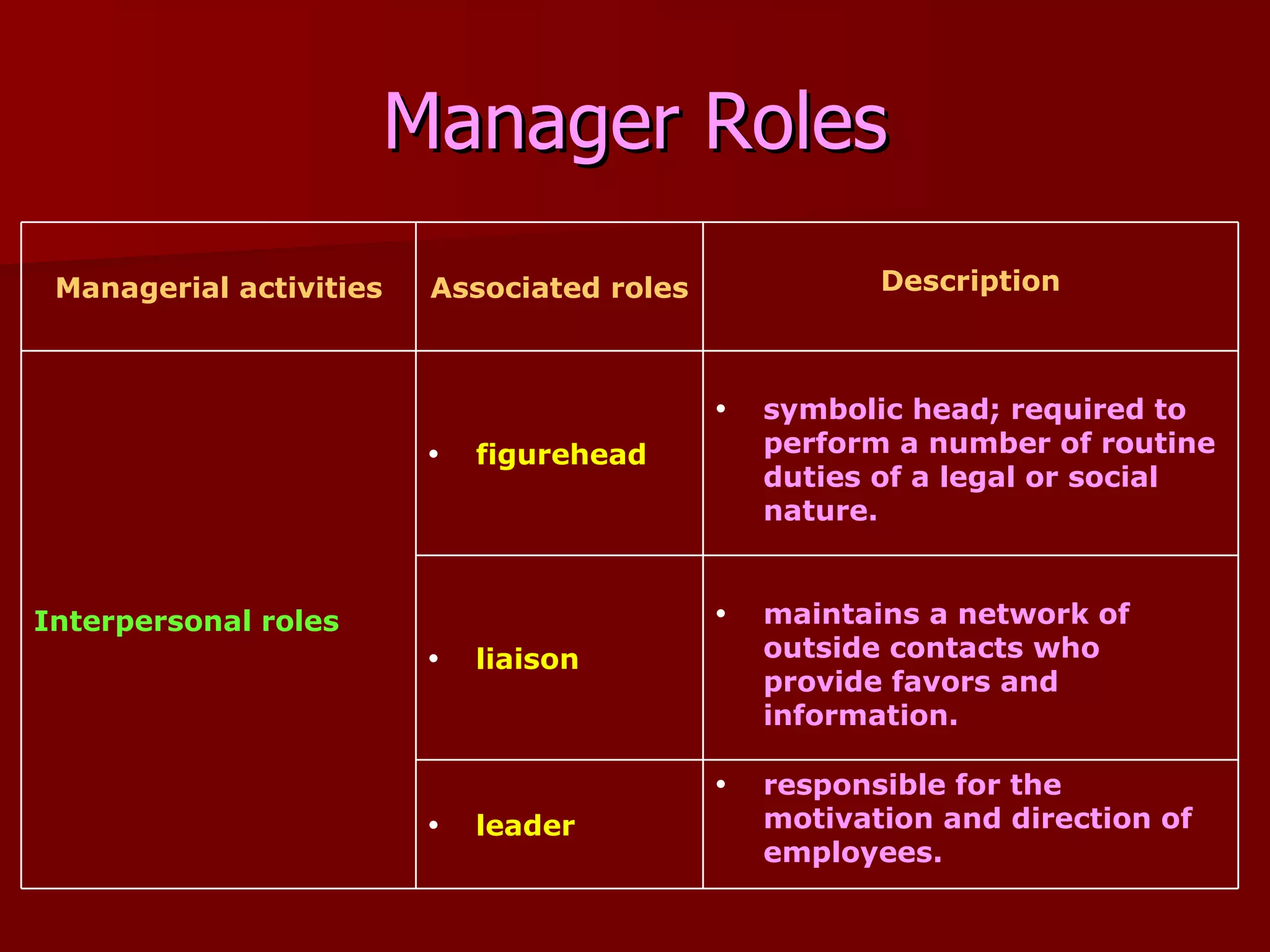
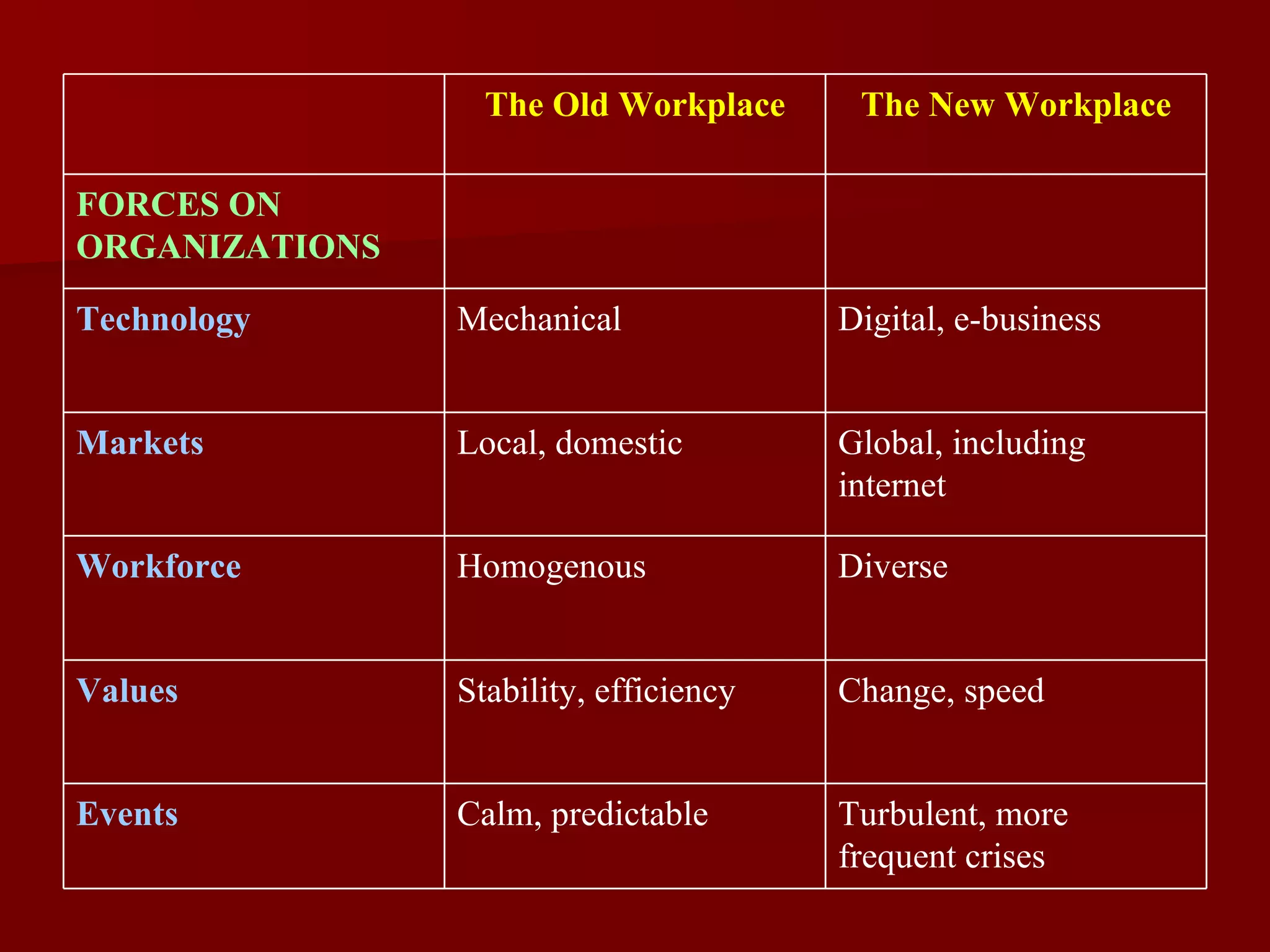
The document discusses key concepts in management including the four main functions of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. It describes organizational effectiveness as achieving goals, and efficiency as using minimal resources to produce output. Different management types and skills are defined, as well as the roles managers perform. The transition to a new digital workplace is outlined, requiring competencies like empowering diverse virtual teams through experimentation and collaboration to adapt to constant change and global markets. Crisis management involves remaining calm, visible, prioritizing people, communicating truthfully, and knowing when to refocus on business.