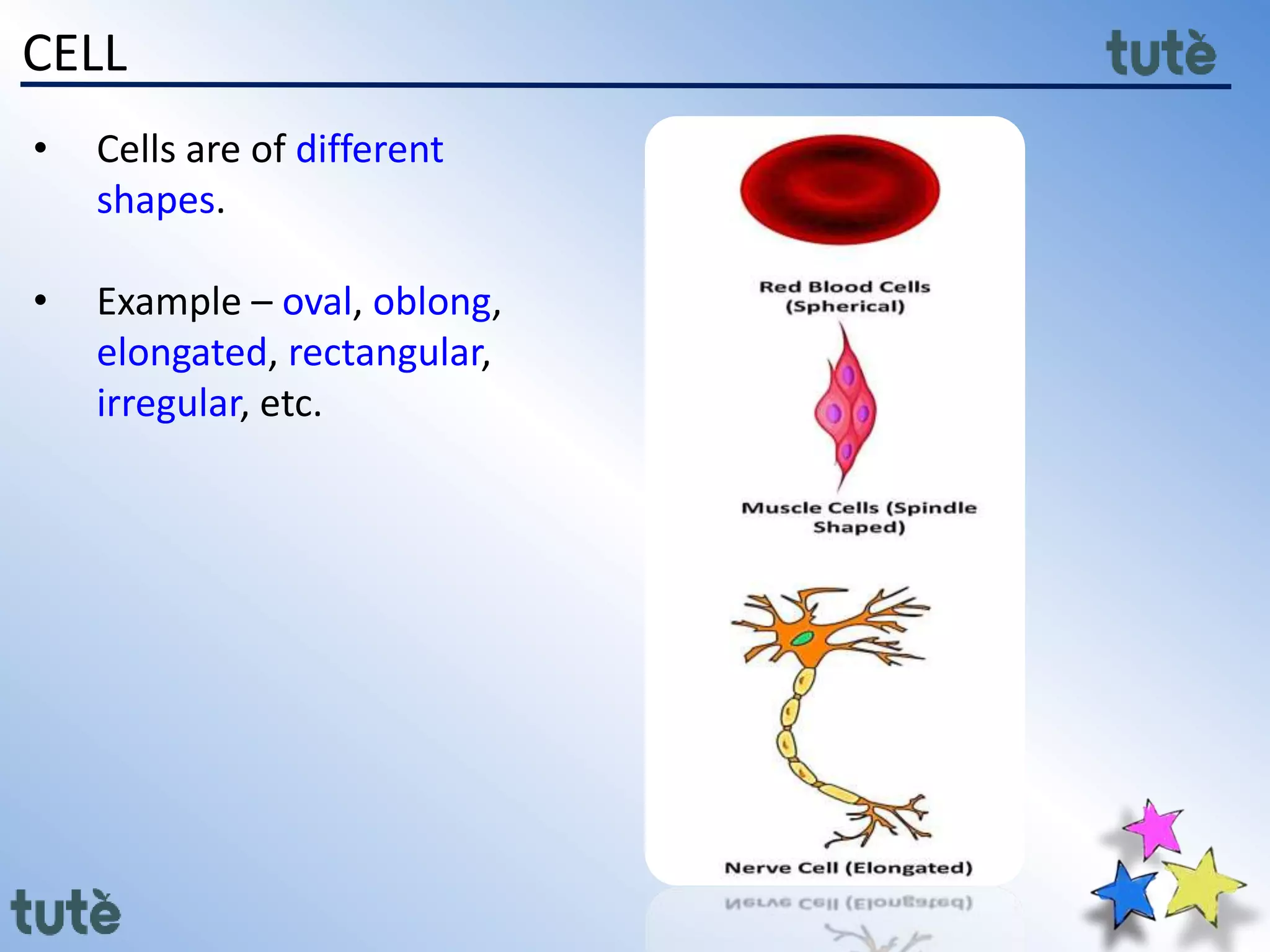
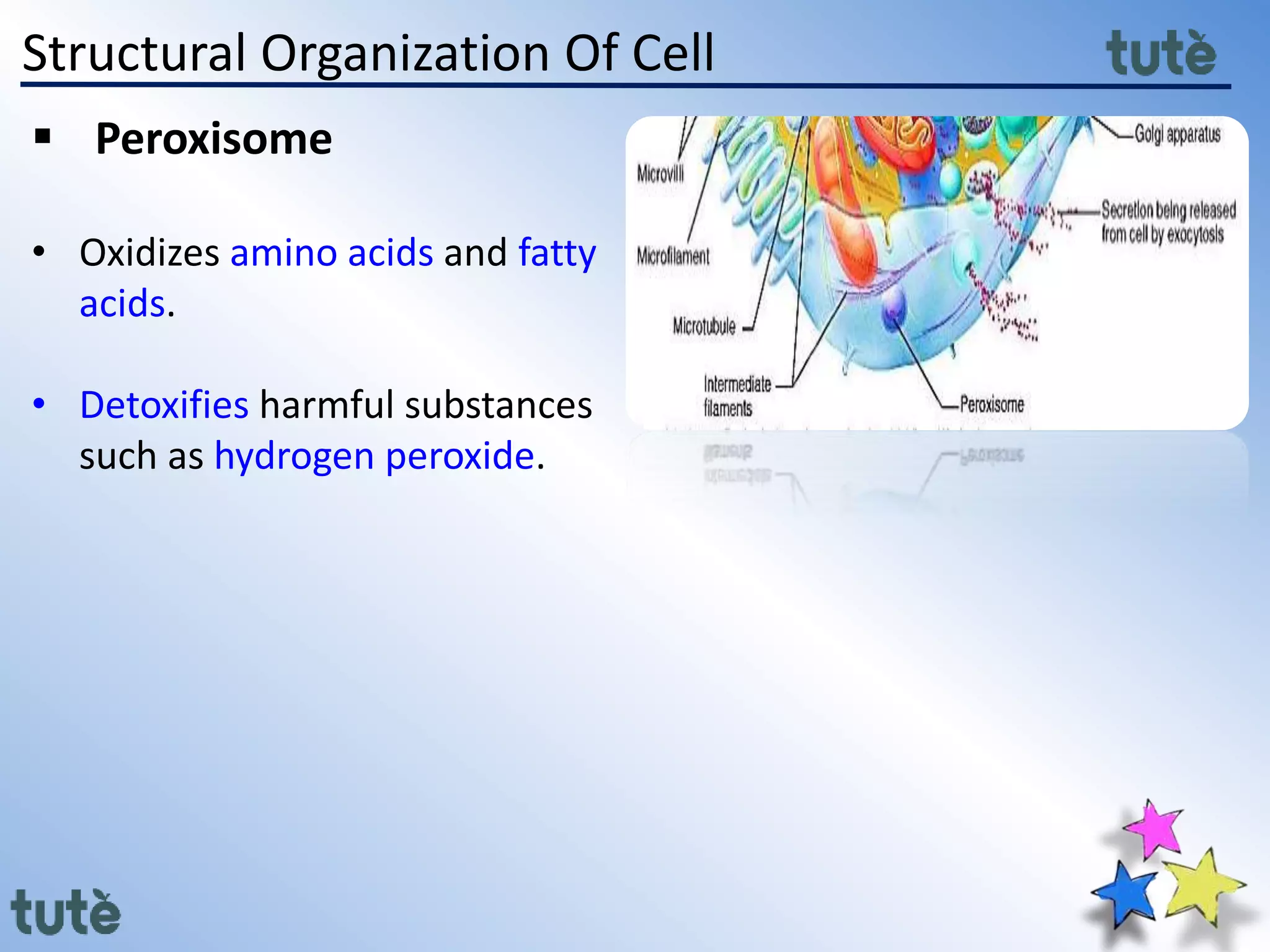
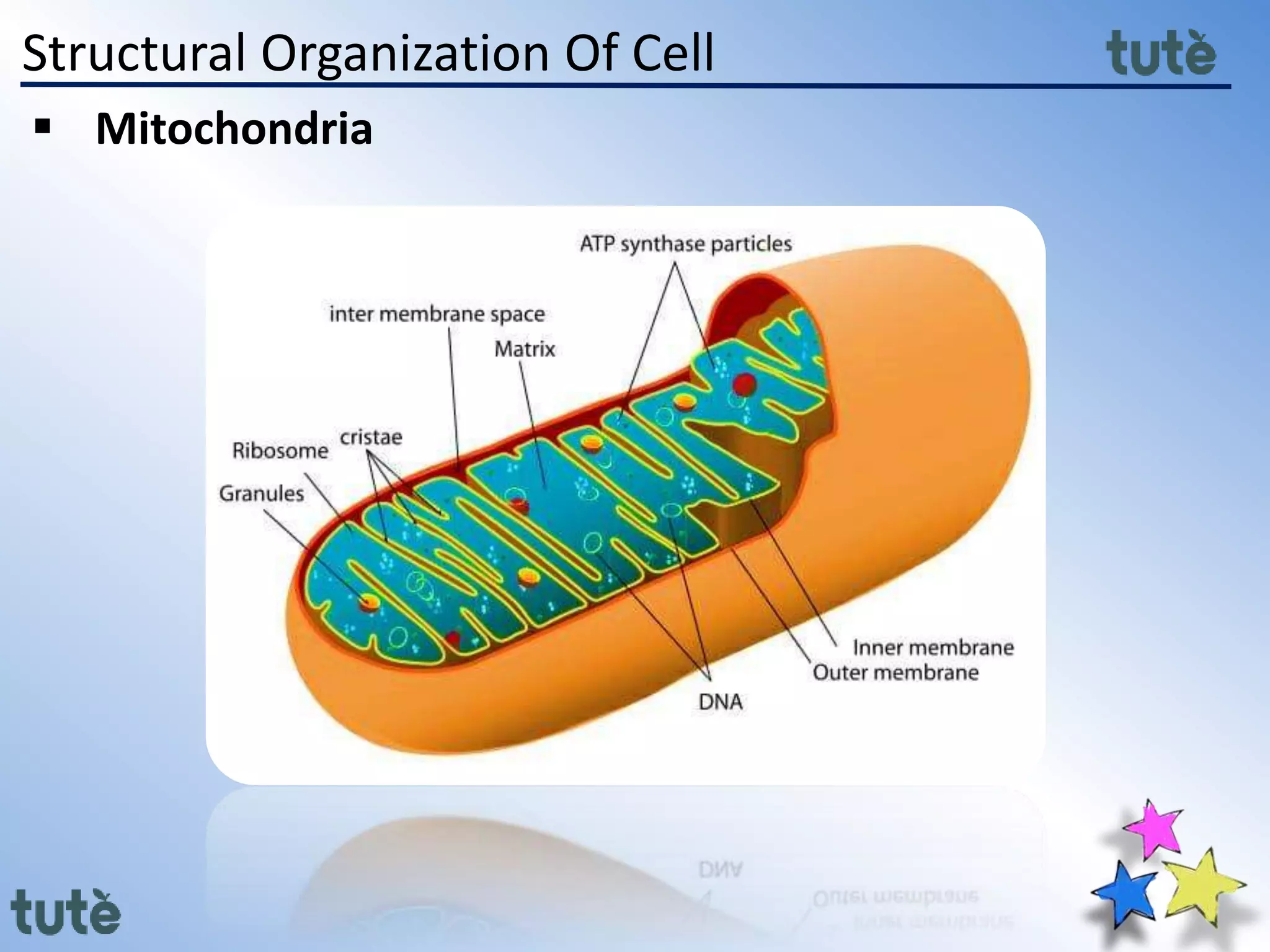
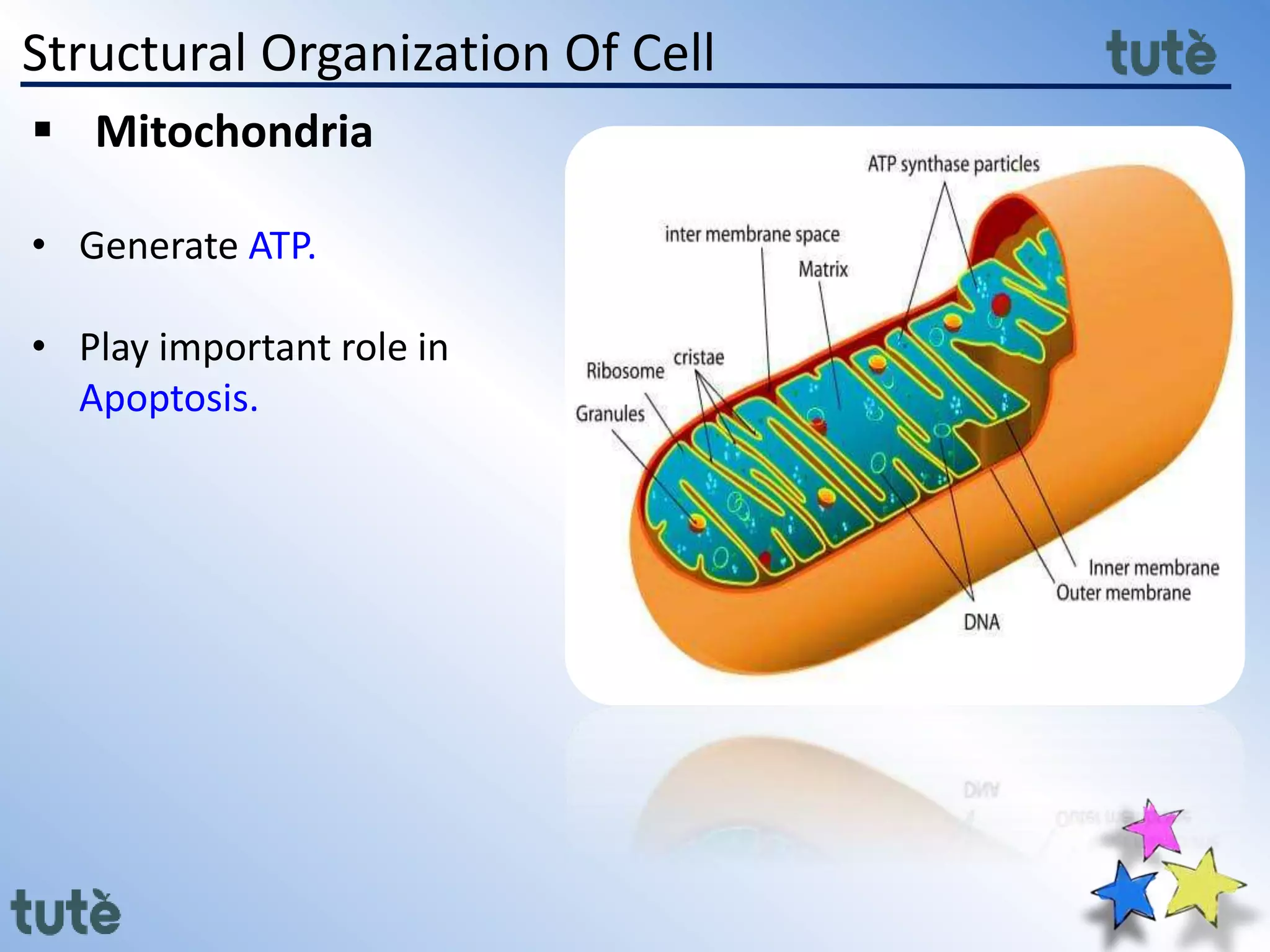
