The human eye. group 1
- 2. By Isaac koomson Nkansah Thomas Gerald marquaye Larbi Papa Kwasi Emmanuel Addai Bridget Fobie Mathias Domlan
- 3. • INTRODUCTION AND ANATOMY OF THE EYE • PARTS OF THE EYE AND THEIR FUNCTIONS • BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE EYE • INNERVATION OF THE EYE • EYE PATHOLOGIES AND VISION PROBLEMS • RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCE OF THE EYE • IMAGING PROCEDURES OF THE EYE
- 4. • 70% of all sensory receptors are in the eye. • The human eye can differentiate between 10 million colours and is possibly capable of detecting a single photon. • The human eye is a sense organ that allows vision. • Human eyes help to provide three dimensional, moving image, normally coloured in daylight
- 5. Includes • bony orbit • eyelids • eyelashes • fat glands • extra ocular muscles • conjunctiva
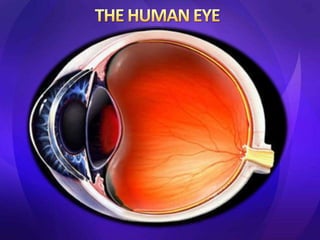
- 7. • Sclera: outer white layer; maintains the shape of the eye; muscles attached control eye movement • Choroid : contains blood vessels • Retina : innermost light-sensitive membrane covering the back wall of the eyeball.
- 10. • The eye is not shaped like a perfect sphere. It is a fused two-piece unit, composed of the anterior segment and the posterior segment. • The anterior segment is made up of the cornea, iris and lens. The cornea is transparent and more curved, and is linked to the larger posterior segment, composed of the vitreous, retina, choroid and the outer white shell called the sclera. • The cornea is typically about 11.5 mm (0.3 in) in diameter. • The cornea and sclera are connected by an area termed the limbus. The iris is the pigmented circular structure concentrically surrounding the center of the eye, the pupil, which appears to be black. • The size of the pupil, which controls the amount of light entering the eye, is adjusted by the iris' dilator and sphincter muscles.
- 12. • The eye is divided into anterior and posterior chambers by the iris. • Anterior portion is filled with aqueous humor where as the posterior is fi lled with vitreous humor. • Aqueous humor: -clear liquid -inflates eye (intraocular pressure). -Nourishes cornea and lens -Provides clear medium for passage of light • Vitreous humor: -Clear, gel-like mass of water and proteins. -Gives shape to the eye. -Holds retina in place against choroid. -Allows easy passage of light.
- 13. There are four rectus and two oblique muscles • Lateral rectus • Medial rectus • superior rectus • Inferior rectus • Inferior oblique • Superior oblique
- 14. Rods and Cones • rod cells: light sensors – 120 million – Functions in less intense light – Used in peripheral vision – Responsible for night vision – Detects black, white and shades of grey • cone cells: detects colour – 7 million – Highest concentration at fovea centralis – Functions best in bright light – Perceives fine details – 3 types of cone cells, each sensitive to one of the three primary additive colours: red, green, and blue
- 15. • transparent covering of the front of the eye • Allows for the passage of light into the eye and it also focuses the light
- 16. the hole where light enters into the eye
- 17. (coloured part) coloured part of eye controls the amount of light entering the eye
- 18. • SCLERA – a tough white skin (made of tissue) that covers all of the eyeball except the cornea
- 22. • On retina where optic nerve leads back into the brain • No rod or cone cells • Other eye compensates for this area
- 23. • The arterial input to the eye is provided by several branches from the ophthalmic artery, which is derived from the internal carotid artery in most mammals. • Venous outflow from the eye is primarily via the vortex veins and the central retinal vein, which merge with the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins that drain into the cavernous sinus, the pterygoid venous plexus and the facial vein.
- 24. • It is a system of protective features that keeps blood borne particles from upsetting the control and stable environment for the proper functions of the optic nerves. • The two components are • Retina vessels and the choroid.
- 25. • Sensory innervation is from the trigeminal (fifth) cranial nerve, via the ophthalmic division (upper lid) and maxillary division (lower lid). • The orbicularis oculi is innervated by the facial (seventh) nerve. • The levator muscle in the upper lid is supplied by the oculomotor (third) nerve
- 26. • The optic nerve II: enters the orbit through the optic foramen and passes to the light receptor cells in the retina. • It allows the movements of the eye and is covered by meninges that it acquired during its development. • The Oculomotor nerve III: control the movement of the eyeball. it enters the orbit through the orbital fissure. – Supply: inferior, medial, Superior Rectus muscle – inferior oblique muscle • The abducens nerve VI: enters through the orbital foramen and innervates most of retractor bulbi and lateral rectus muscles.
- 27. • Parasympathetic fibres to the lacrimal gland pursue a complex course, passing with the facial nerve and then following the maxillary division of the trigeminal. • The sensory and parasympathetic nerve fibres reach the eyeball via the short and long ciliary nerves which pierce the sclera posteriorly.
- 28. • Age-Related Macular Degeneration • Bulging Eyes(proptosis) • Cataracts • CMV Retinitis • Color Blindness • Crossed Eyes (Strabismus) • Diabetic Macular Edema • Glaucoma • Keratoconus • Retinal Detachment • Uveitis • Eyelid Twitching
- 29. • Myopia (near sightedness) • Hyperopia (far sightedness) • Presbyopia • Astigmatism
- 30. • inability of the eye to focus light from distant objects • see close objects clearly • image focuses in front of the retina • Develops in childhood and progressively worsens • Tends to stabilize in adulthood • Has a genetic component • Affects a major part of the population
- 31. Cause: • Distance between lens and retina is too long (long eyeball) • Cornea & lens converge light too strongly • (strong refractive power) • Corrected with a diverging lens
- 32. • inability of the eye to focus light from near objects no difficulty seeing distant objects • Babies are born slightly hyperopic. As eye grows, condition fixes itself. • image focused behind retina Cause: • Distance between lens and retina is too small (short eyeball) • Cornea & lens is too weak (doesn’t Diverge rays enough) • Corrected with converging lens
- 35. • X-RAY • ULTRASONOGRPHY • CT SCAN • MRI
- 36. • Not commonly used nowadays • A three-dimensional structure is seen in two dimensional plane, giving rise to disturbing superimposition. • Moreover, its sensitivity to small differences in the attenuation is low, i.e., its contrast resolution is poor Positions in imaging • WATERS VIEW • CALDWELL’S VIEW • LATERAL VIEW • SUBMENTOVERTEX VIEW • RHESE VIEW
- 37. ADVANTAGES: • BONY DETAILS /CALCIFICATION • STRUCTURES LIKE EOM, OPTIC NERVECAN BE VISUALISED • IN ORBITAL TRAUMA FOR DETECTING DISADVANTAGES • INABILITY TO DISTINGUISH BETWEEN PATHOLOGICAL SOFT TISSUE MASS WHICH ARE RADIOLOGICALLY ISODENSE • RADIATION INDUCED CATARACT
- 38. Advantages of MRI Excellent soft tissue details • Entire course of optic nerve well studied • No exposure to radiation • Disadvantages: • Less sensitive for detecting bony abn. And calcification. • Fat saturation artifacts can mimic pathology. MRI in retinoblastoma &cavernous hemangioma
- 39. • Non invasive • Well tolerated • Safe technique Perineural inflammation of optic nerve
- 40. THANK YOU