This document provides an overview of ergonomics and musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) including:
1. Defining ergonomics as modifying jobs to fit people's capabilities and reduce MSDs through engineering controls, safe work practices, and PPE.
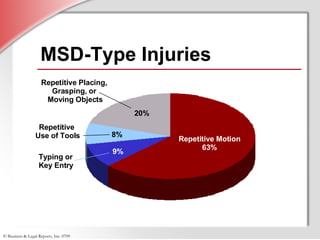
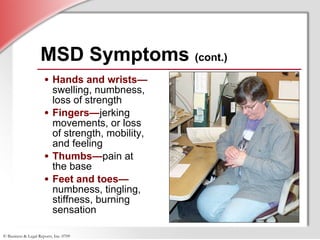
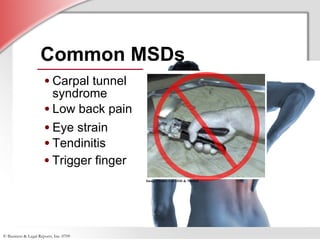
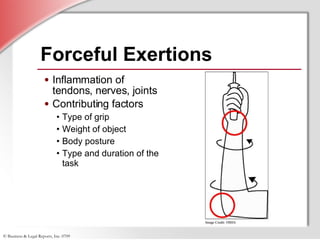
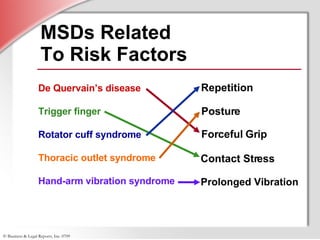
2. Detailing that MSDs are injuries caused by repetitive motions, forceful exertions, awkward postures, contact stress, or vibrations and affect over 1.8 million workers annually.
3. Explaining employers have a general duty to provide a hazard-free workplace under OSHA regulations regarding unregulated hazards like MSDs.