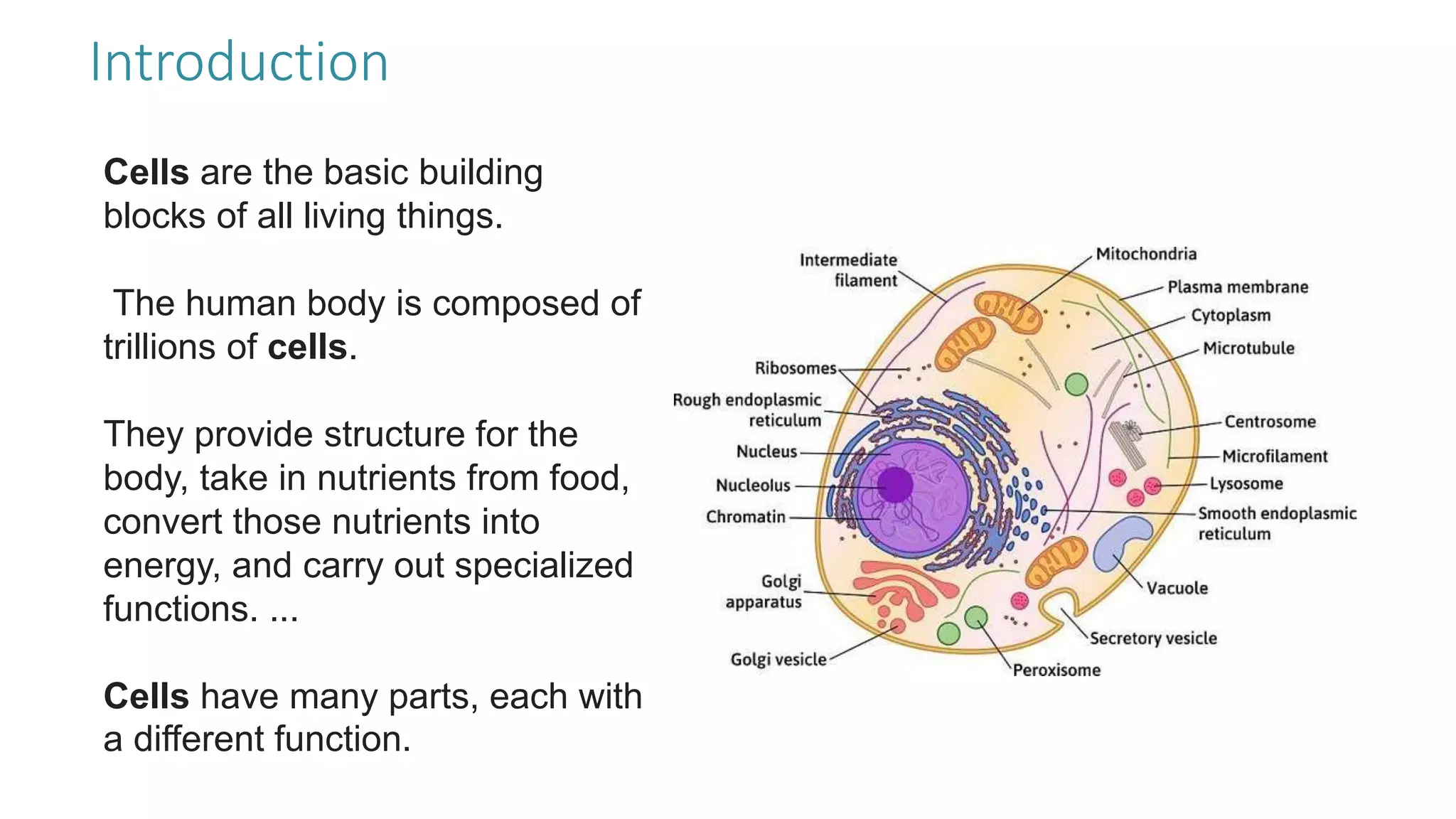
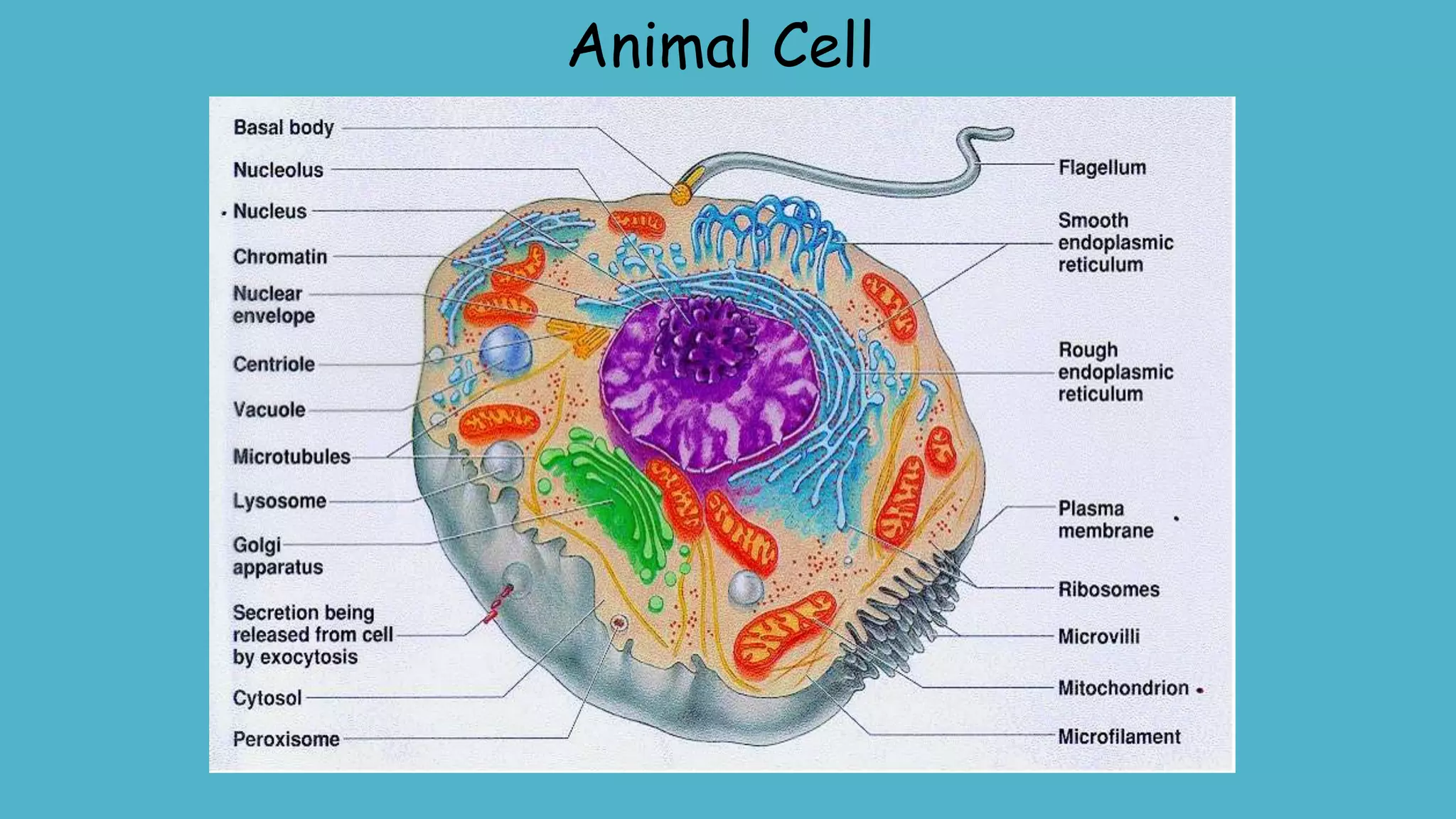
