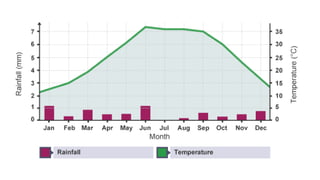
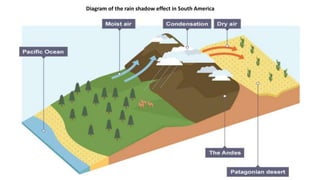
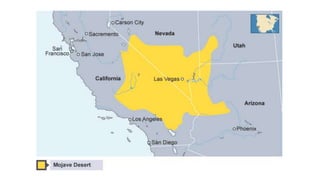
The document discusses the characteristics and challenges of desert climates, focusing on Las Vegas and the Mojave Desert. It highlights extreme temperature variations, low rainfall, survival adaptations of plants and animals, and human impacts such as urban growth and water management issues. Key problems include soil erosion, desertification, and cultural changes due to population increase and tourism.