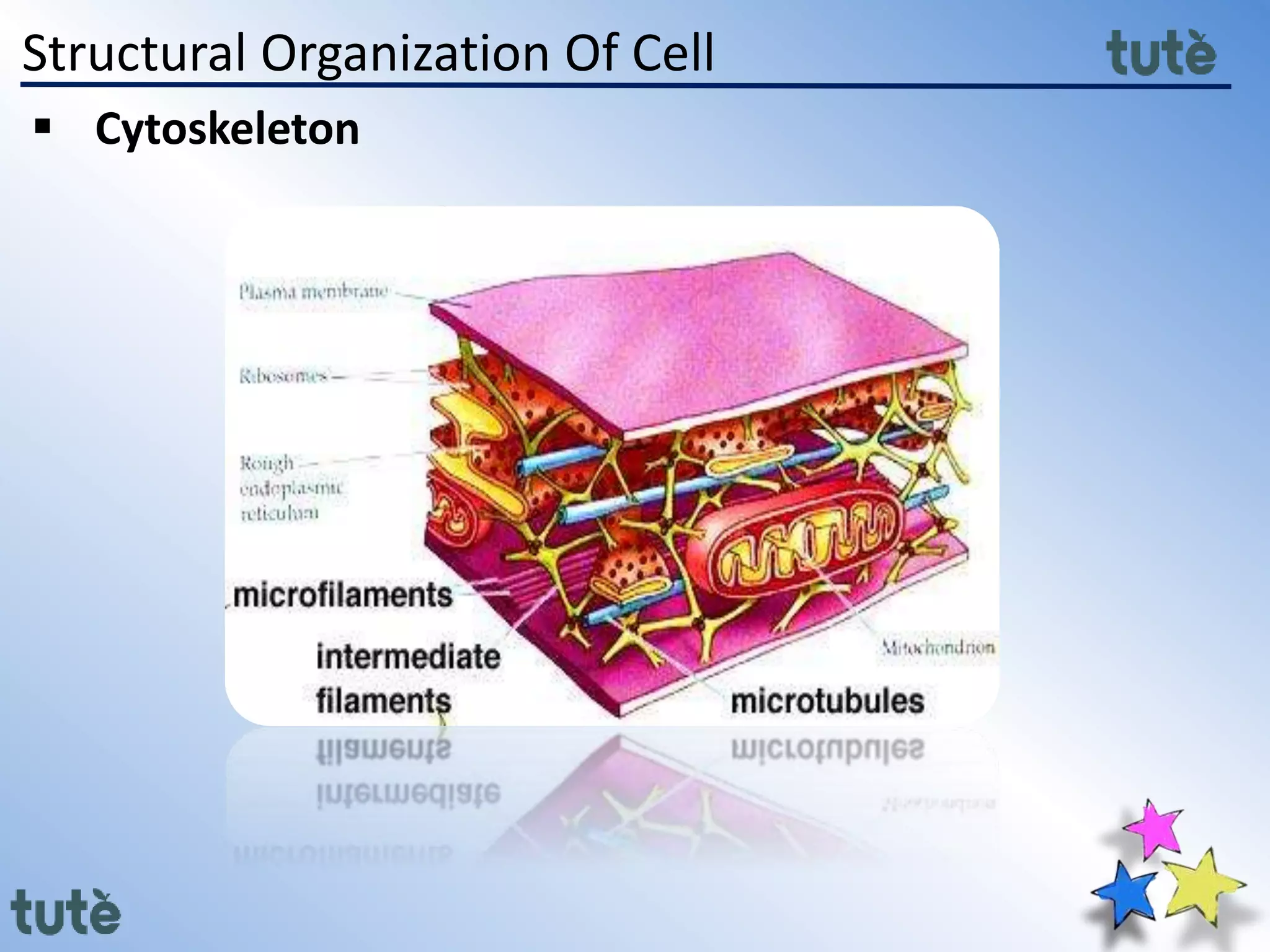
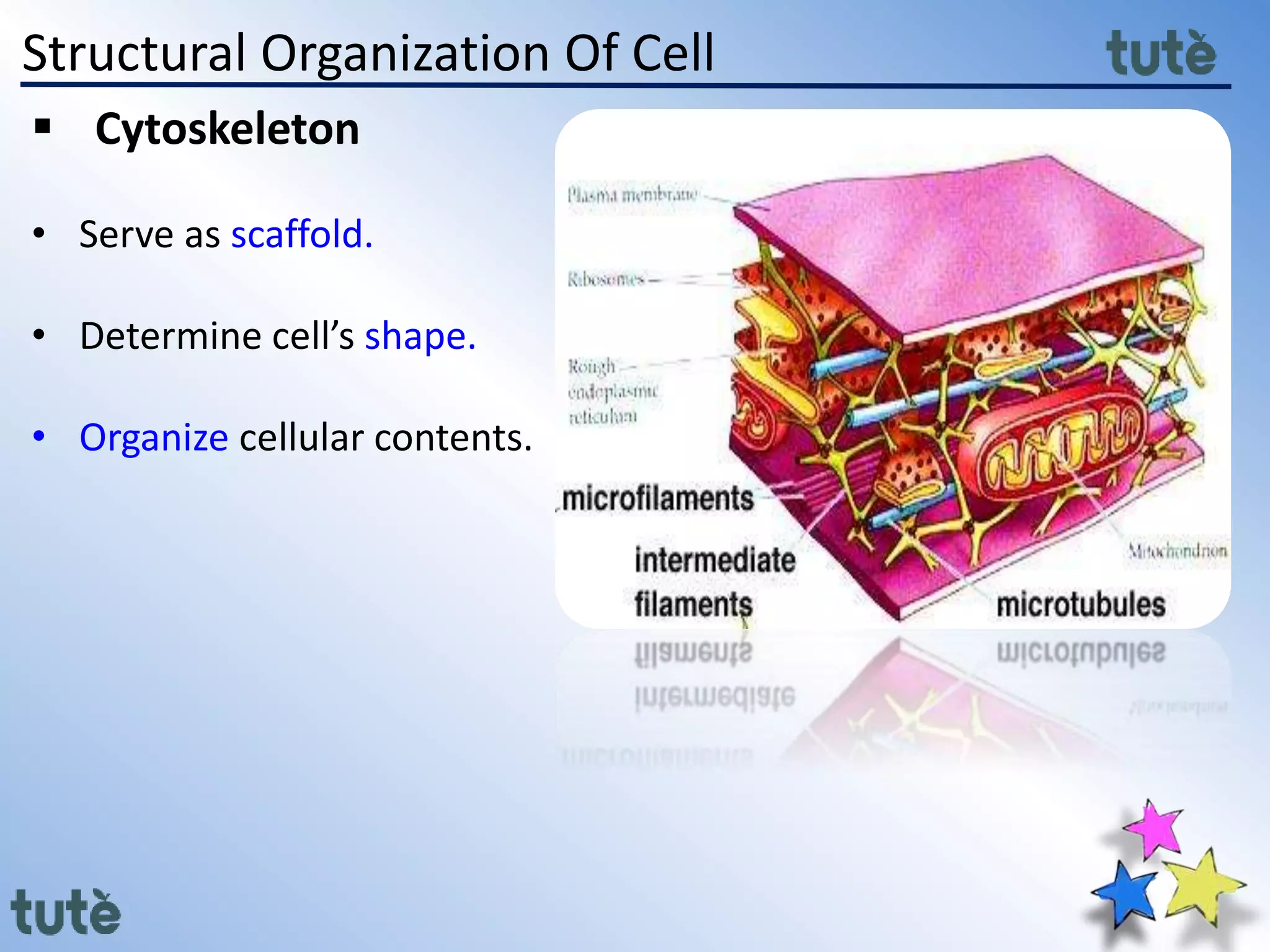
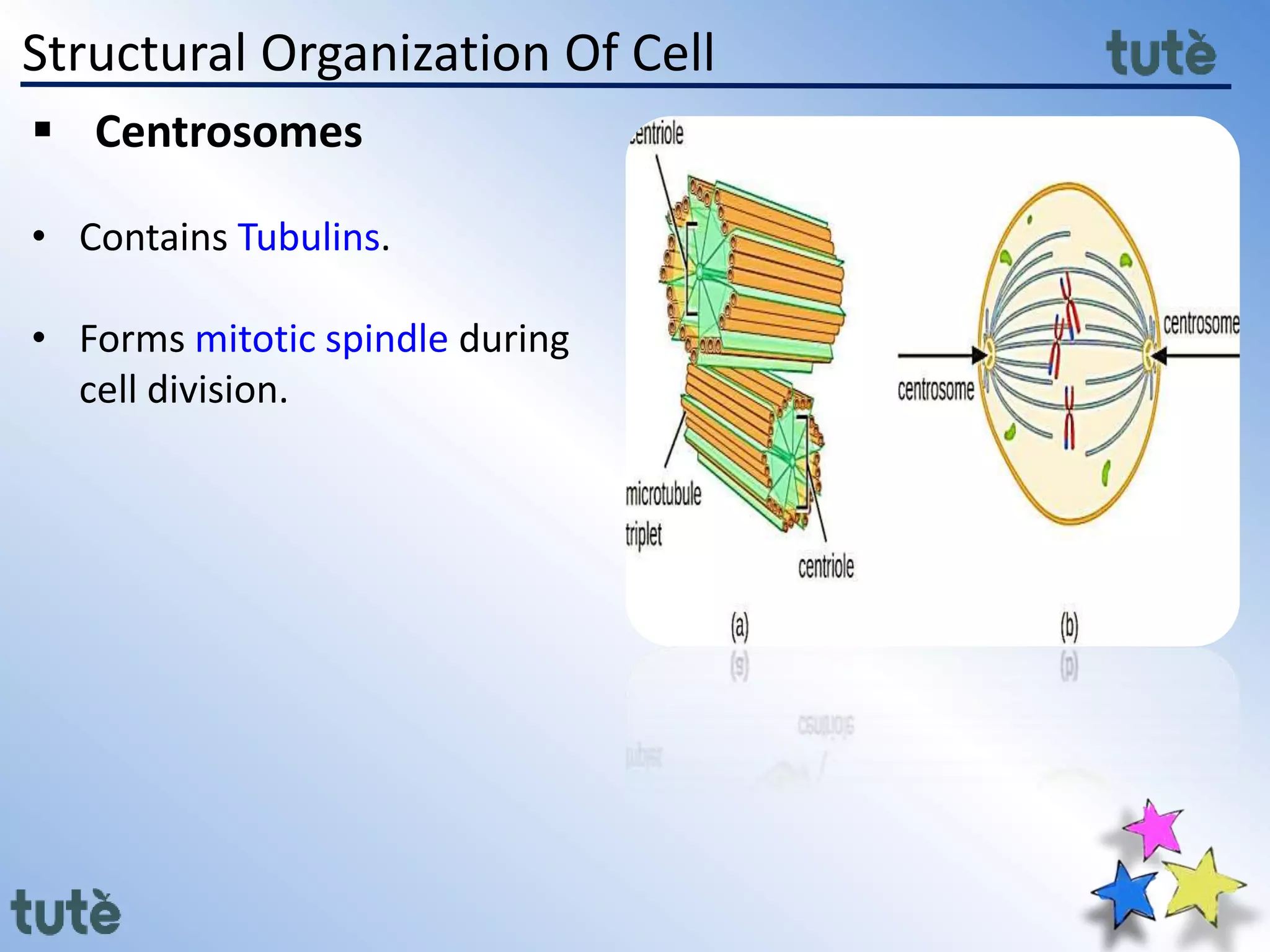
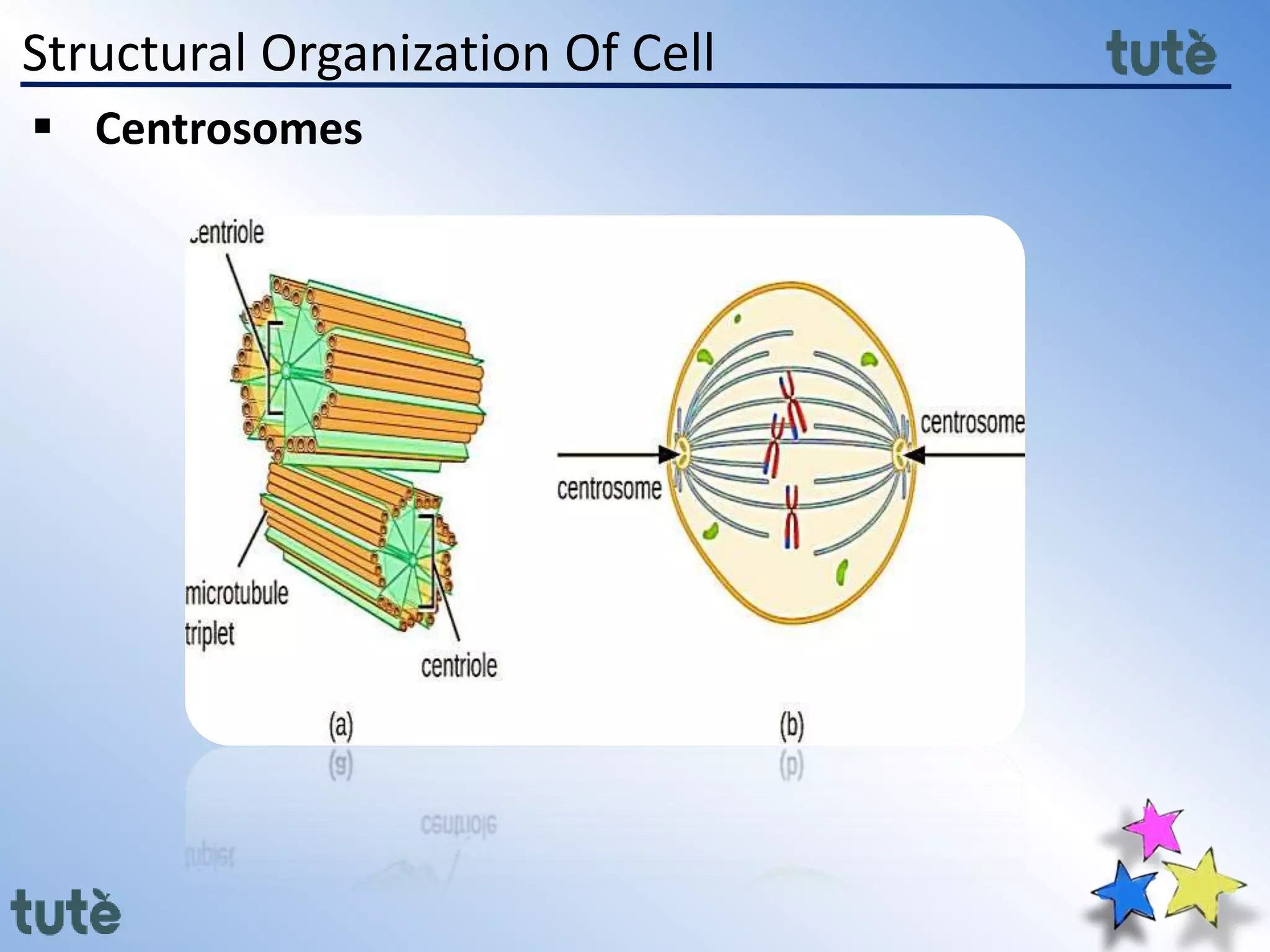
