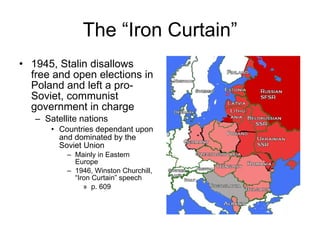
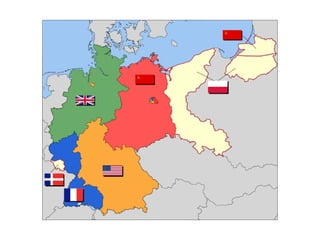
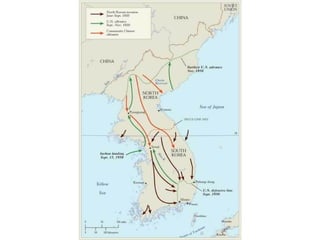
The document summarizes key events in the early Cold War between 1945-1963, including the establishment of Soviet satellite states in Eastern Europe, the Truman Doctrine and Marshall Plan to contain communism, the Berlin Airlift and formation of NATO, China falling to communism, the start of the Korean War, Eisenhower's presidency and civil rights issues, the Cuban Missile Crisis under JFK, and America's space program.