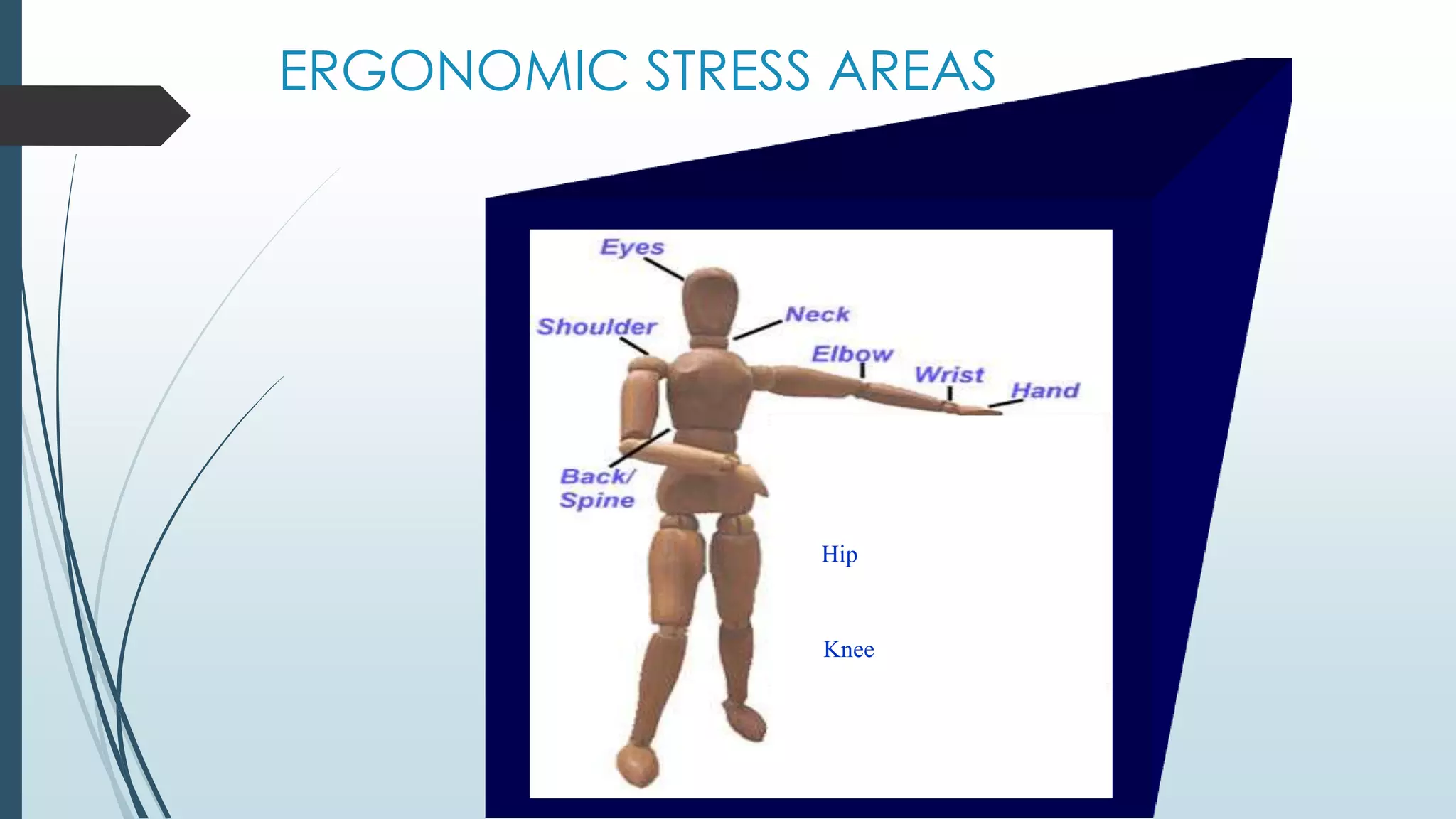
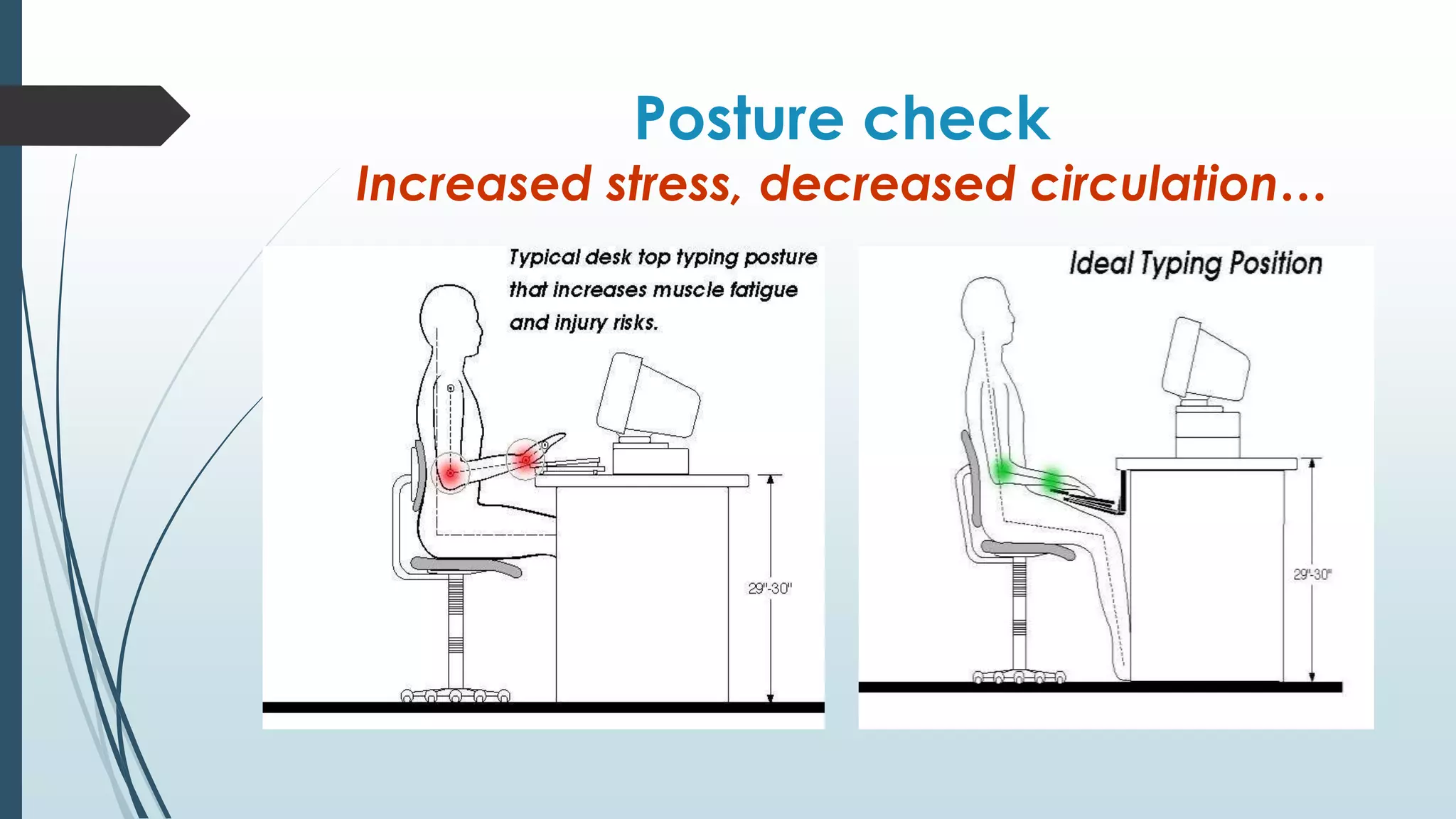
Ergonomics is the study of people's efficiency in their working environment and focuses on preventing repetitive stress injuries. It considers differences in individual workers as well as environmental and physical stressors. The document outlines key ergonomic principles like permitting various postures and using large muscle groups. It discusses common injuries from overexertion and improper lifting as well as how to address issues through stretching, taking breaks, and assessing task setups. Proper ergonomics of computer workstations, equipment sizes, and neutral postures are emphasized.