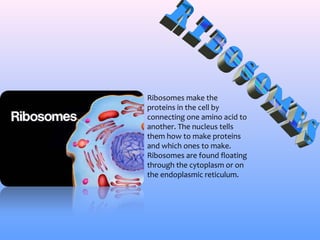
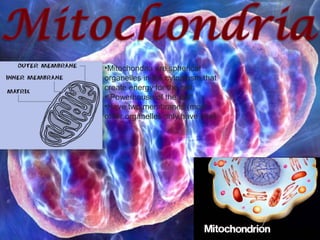
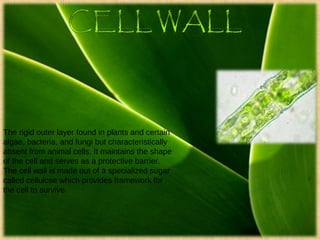
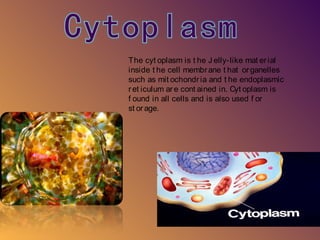
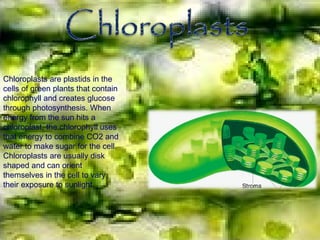
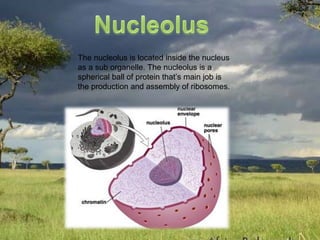
The document provides a map and descriptions of the major cellular organelles. It describes the nucleus, which contains the cell's DNA and directs protein production. The cell membrane separates and protects the cell, controlling what enters and exits. Ribosomes build proteins using instructions from the nucleus. Lysosomes digest molecules. Mitochondria produce energy. Other organelles described include the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, vacuoles, cytoskeleton, and centrioles.