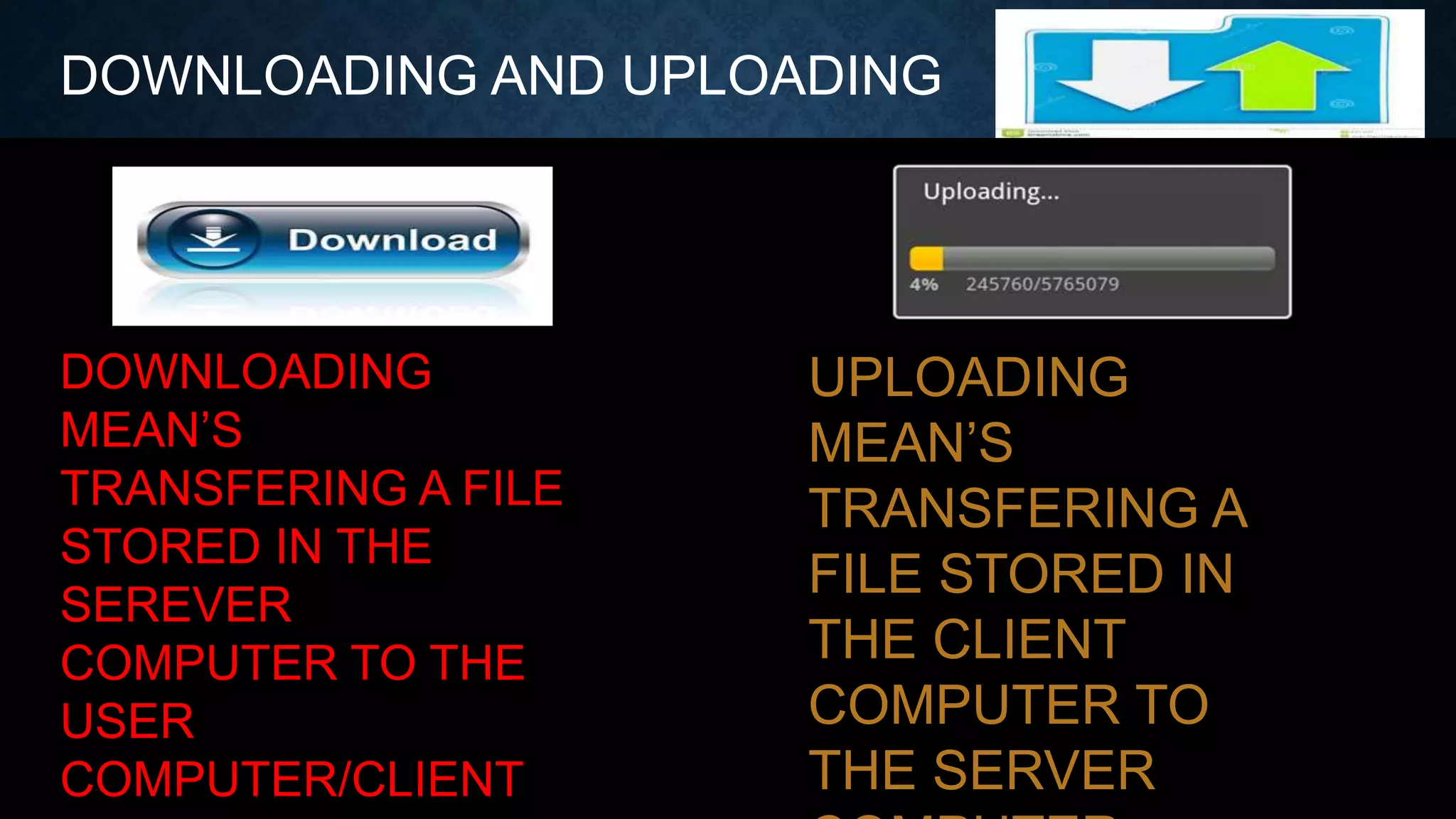
The presentation by Muhammed Shaloof details the history, workings, and various services of the internet, highlighting its evolution from ARPANET in 1969 to a vast global network. It distinguishes between the internet and the World Wide Web, explaining that while the internet connects networks, the web is a way to access information on these networks through web pages and browsers. The presentation also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of internet usage including faster communication, e-commerce, and the risks of personal information theft and cyber crimes.