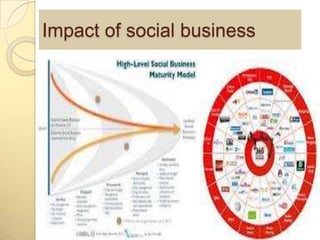
The document discusses the evolution of media from traditional to social media. It notes that traditional media like newspapers struggled to keep up with rapidly changing technology. Social media allows for two-way conversation and has changed how news is covered and consumed by giving audiences direct access. The rise of social media has brought issues of media trust, local news coverage, and how social media will influence journalism to the forefront. Overall, the document examines the shift from traditional to social media and some of the impacts and opportunities this shift has created.