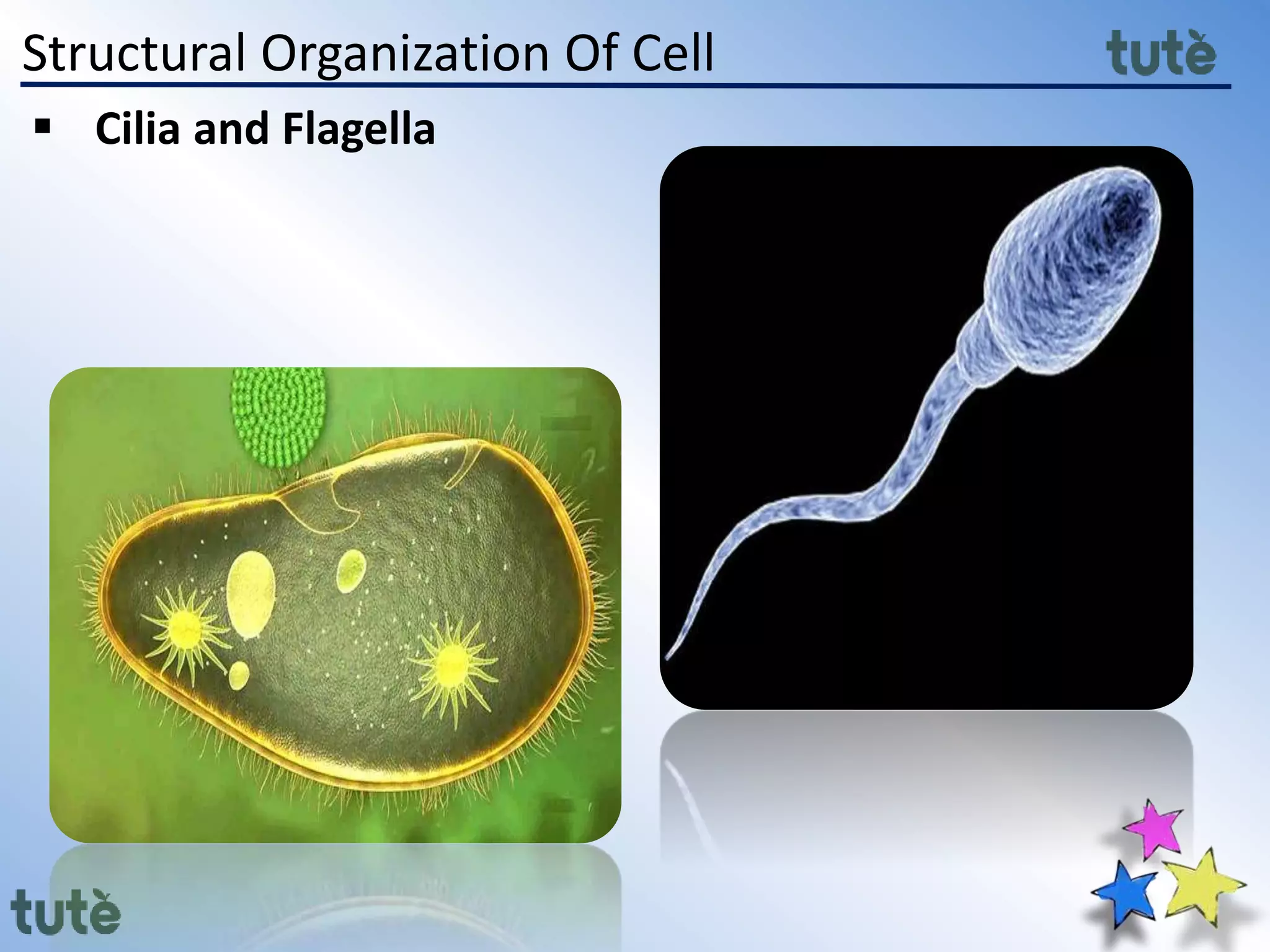
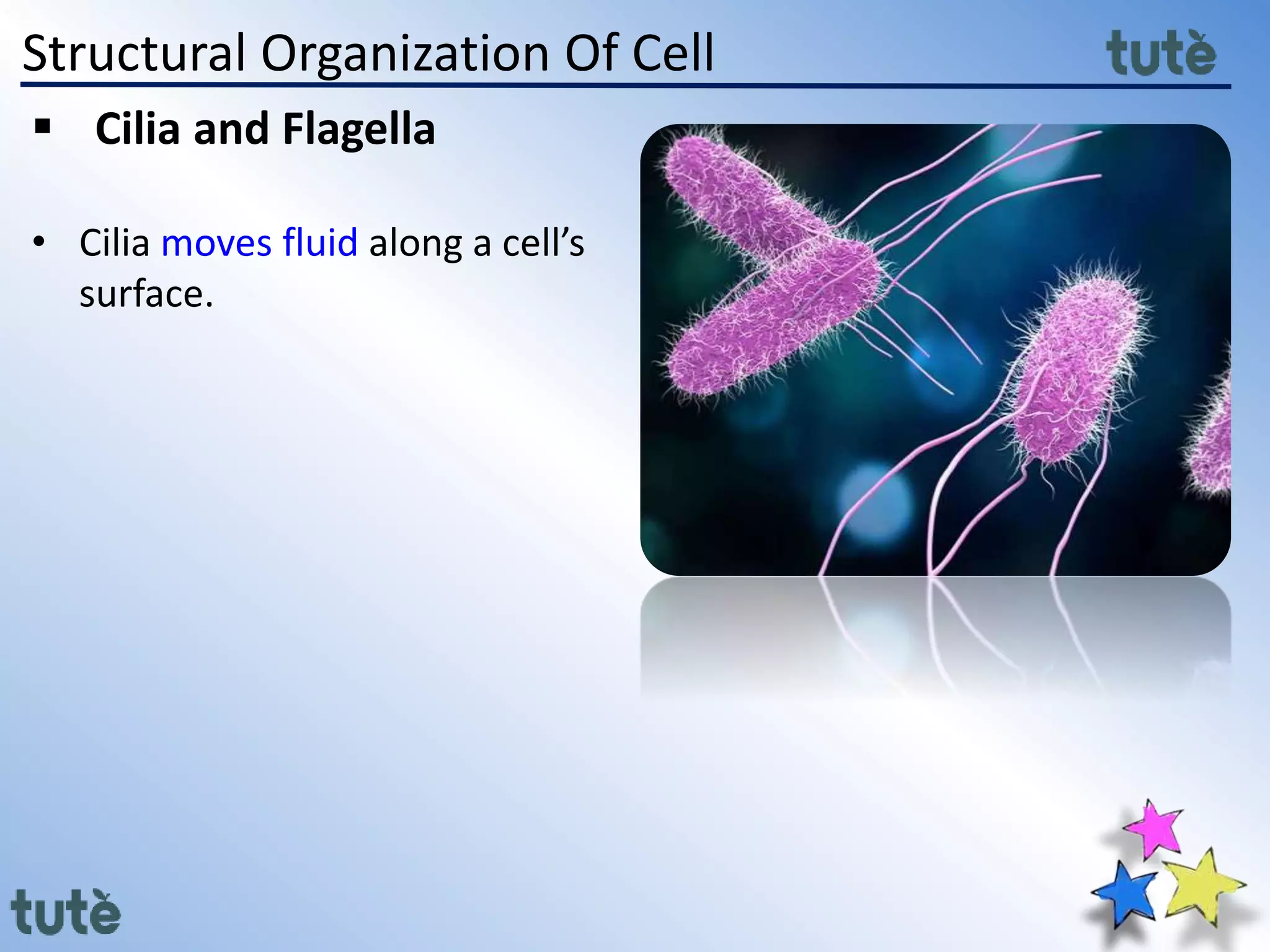
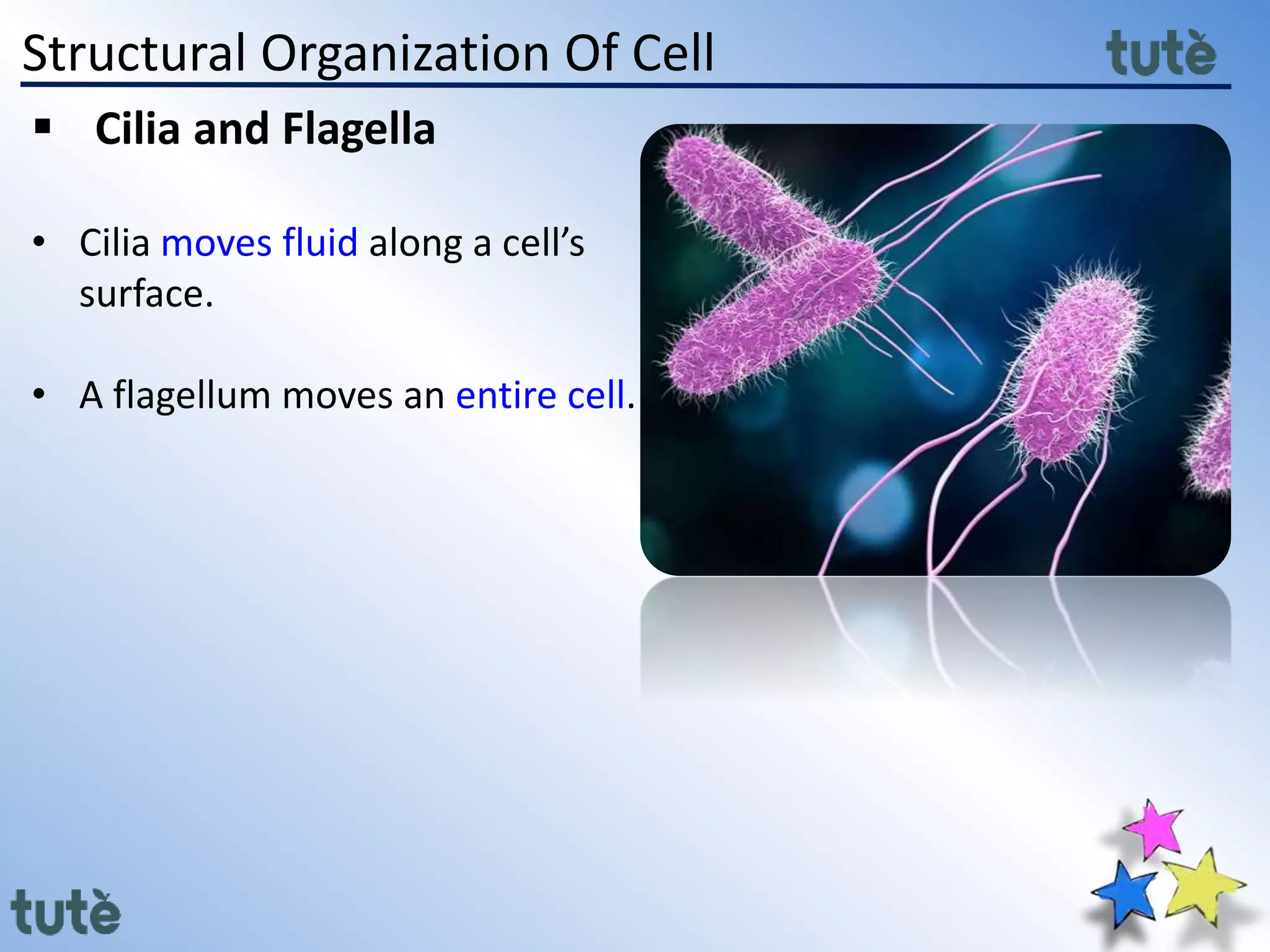
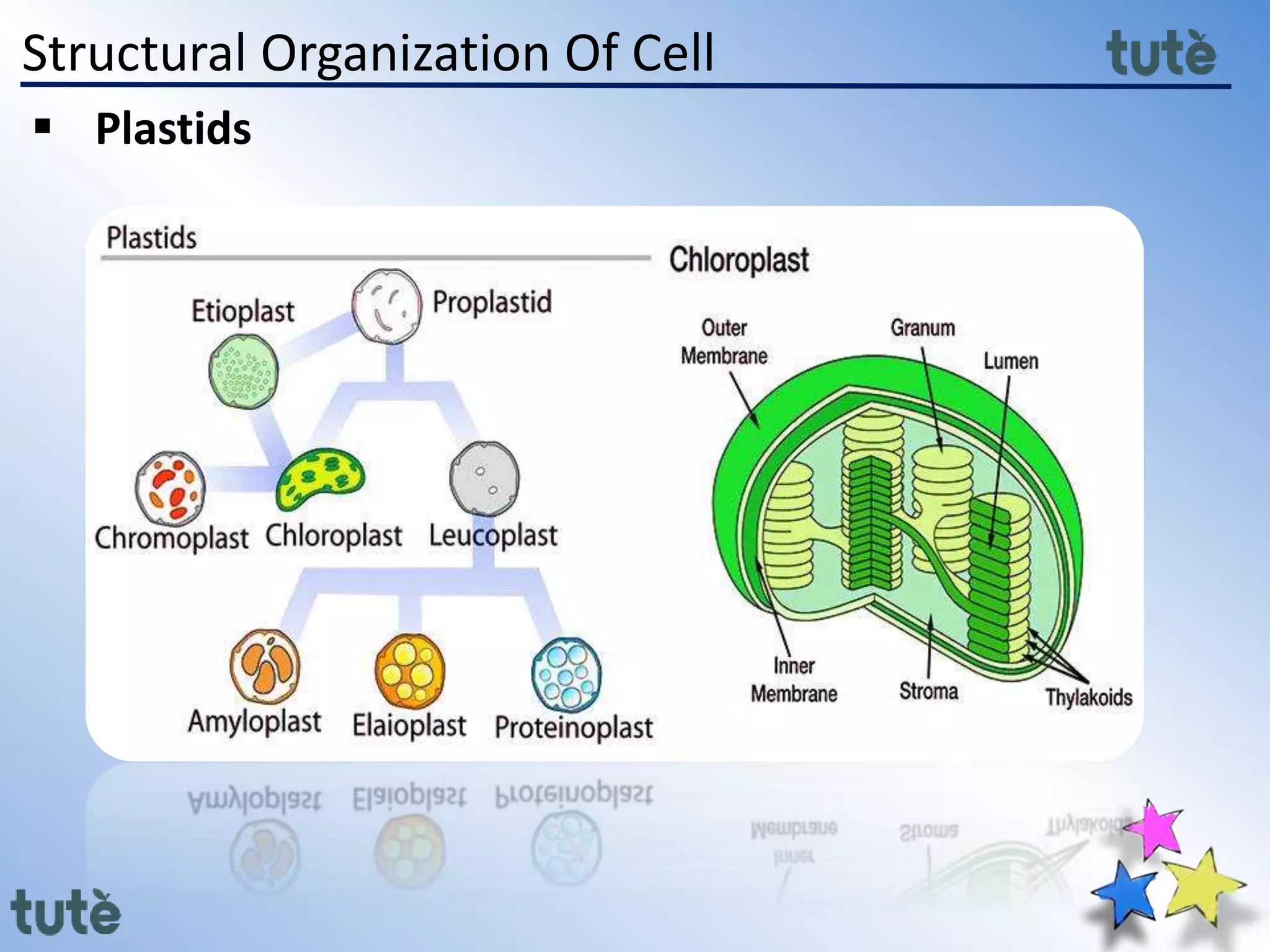
