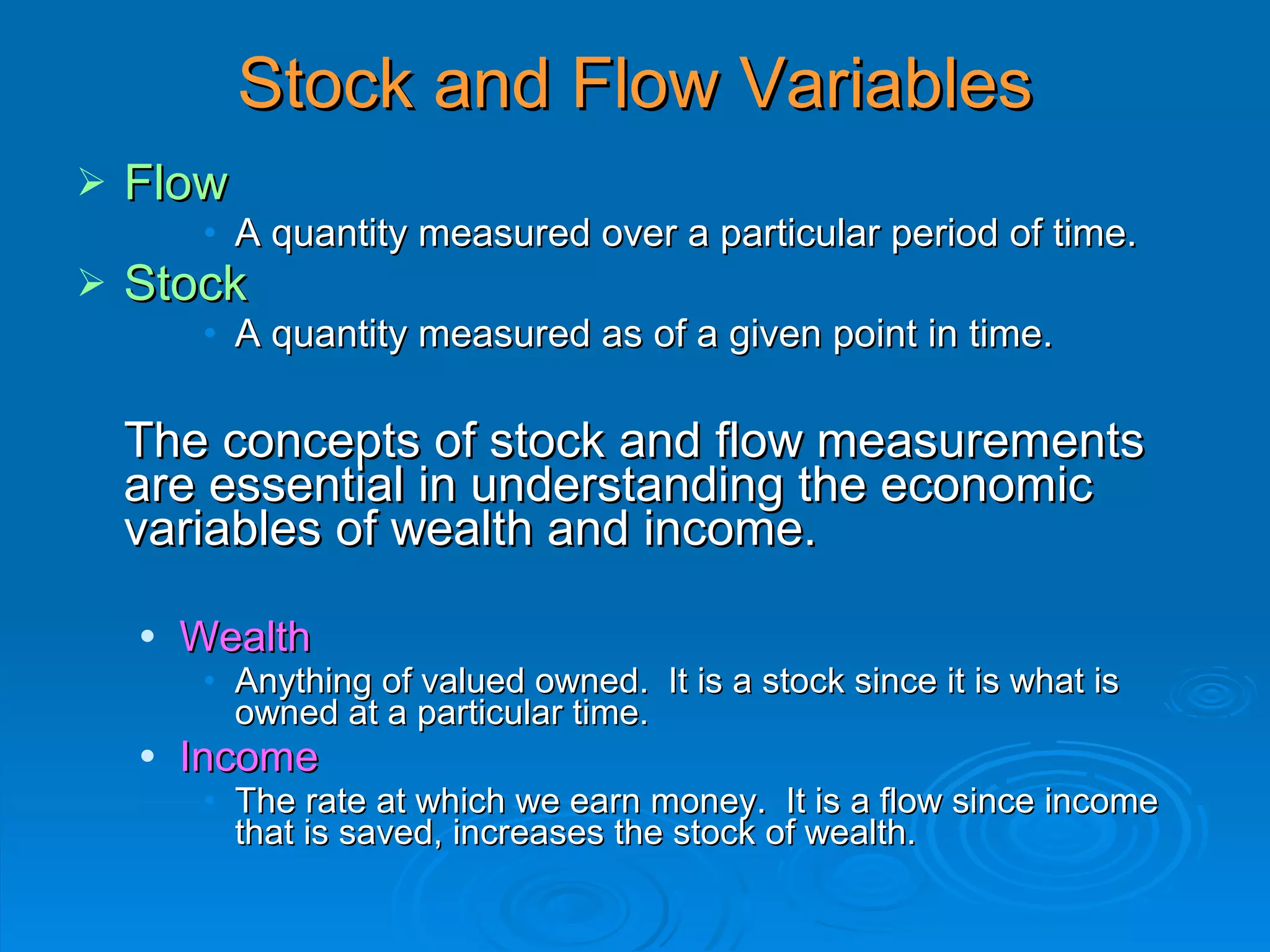
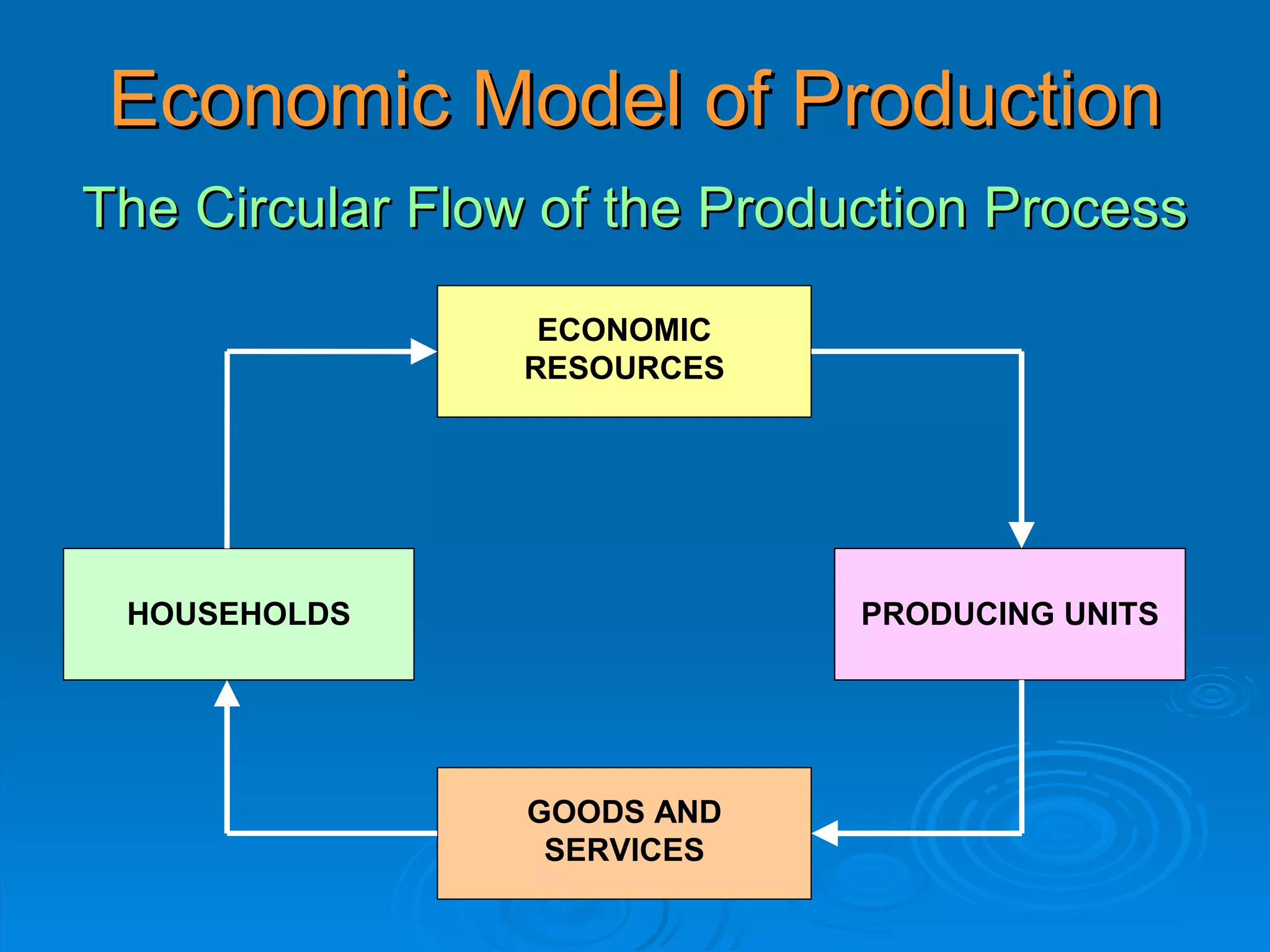
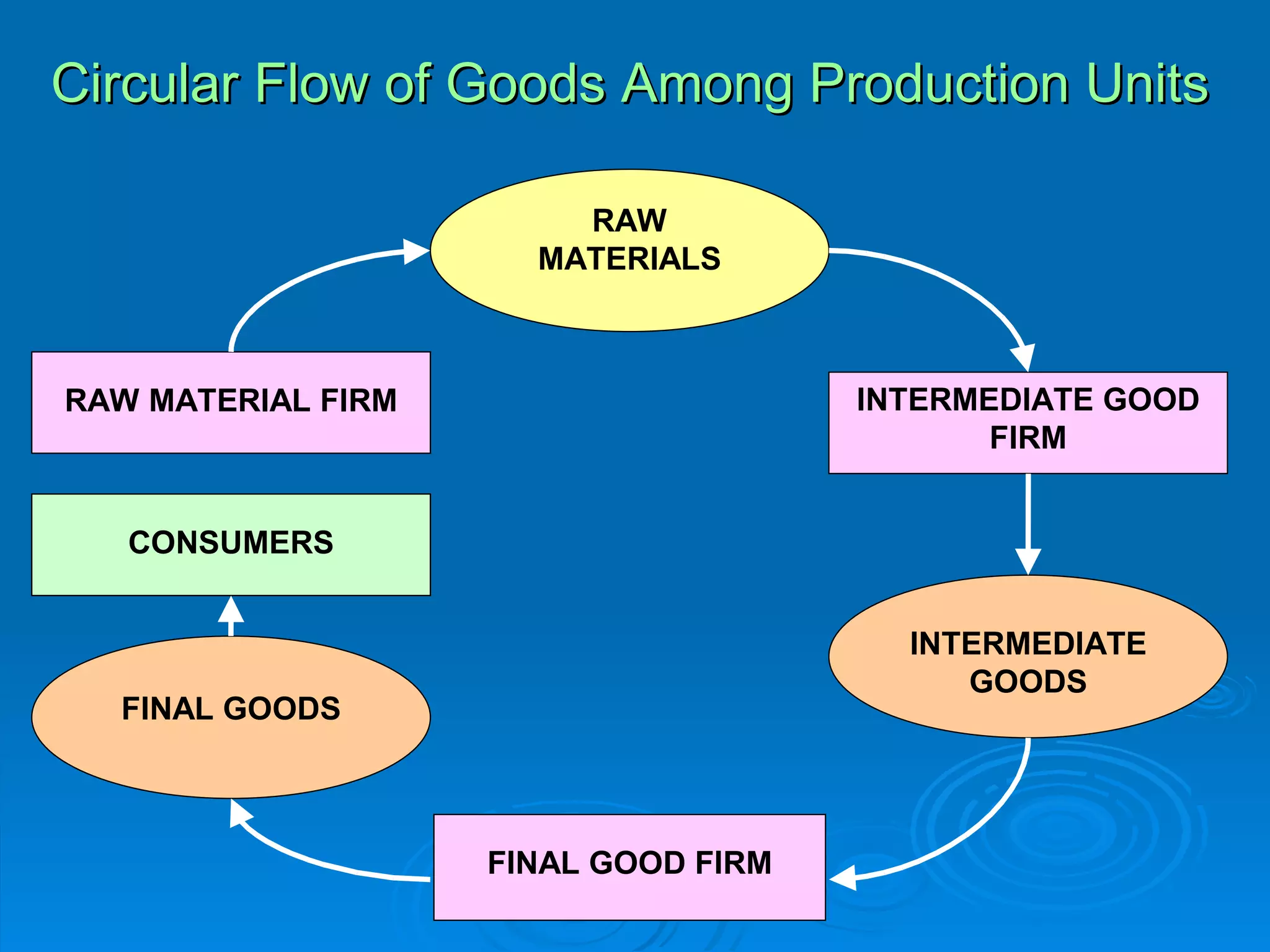