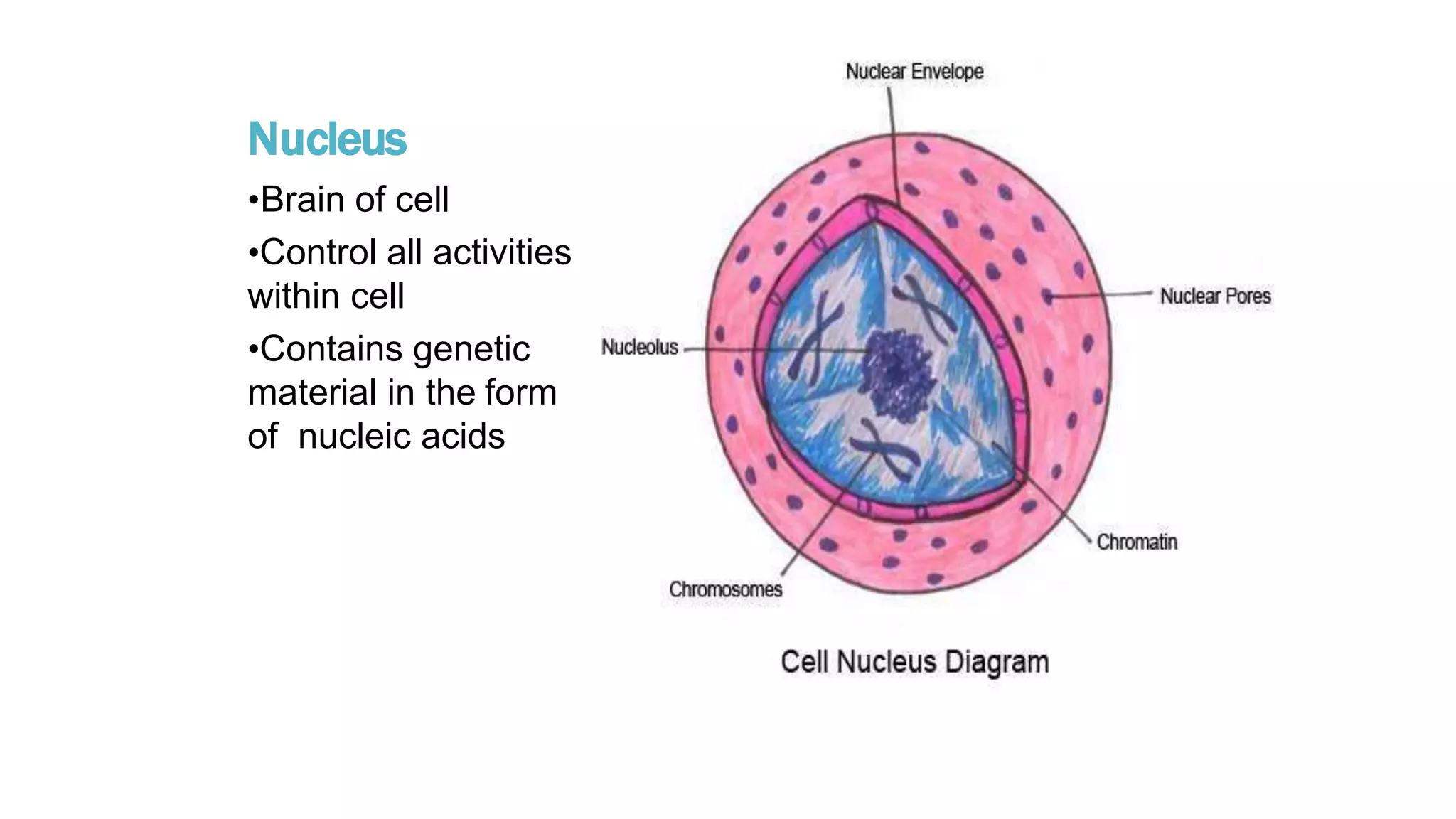
