Embed presentation
Downloaded 69 times

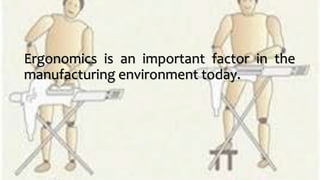
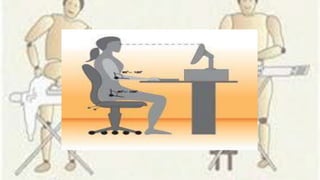







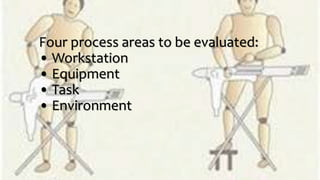

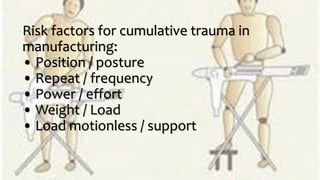




The document emphasizes the significance of ergonomics in manufacturing, highlighting its role in improving the relationship between workers and their environment to reduce injuries. It outlines components of an effective ergonomics program, such as management commitment and job analysis, alongside key risk factors contributing to cumulative trauma. By evaluating workstations, equipment, tasks, and surroundings, and incorporating employee feedback, manufacturers can create a safer and more efficient workplace.

