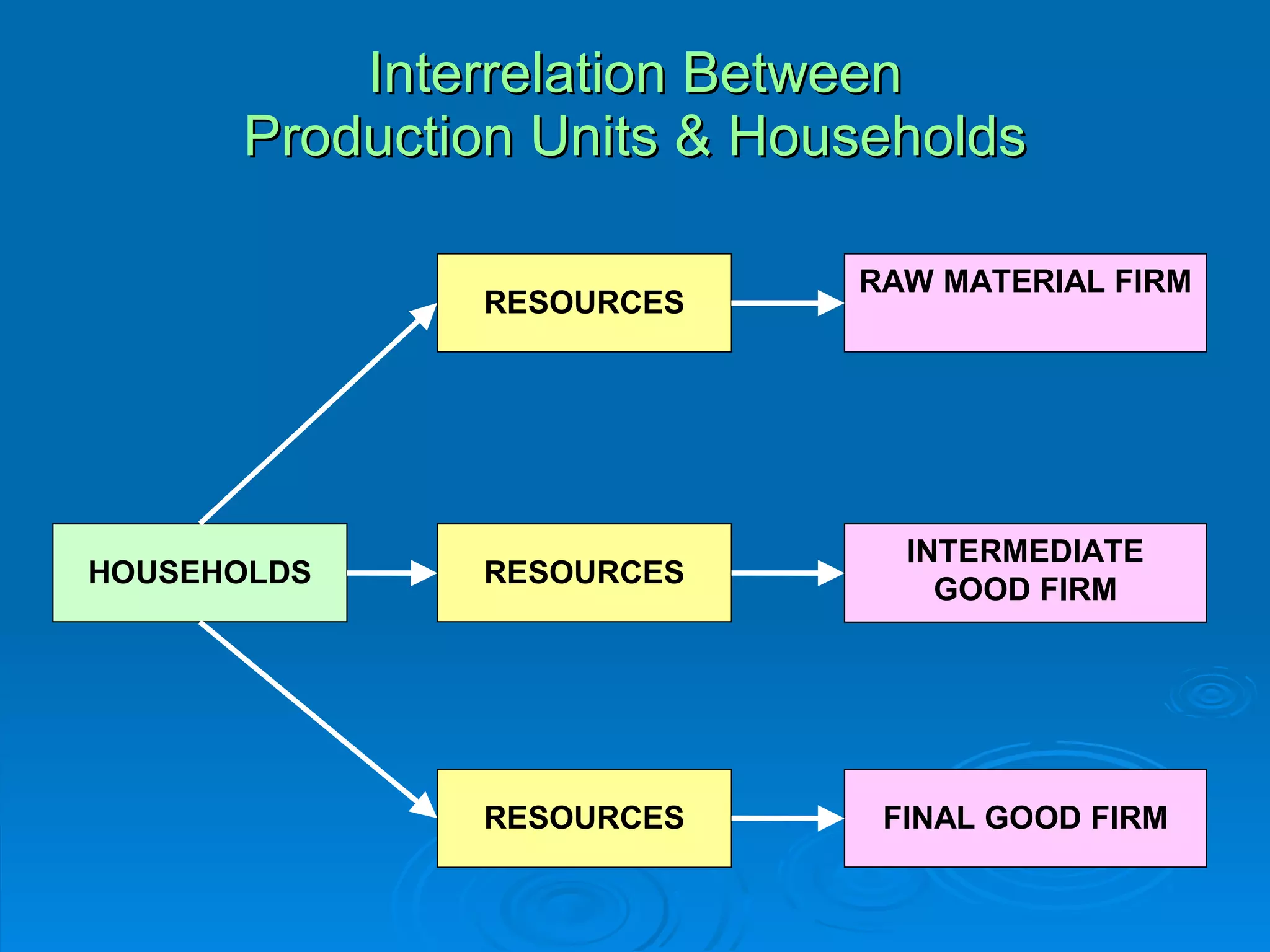
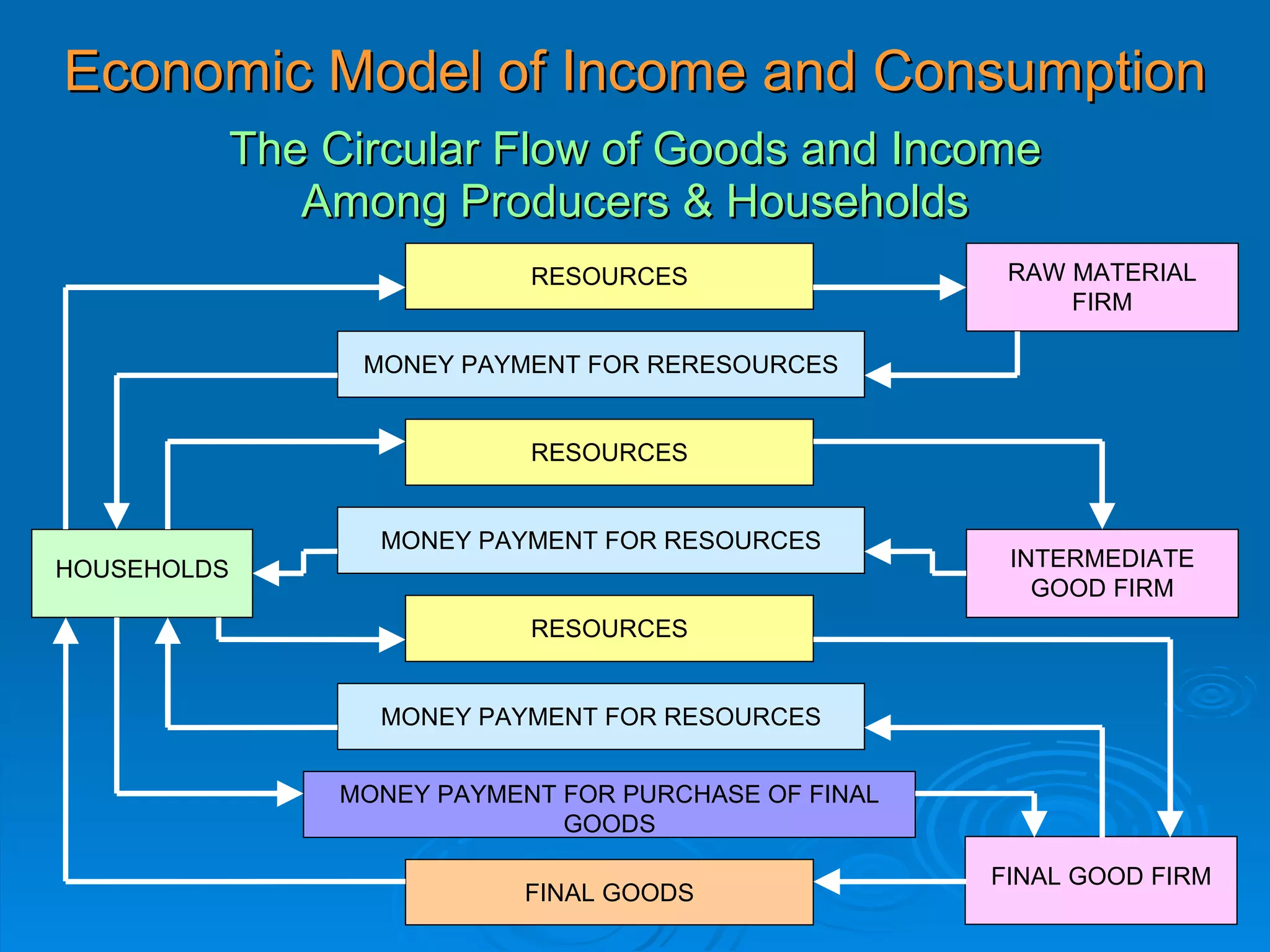
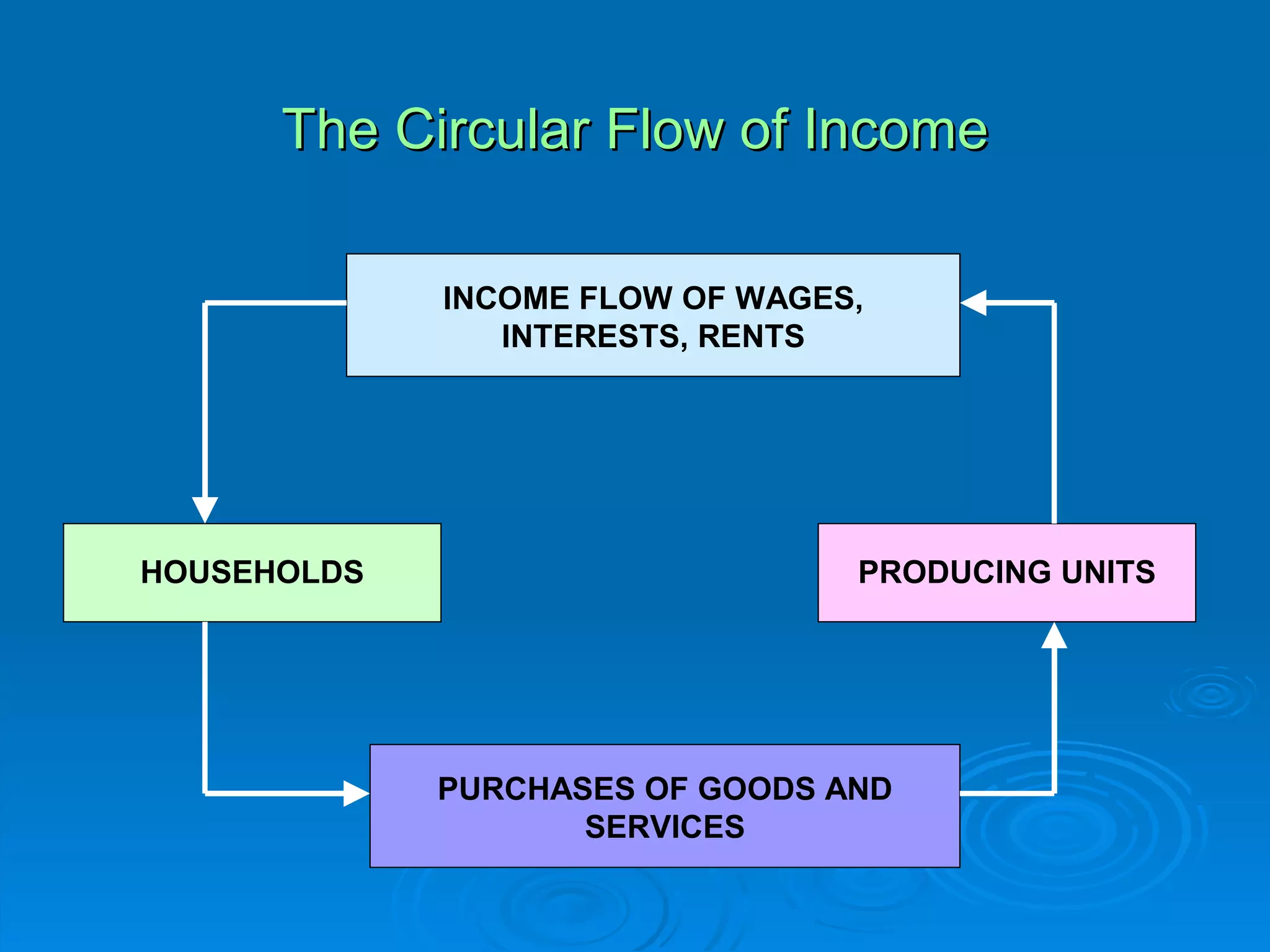