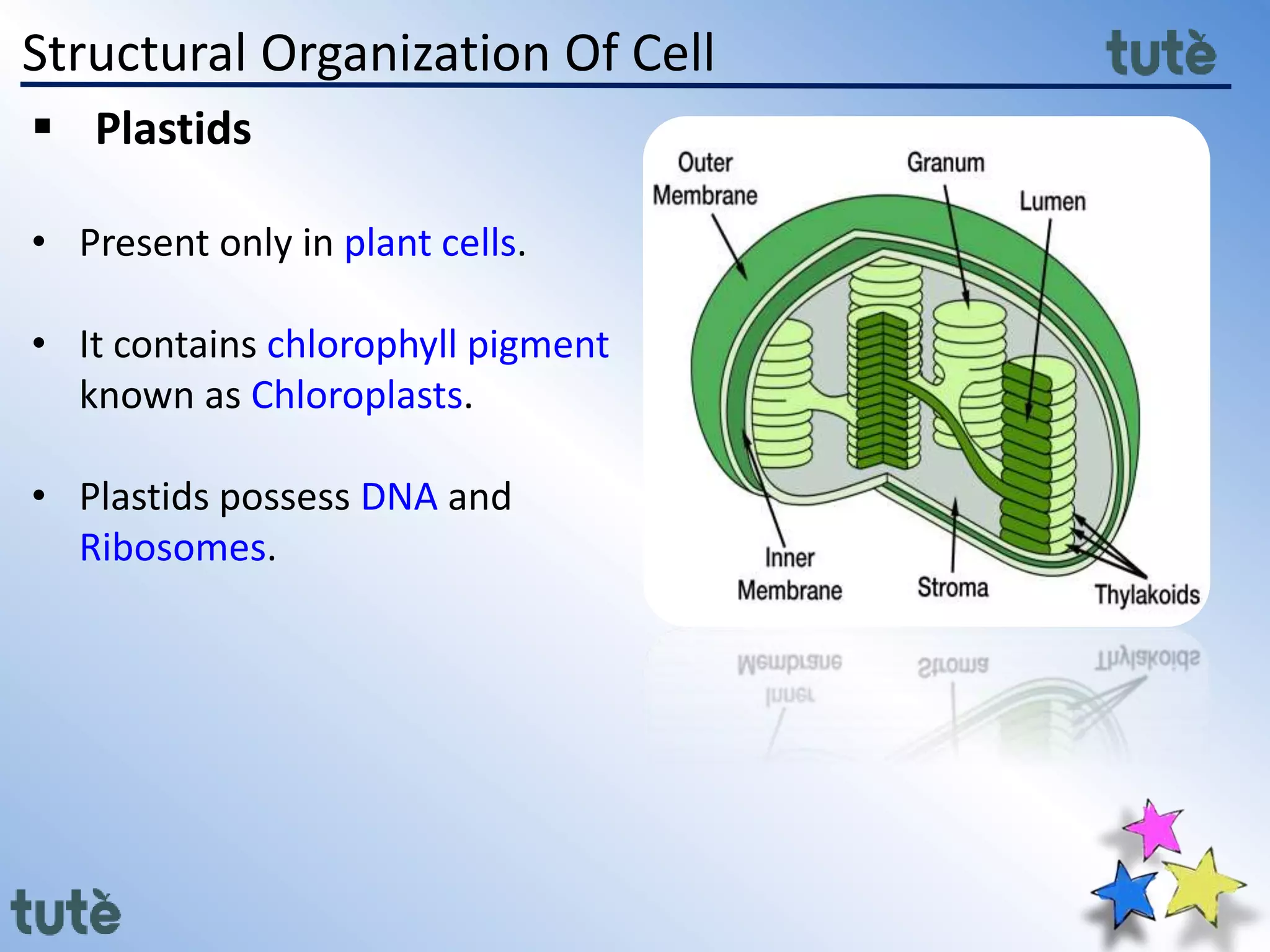
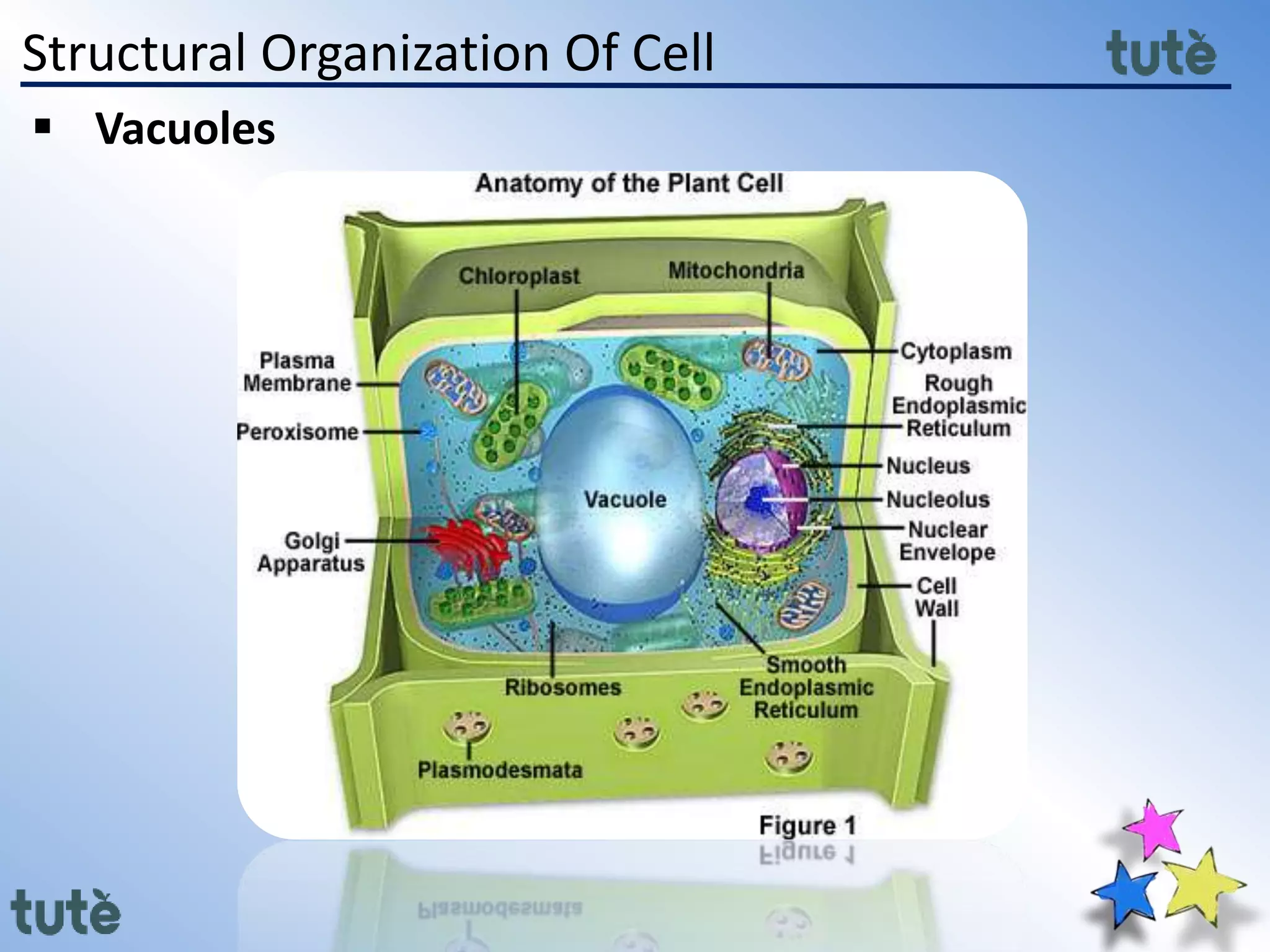
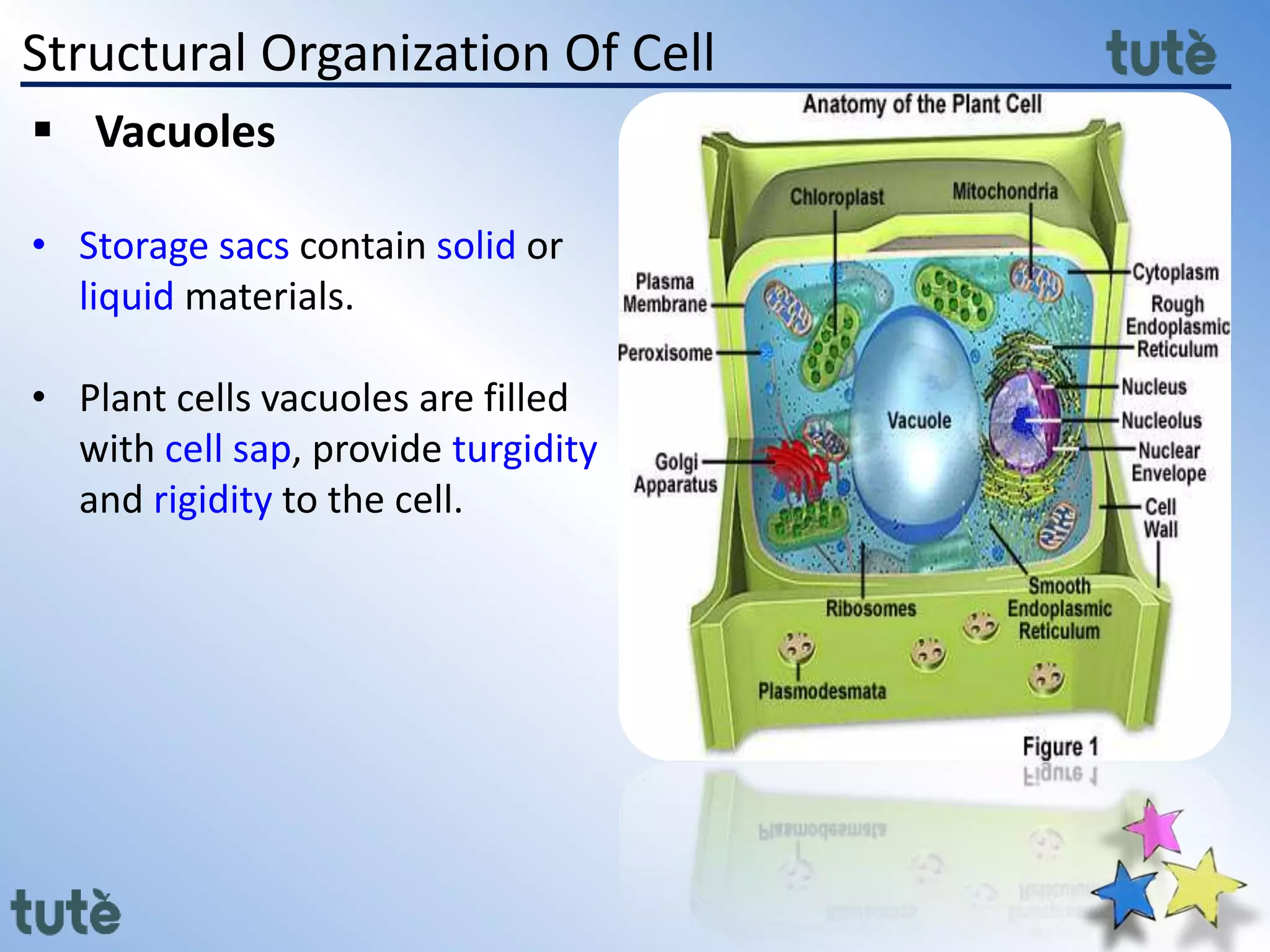
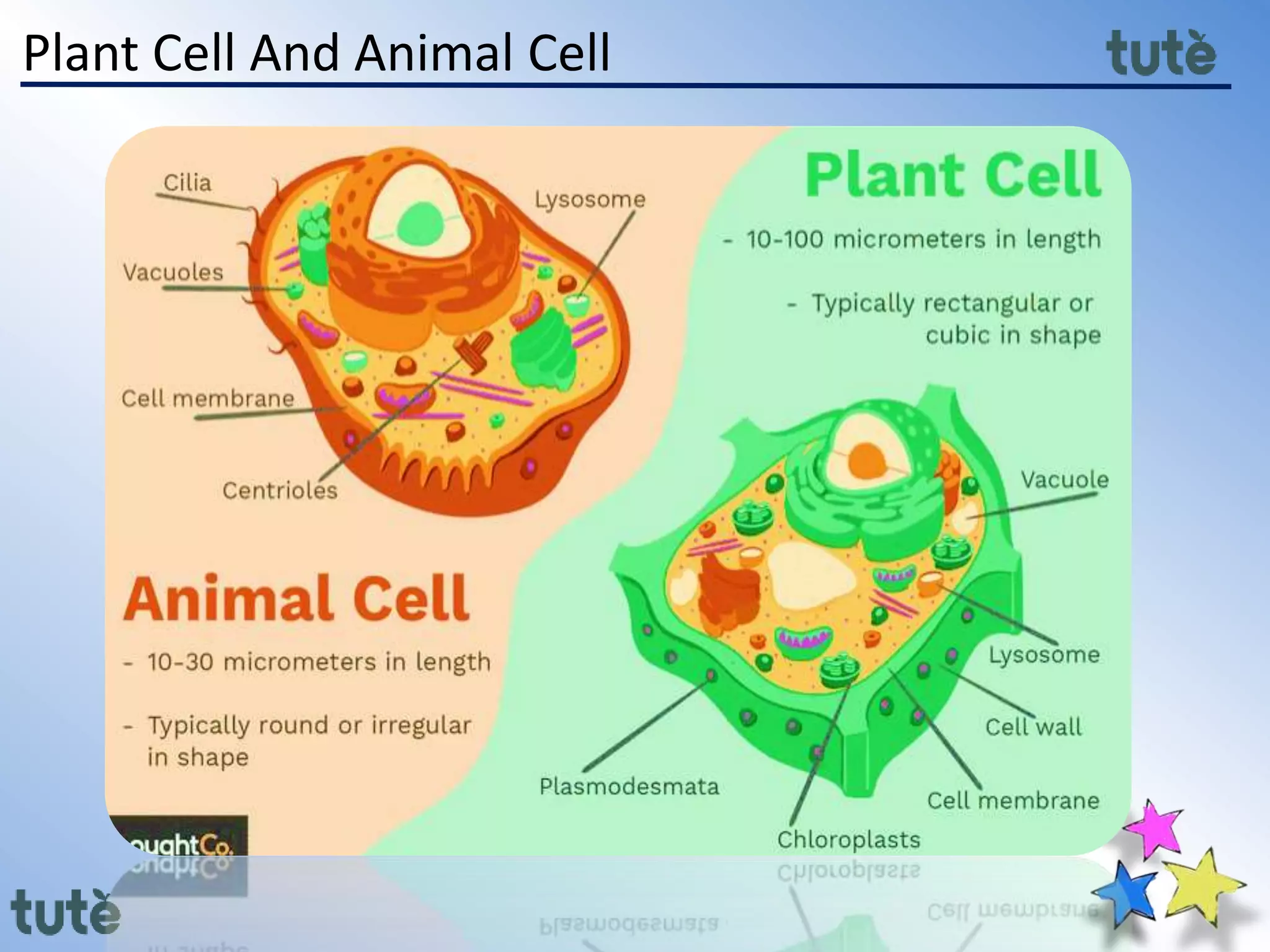