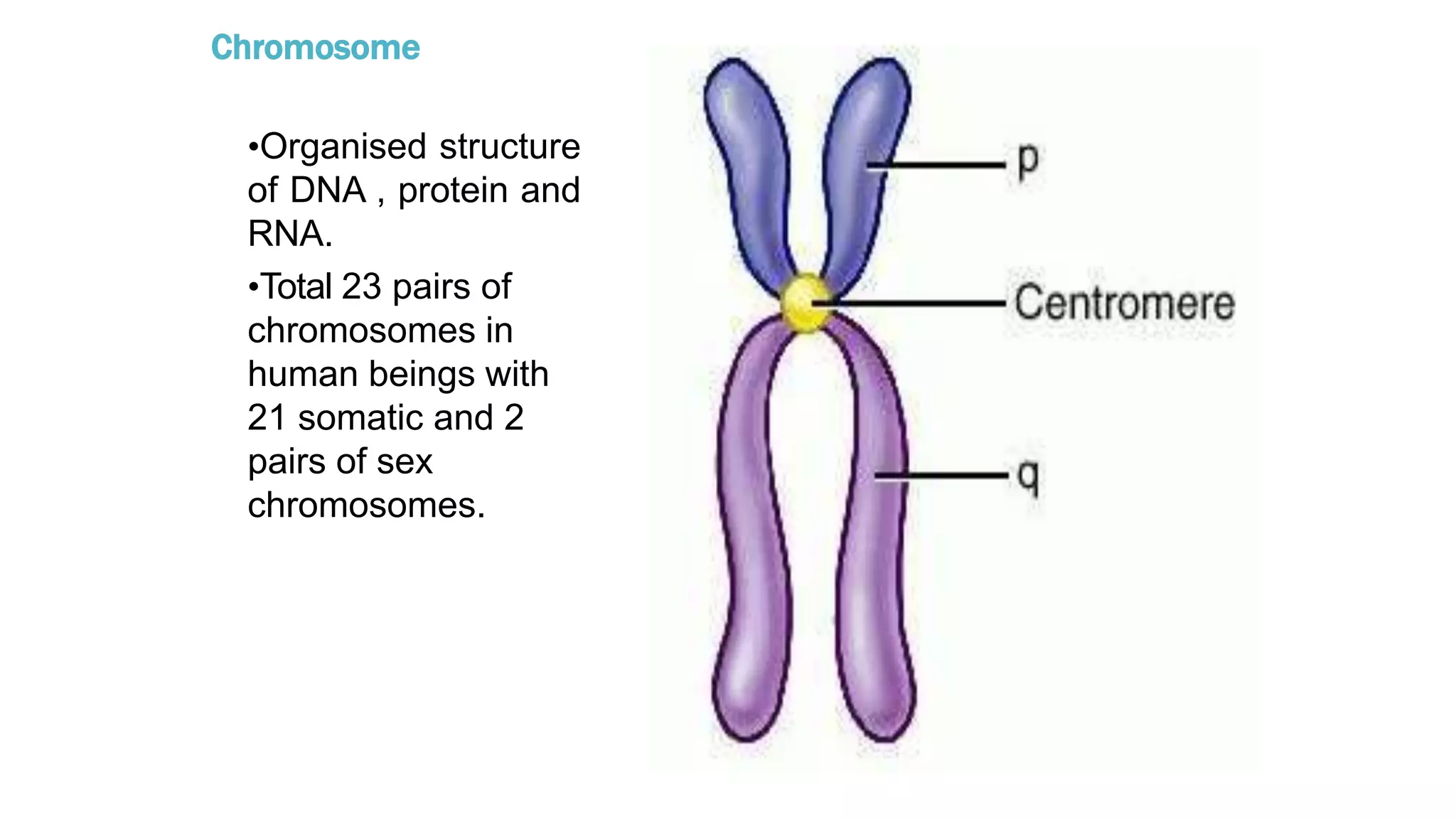
