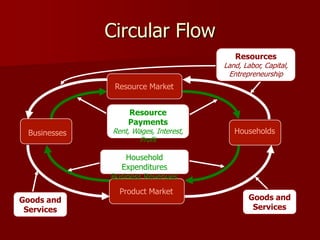
Economics studies economic products which are goods and services that are useful, scarce, and transferable. Goods are items that satisfy wants, and can be consumer goods for individuals or capital goods used to produce other goods. Services are work performed for others. Consumers use goods and services. The circular flow shows resources going to businesses, which pay households who then buy goods and services, in a loop between markets. Productivity and specialization are key to economic growth by increasing output from the same inputs over time.