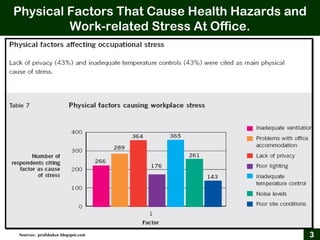
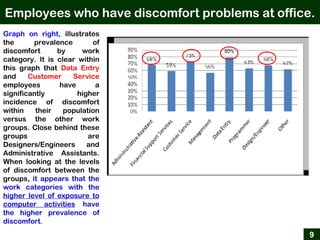
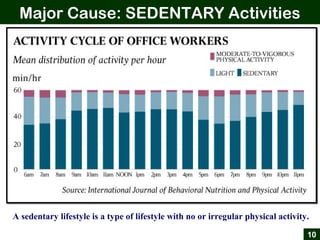
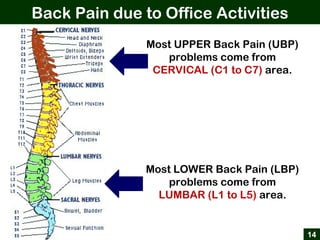
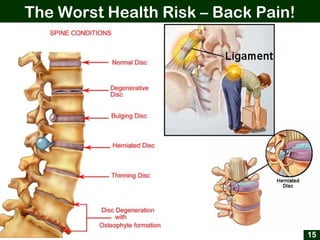
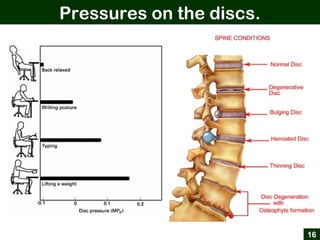
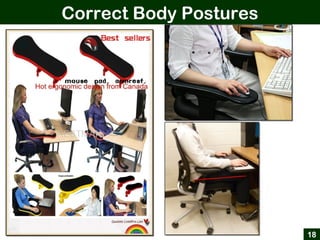
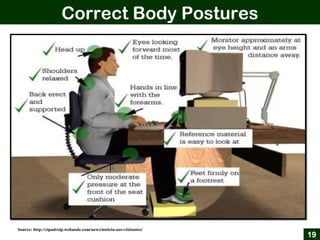
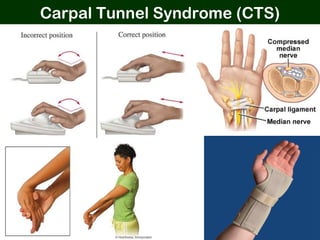
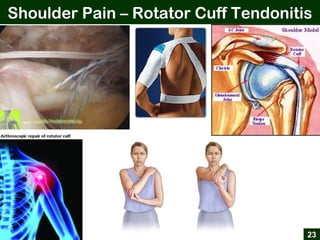
This document provides an overview of office ergonomics presented by Associate Professor Abdul Shukor. It begins by outlining the objectives of discussing national regulations on occupational safety and health hazards, office ergonomics, and practical countermeasures. It then discusses physical and environmental factors that can cause health issues and stress at the office, including sedentary lifestyles. Specific issues addressed include awkward postures, slippery floors, lighting, and improper chairs. The document emphasizes the risks of prolonged sitting and identifies back pain as a major risk. It provides tips for correct posture and suggests countermeasures like forming safety committees, identifying hazards, selecting solutions, and implementing workplace exercise programs.