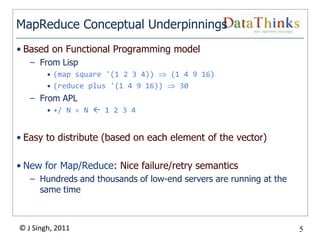
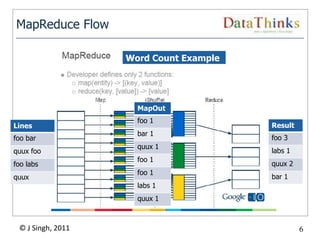
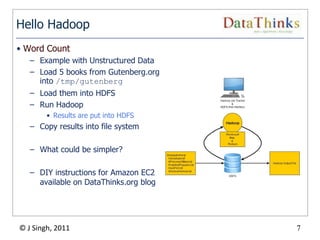
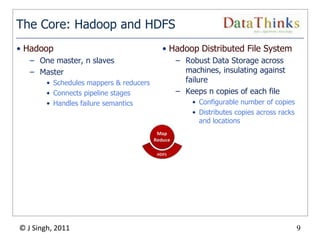
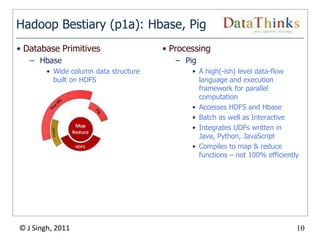
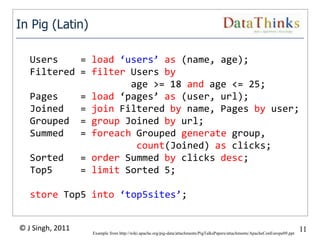
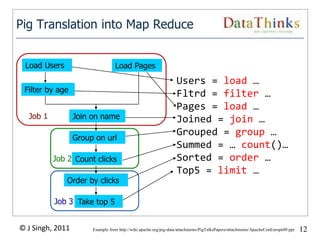
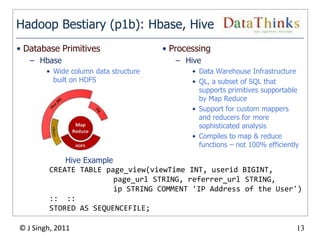
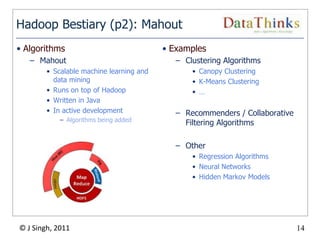
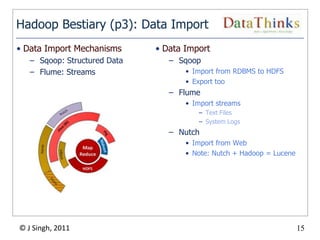
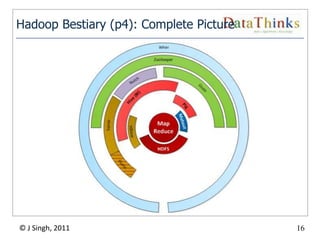
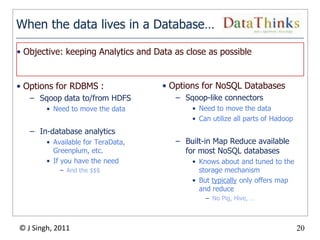
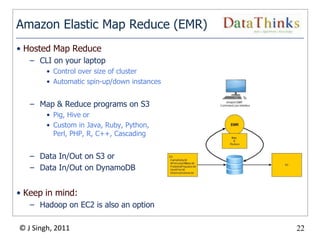
The document provides an overview of the Hadoop ecosystem. It introduces Hadoop and its core components, including MapReduce and HDFS. It describes other related projects like HBase, Pig, Hive, Mahout, Sqoop, Flume and Nutch that provide data access, algorithms, and data import capabilities to Hadoop. The document also discusses hosted Hadoop frameworks and the major Hadoop providers.