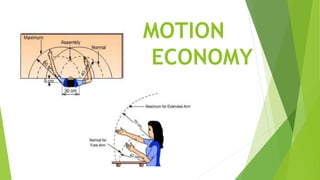
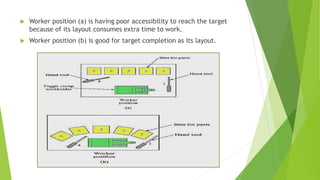
Motion economy is a process aimed at minimizing physical and perceptual demands on workers by optimizing workplace layout and processes. It involves four main principles: reducing the number of motions, performing motions simultaneously, shortening motion distances, and making motions easier. The application of these principles is relevant across various fields including machining, maintenance, assembly, and office work.