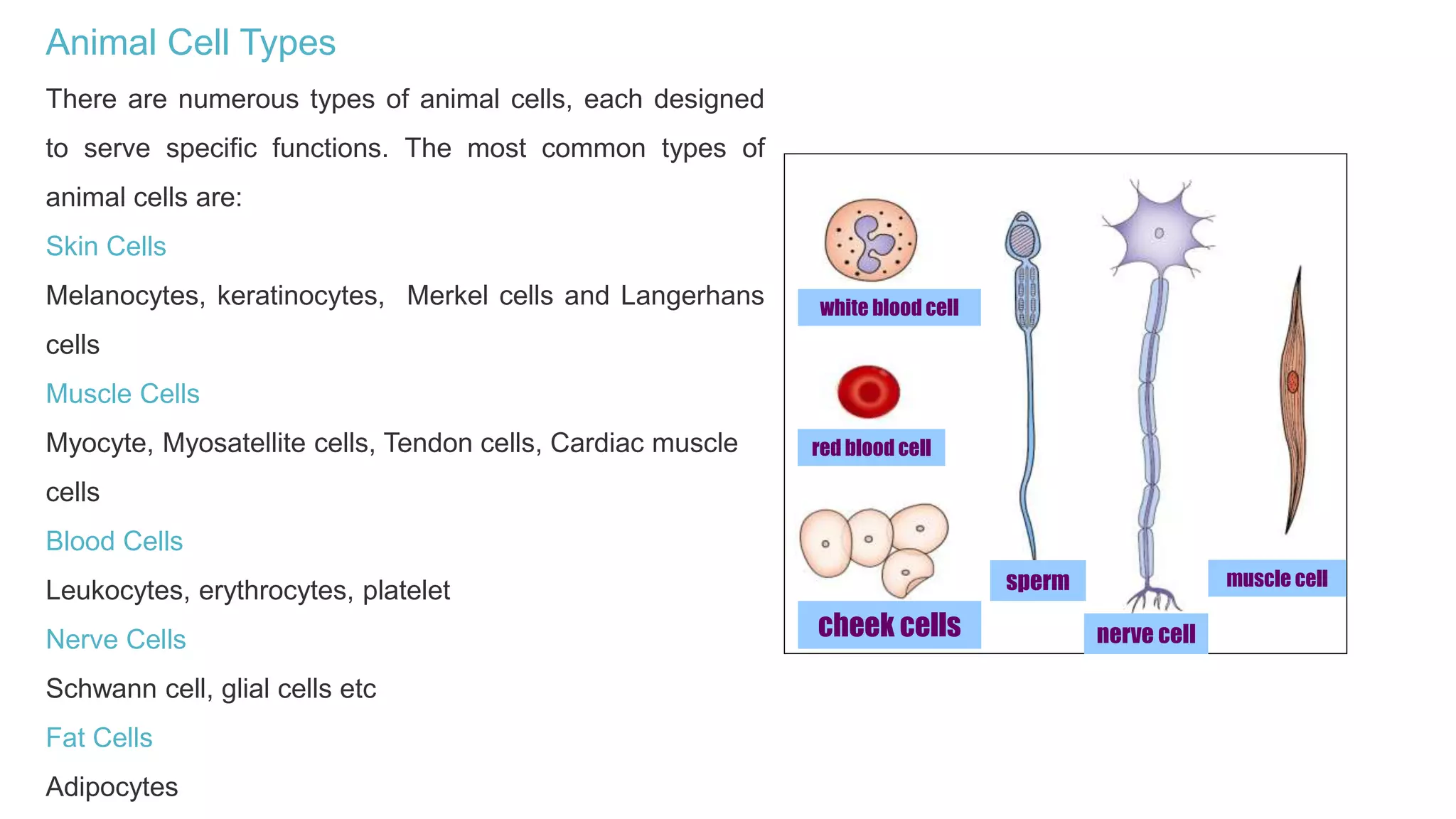
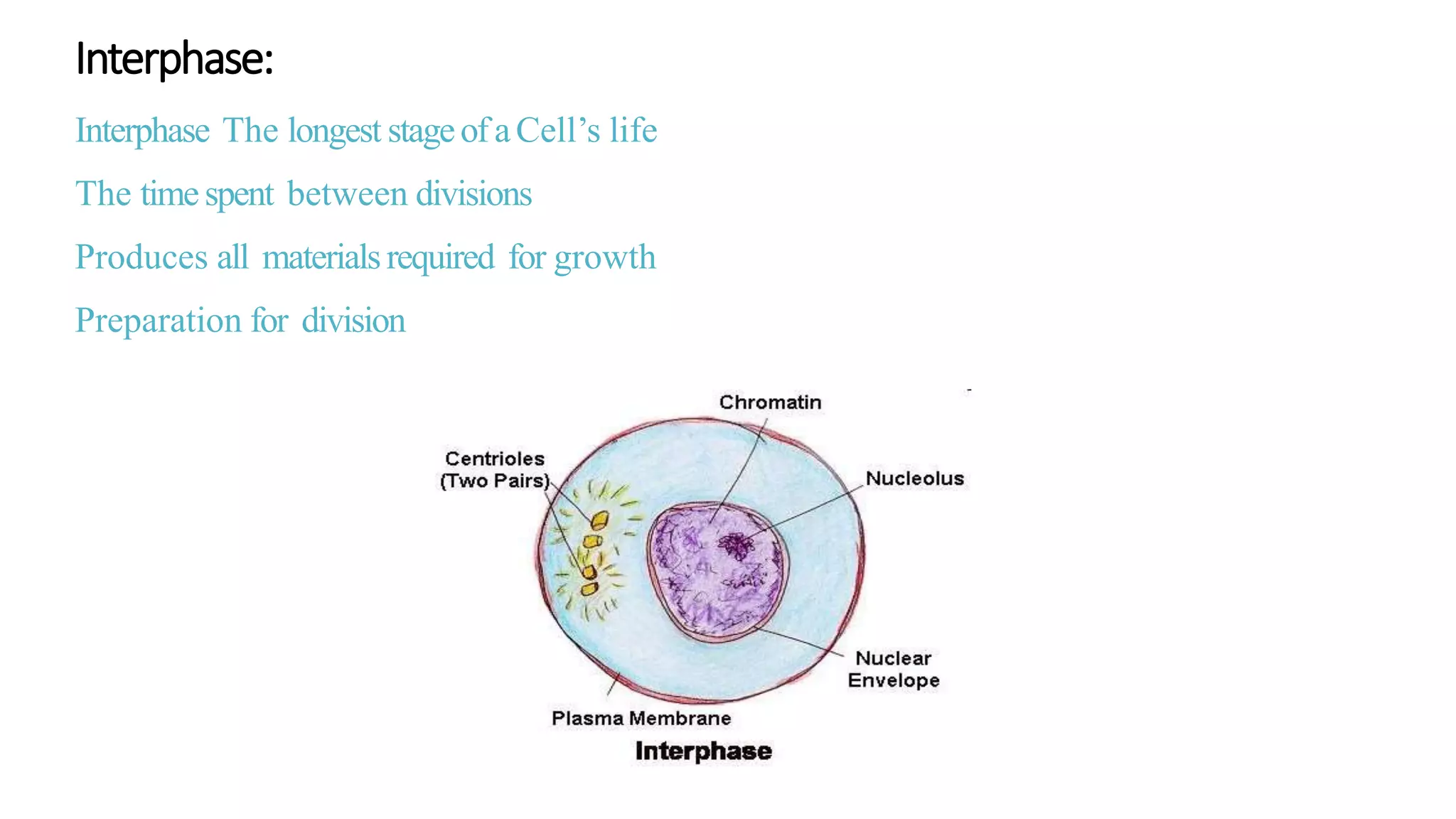
