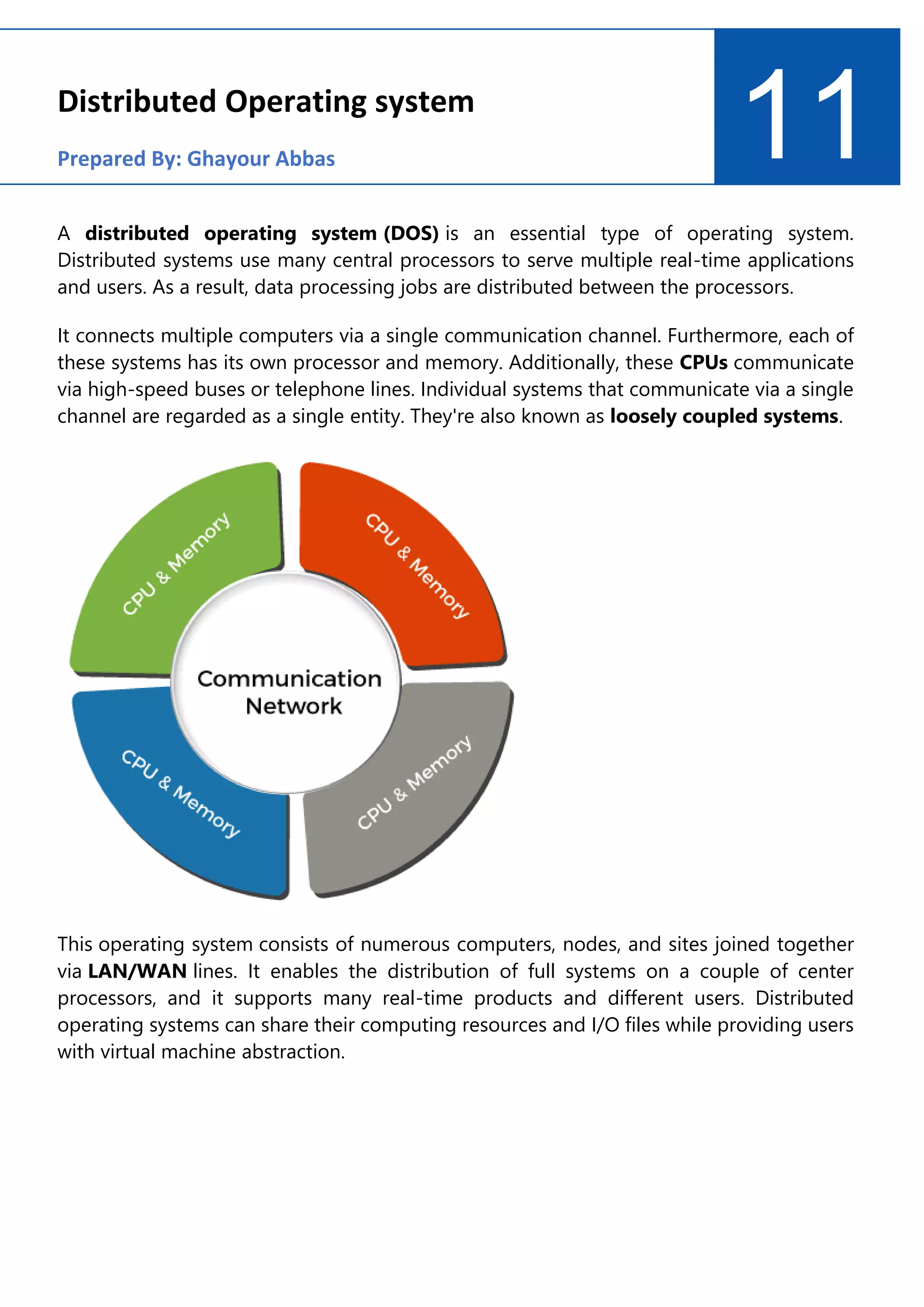
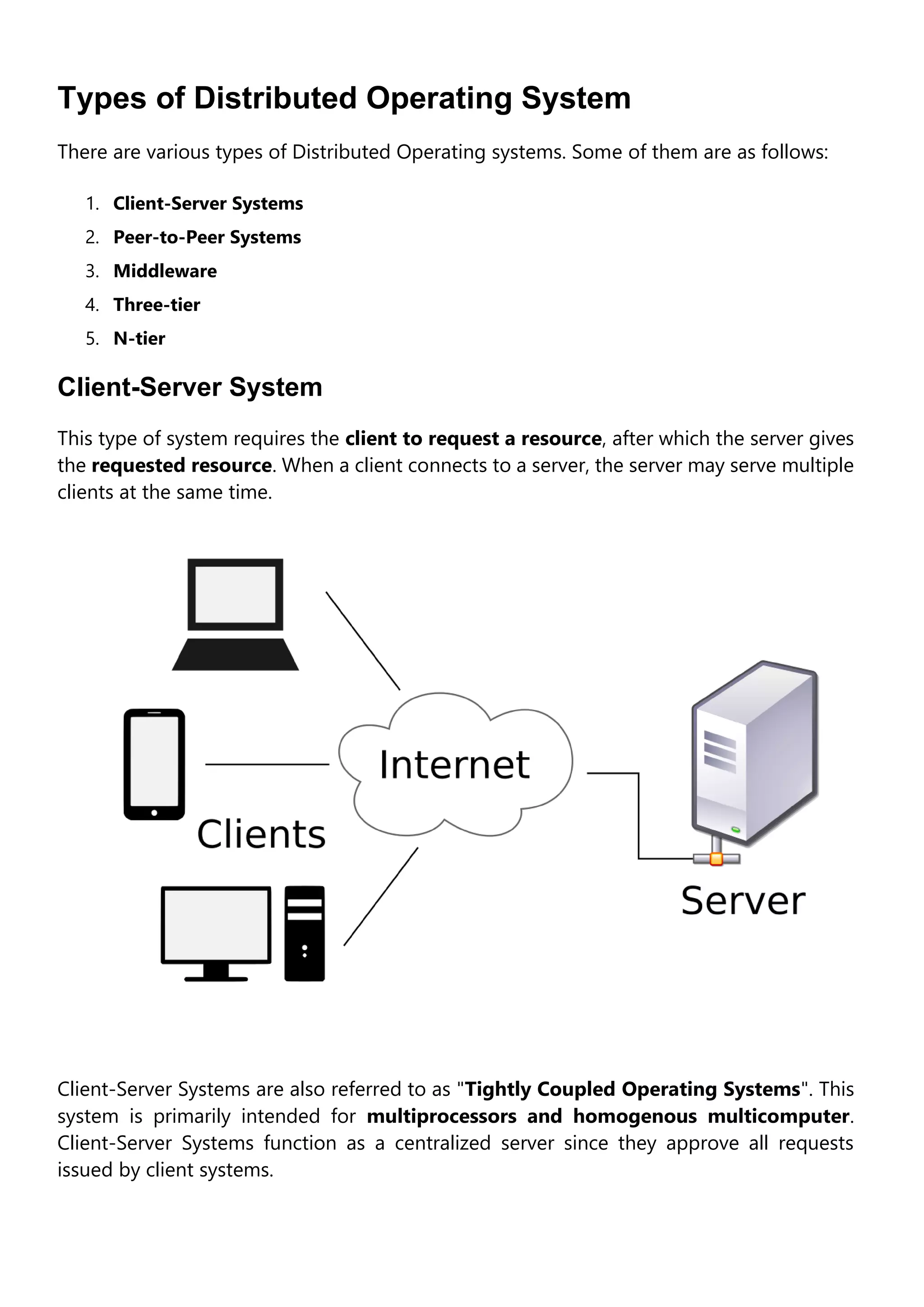
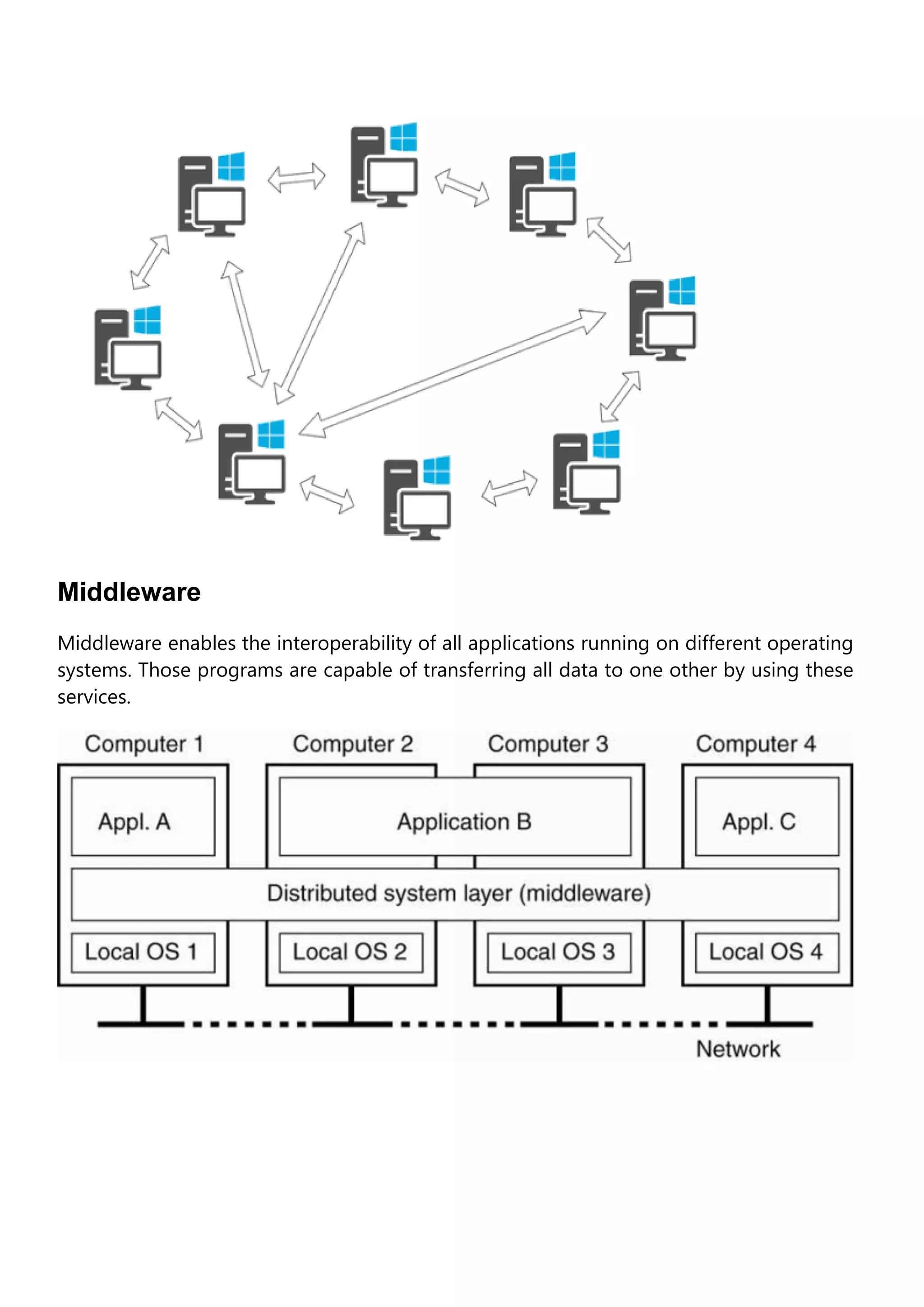
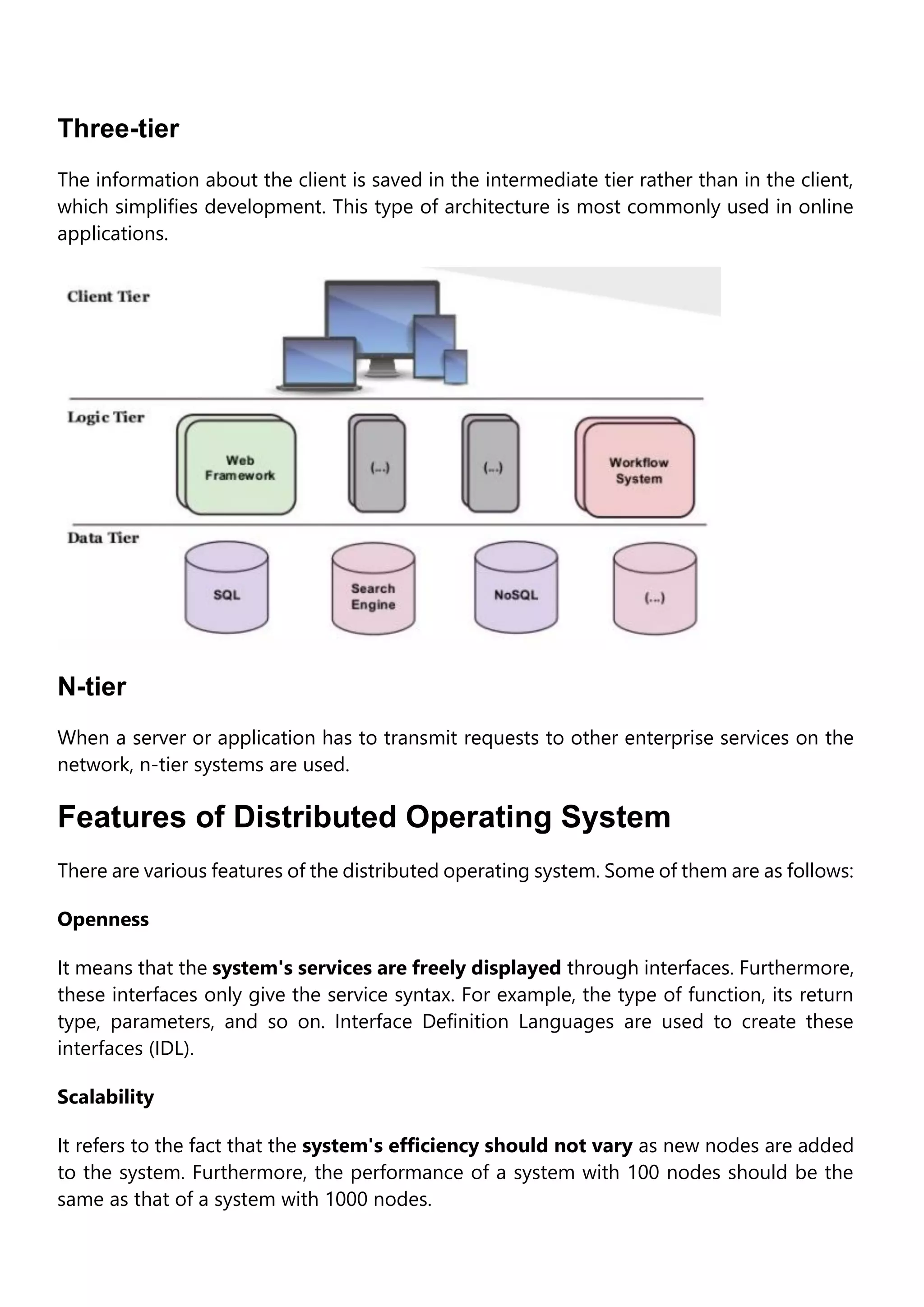
A distributed operating system connects multiple computers via a single communication channel. It allows for the distribution of computing resources and I/O files across several central processors to serve multiple users and real-time applications simultaneously. Distributed operating systems come in various types, including client-server systems, peer-to-peer systems, middleware, three-tier, and n-tier architectures. Their key features are openness, scalability, resource sharing, flexibility, transparency, and heterogeneity. Examples include Solaris, OSF/1, Micros, and DYNIX. Distributed operating systems find applications in network applications, telecommunication networks, parallel computation, and real-time process control.