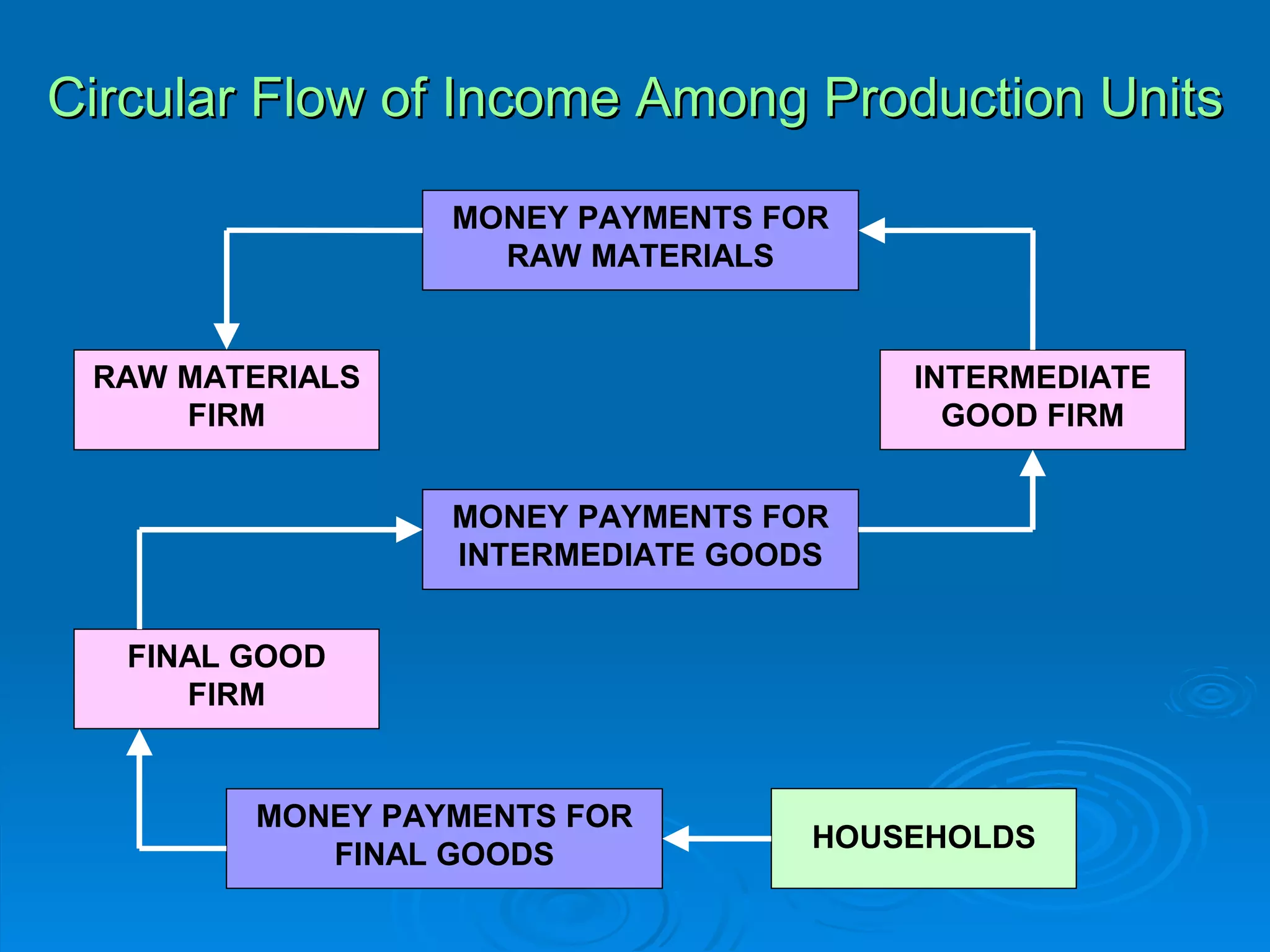
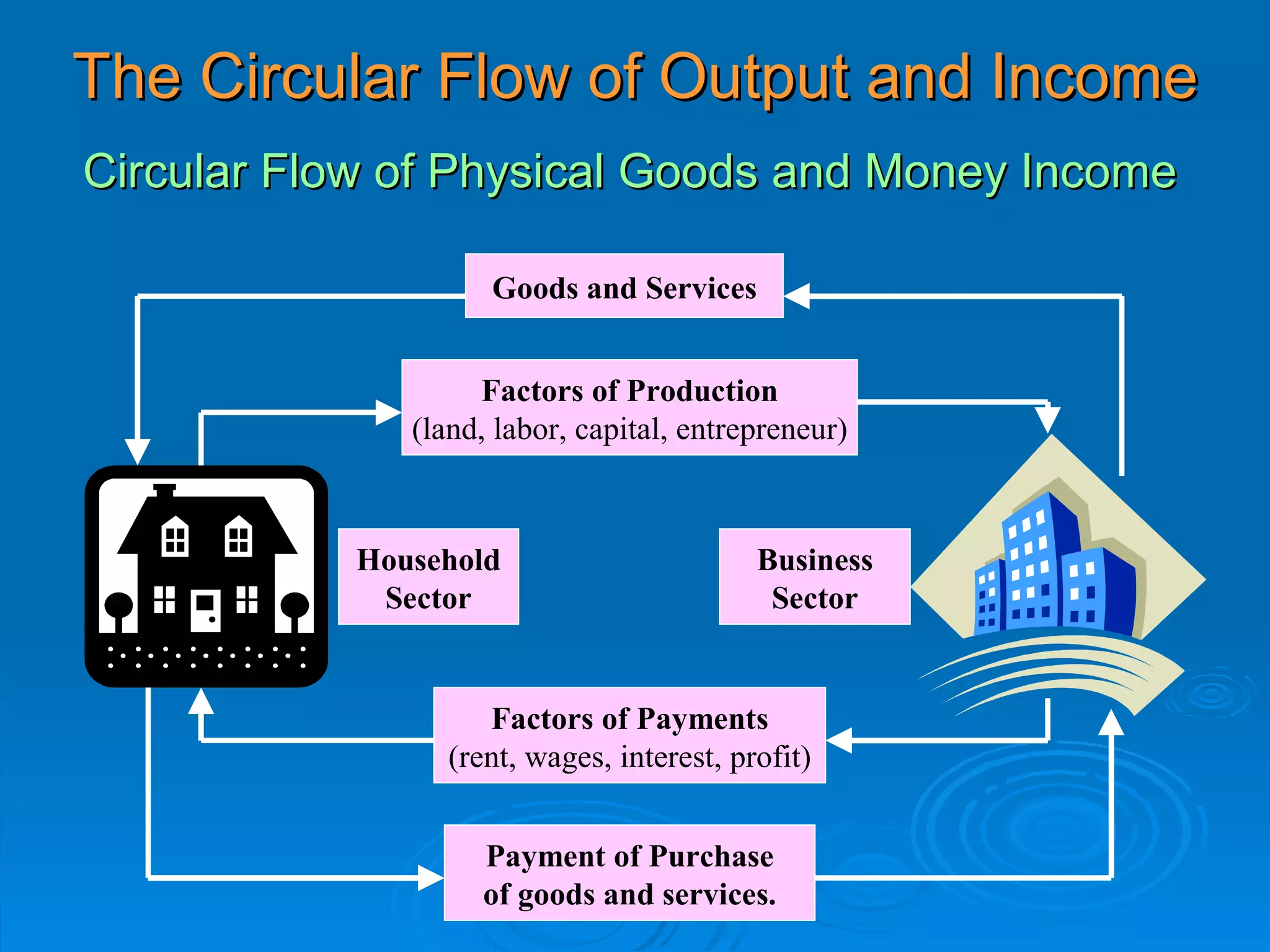
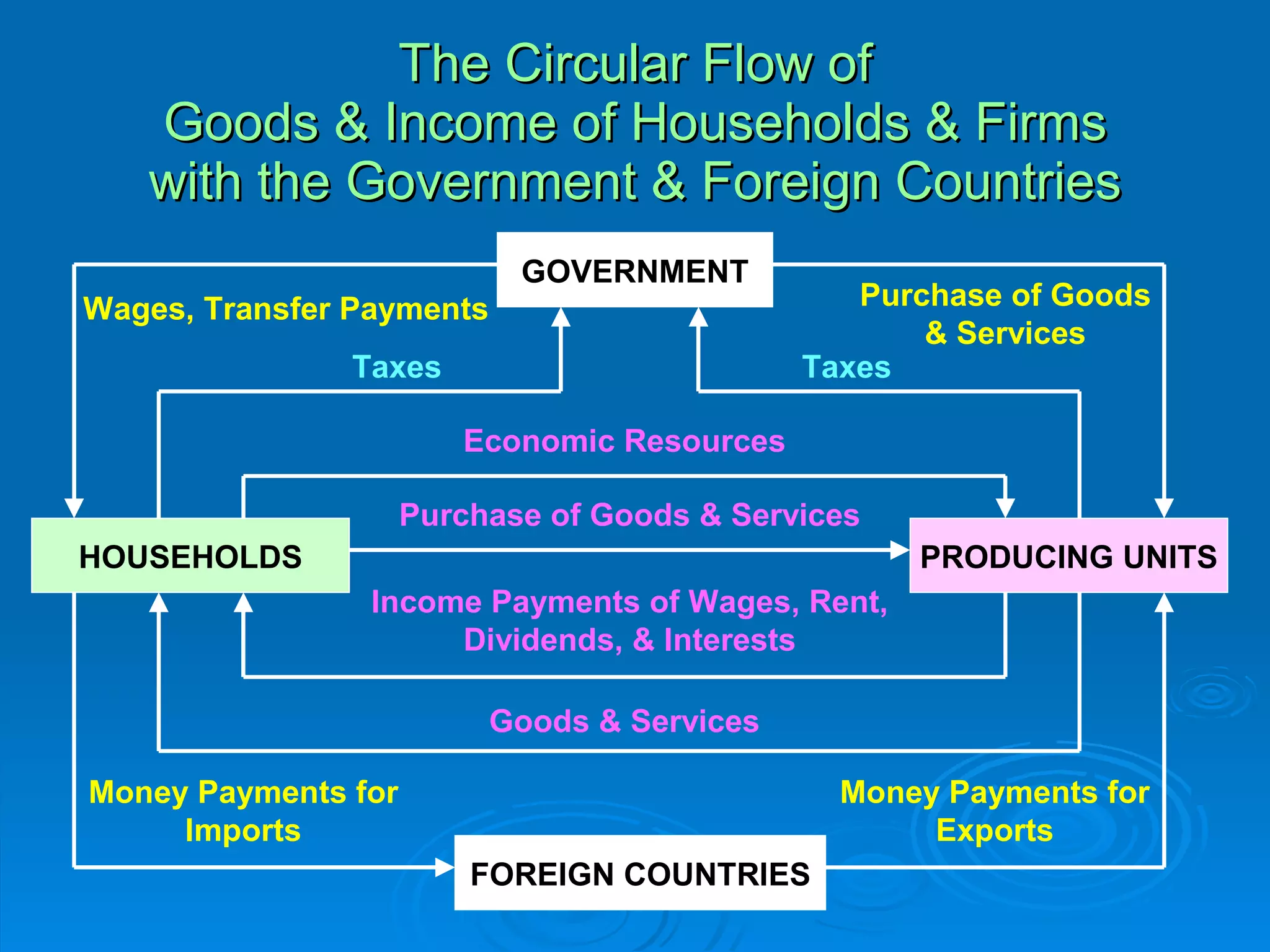