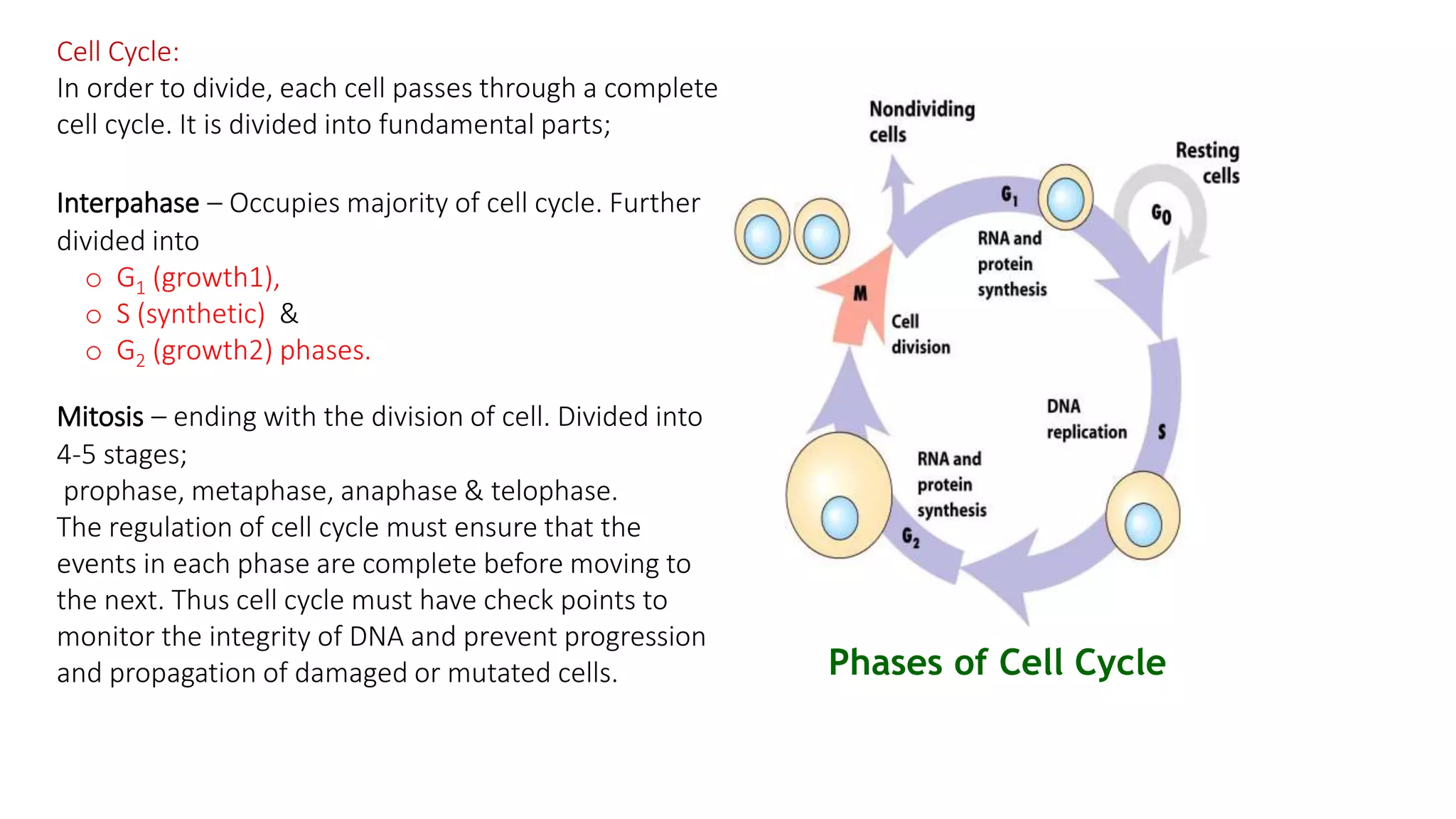
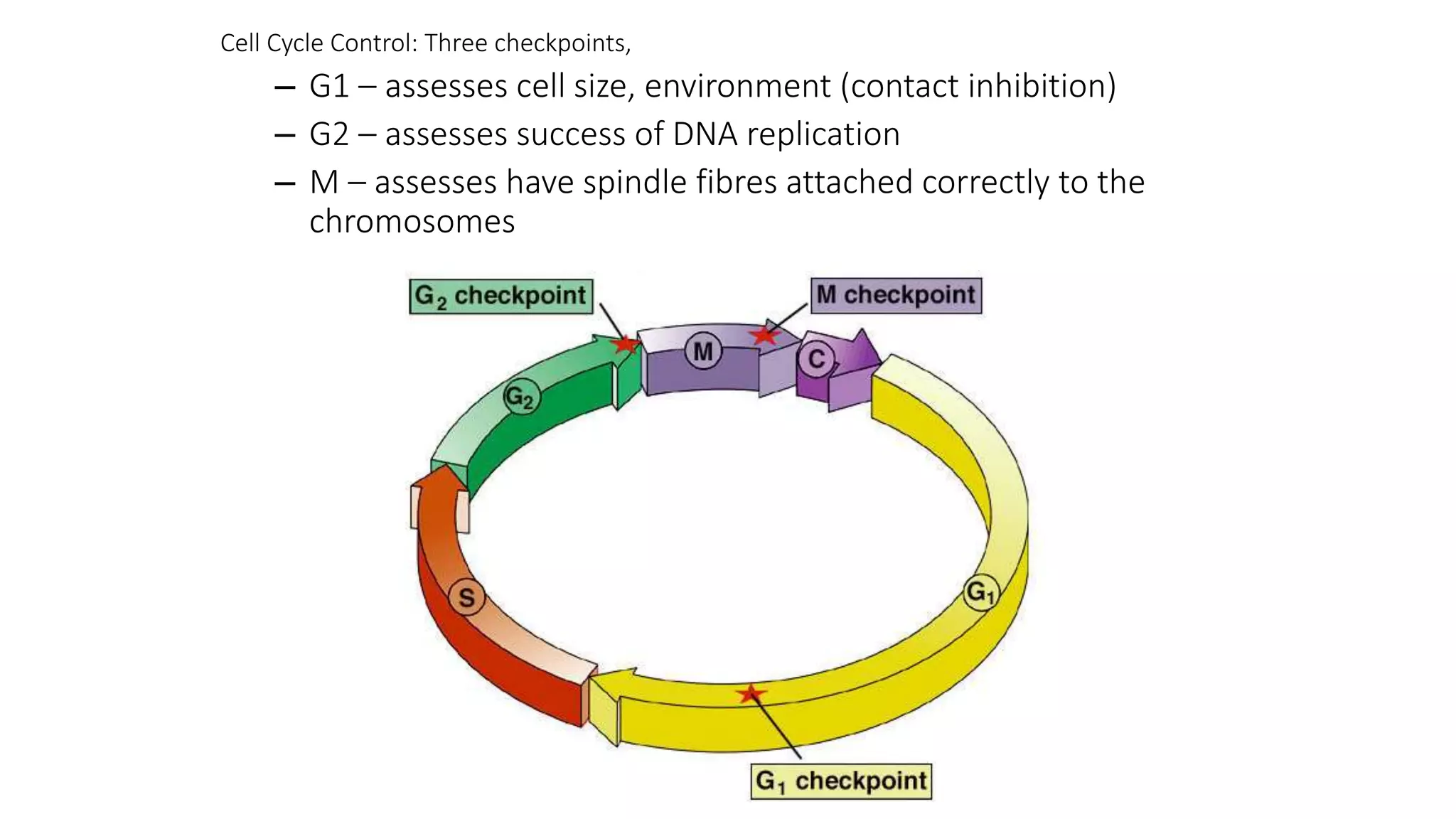