Here are the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
Prokaryotic Cells:
- Lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles
- Have circular DNA located in the nucleoid region
- Typically smaller than eukaryotic cells
- Include bacteria and archaea
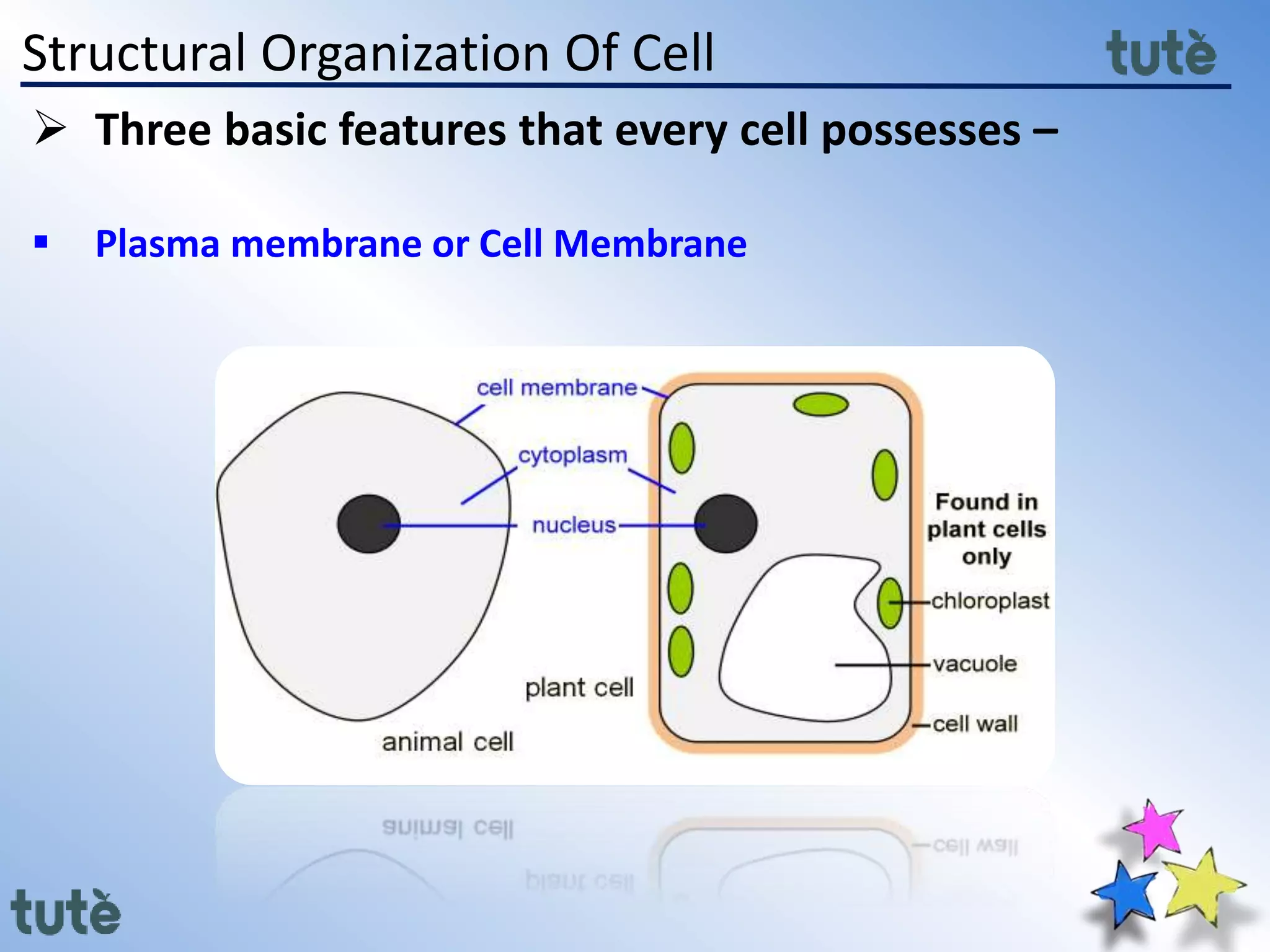
Eukaryotic Cells:
- Have a clearly defined nucleus enclosed in a nuclear membrane
- Contain membrane-bound organelles such as the mitochondria, chloroplasts, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, etc.
- Have linear DNA packaged with histone proteins into chromosomes within the nucleus
- Include plant and animal cells as well as protists, fungi and algae