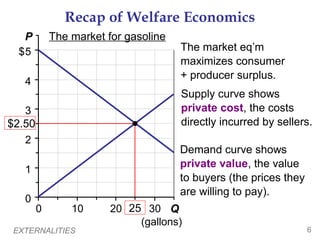
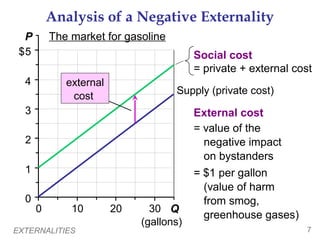
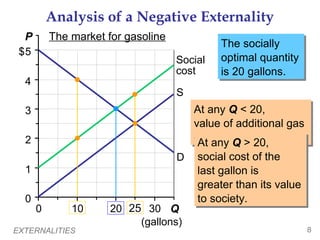
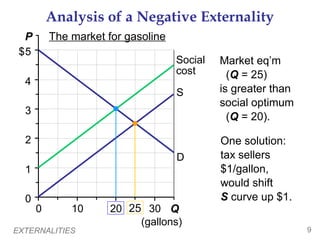
This document provides an overview of externalities and how they can lead to inefficient market outcomes. It discusses:
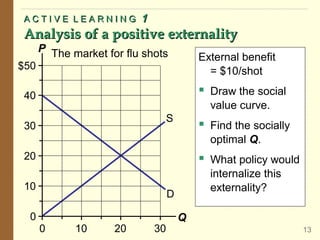
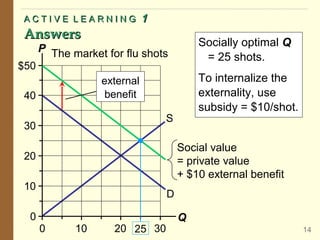
1) What externalities are and how they can be negative or positive, depending on their impact on third parties. Negative externalities like pollution mean the market produces too much of a good, while positive externalities mean too little is produced.
2) How public policies like taxes or subsidies can "internalize" externalities by making producers and consumers consider these external impacts. A tax on pollution would align private and social costs, leading to the efficient level of production.
3) Examples of both negative externalities like air pollution and positive externalities like vaccination. The document analyzes these situations using demand