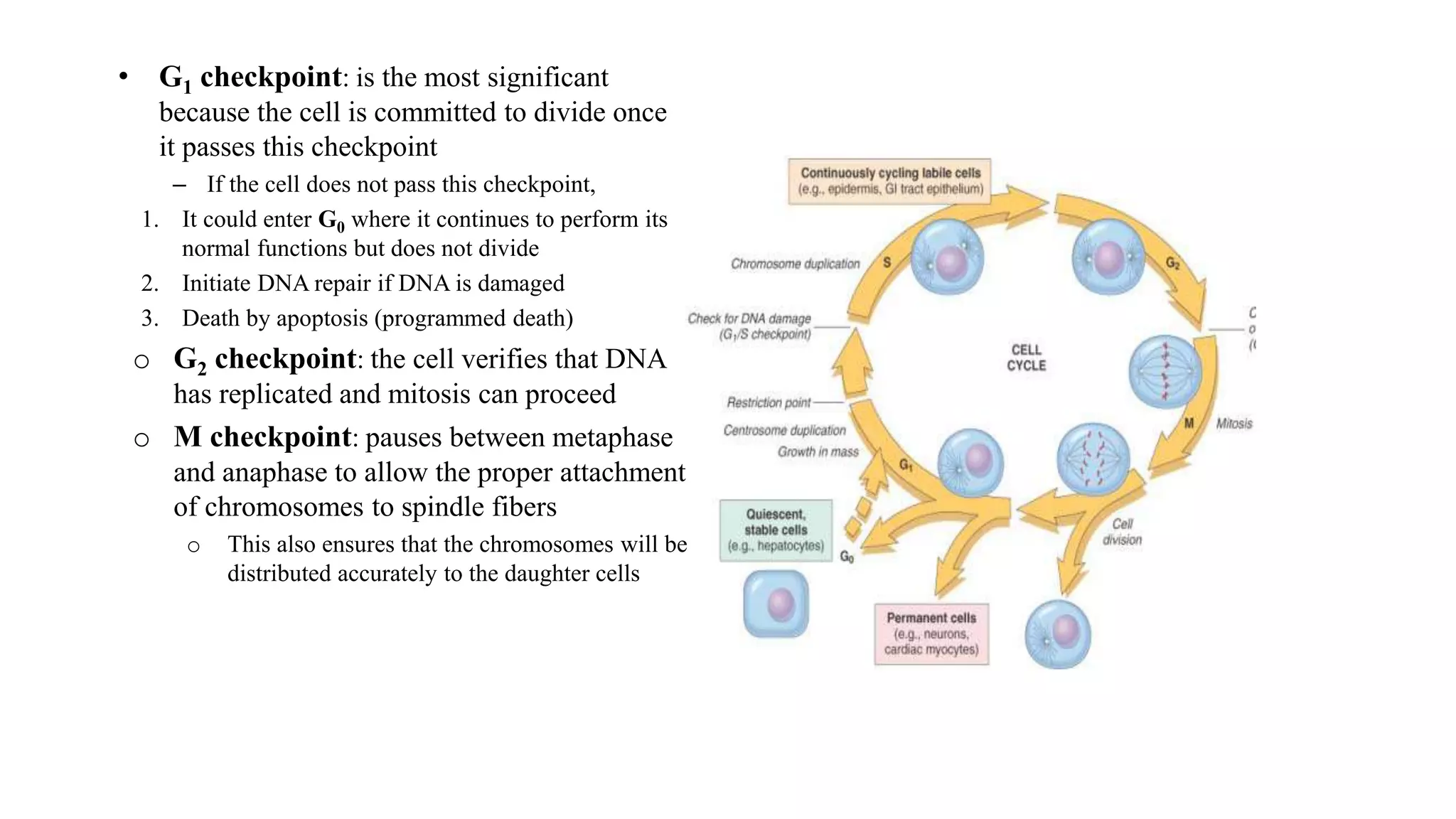