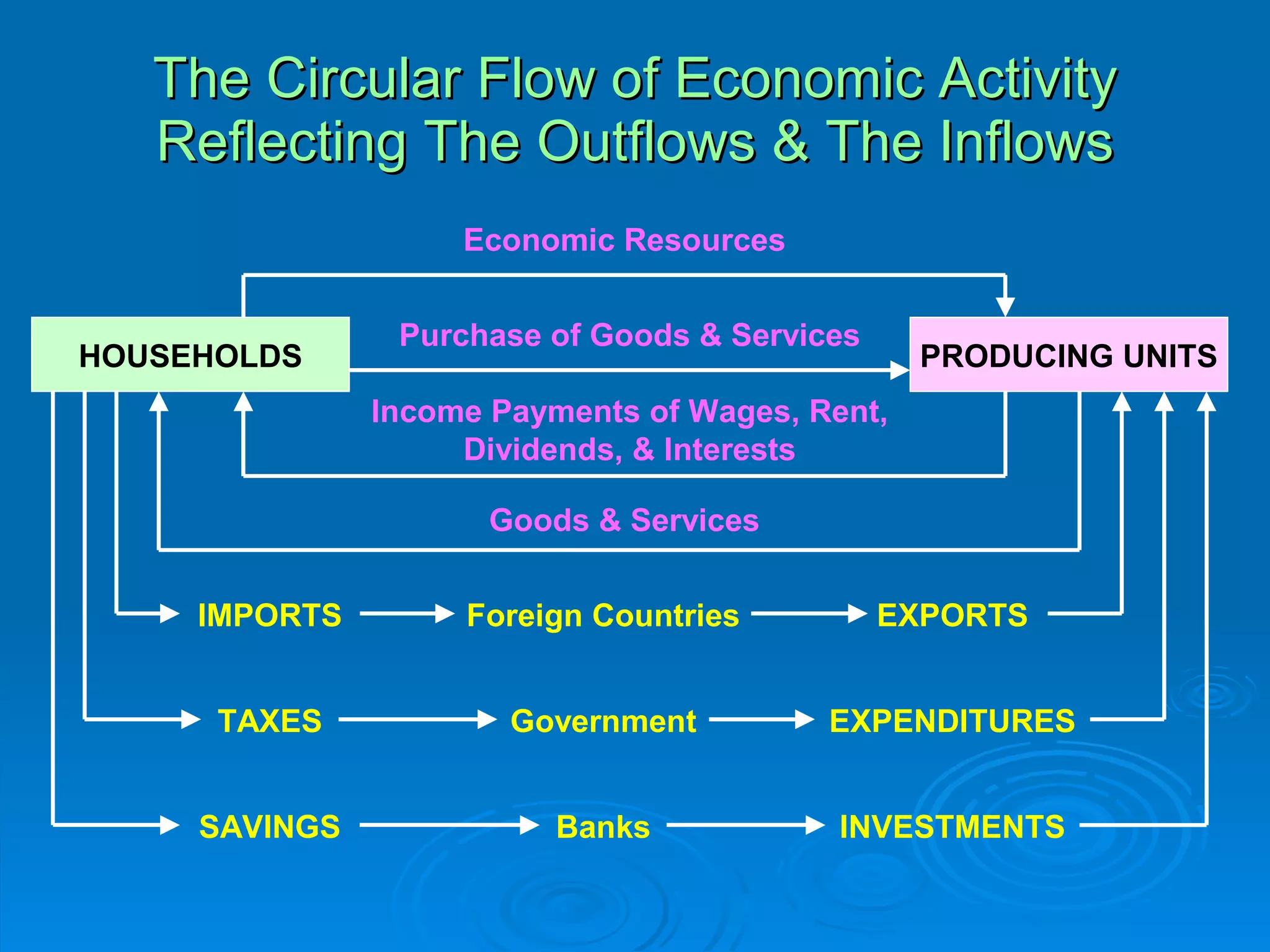
The document describes the circular flow of economic activity between households and firms. It shows that households receive income from firms for supplying factors of production like labor, capital and land. Households then use this income to purchase goods and services from firms. Firms take these factor payments and use them to pay for costs like wages, rent, interest and profit. The cycle then repeats with firms producing goods that households demand. This circular flow involves the continuous movement of goods, services and money between households and firms.