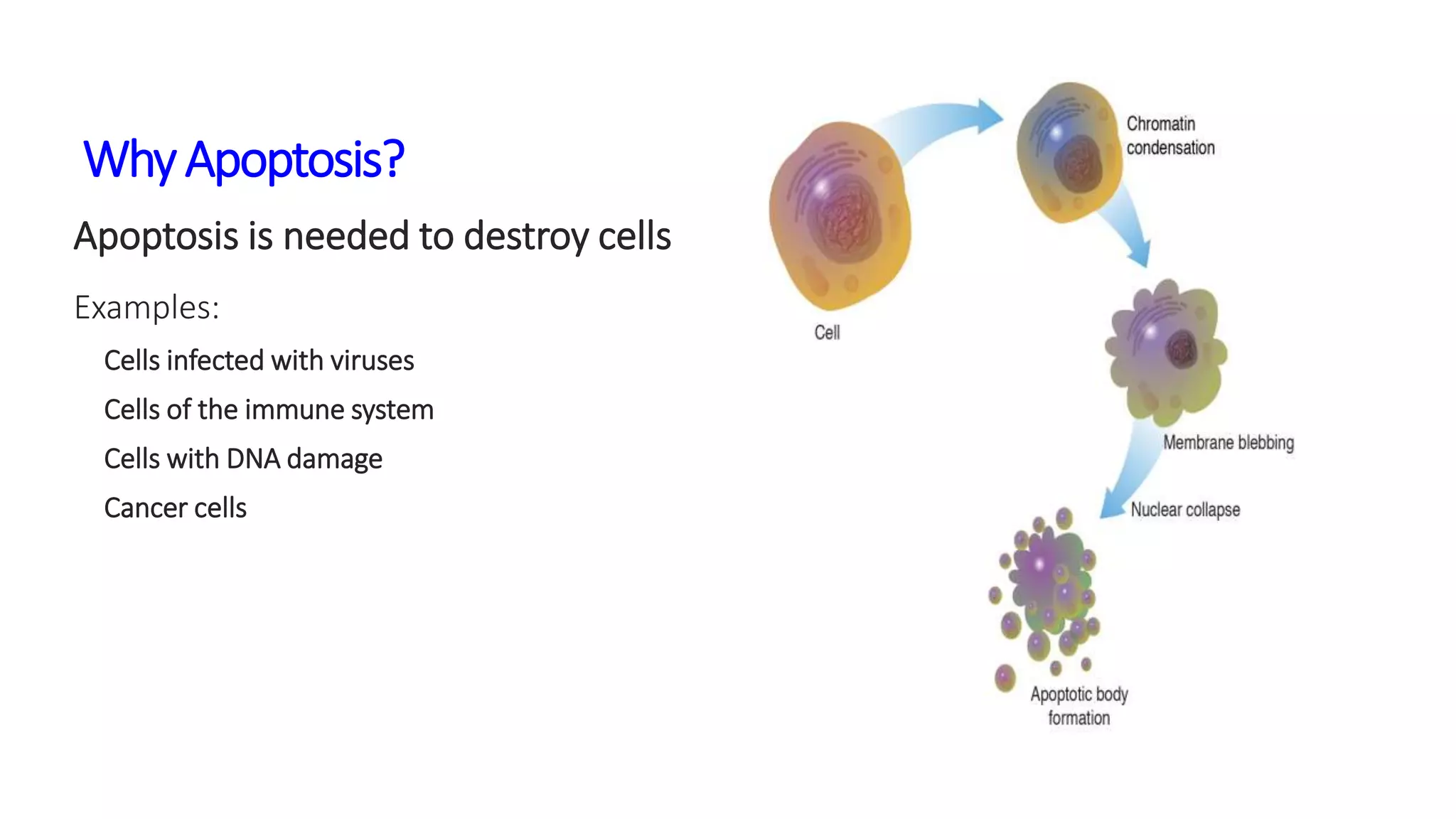
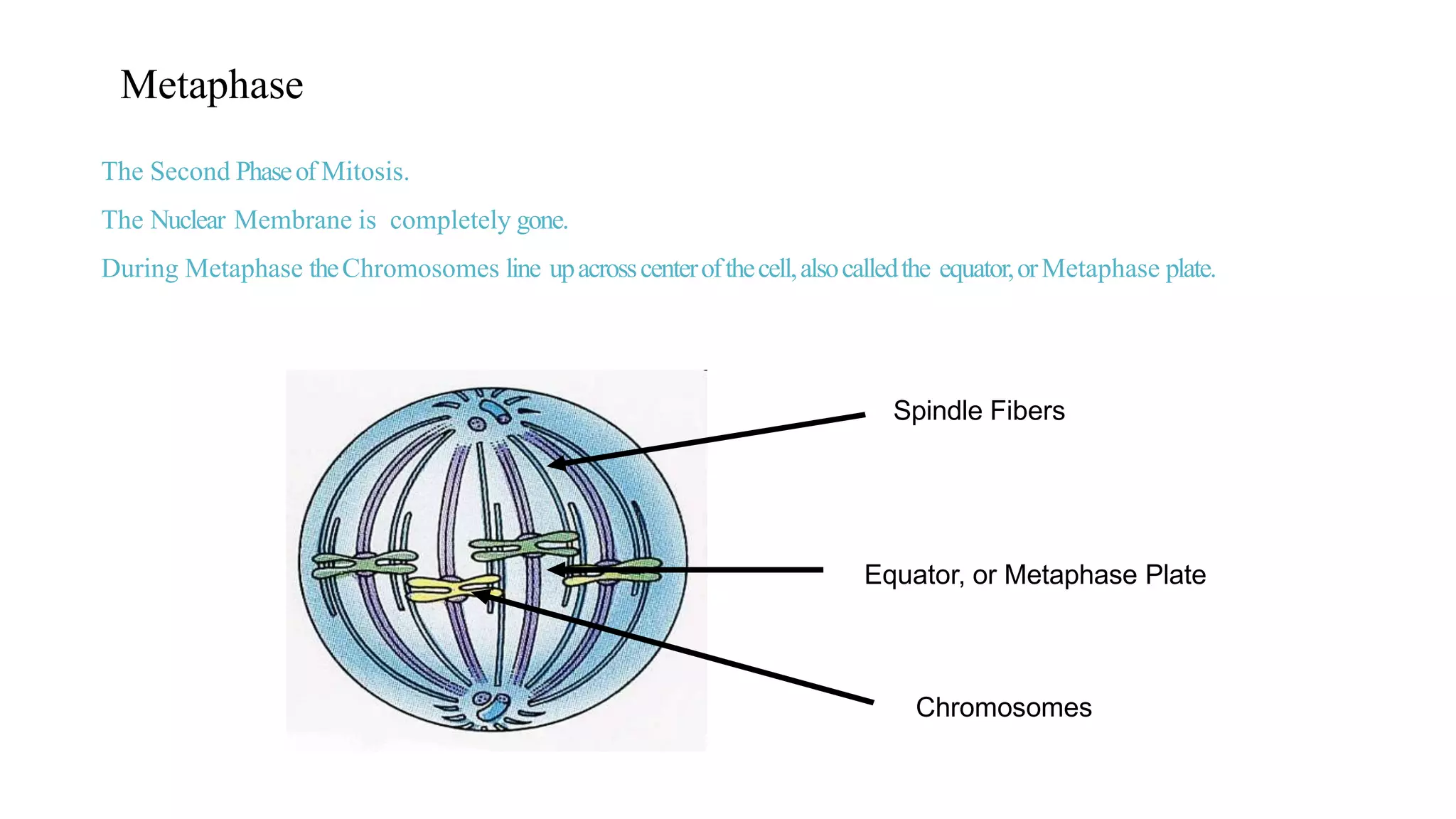
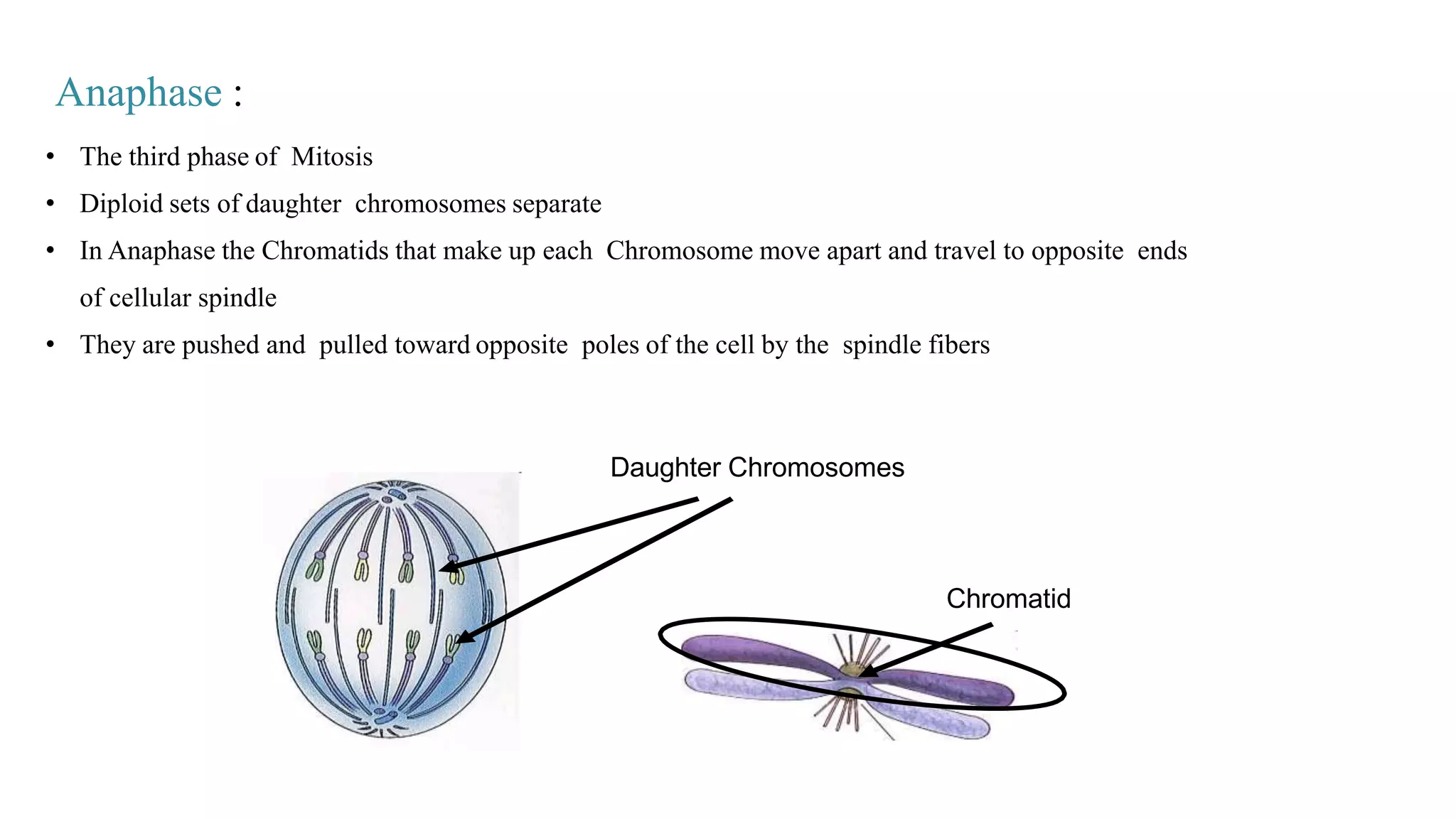
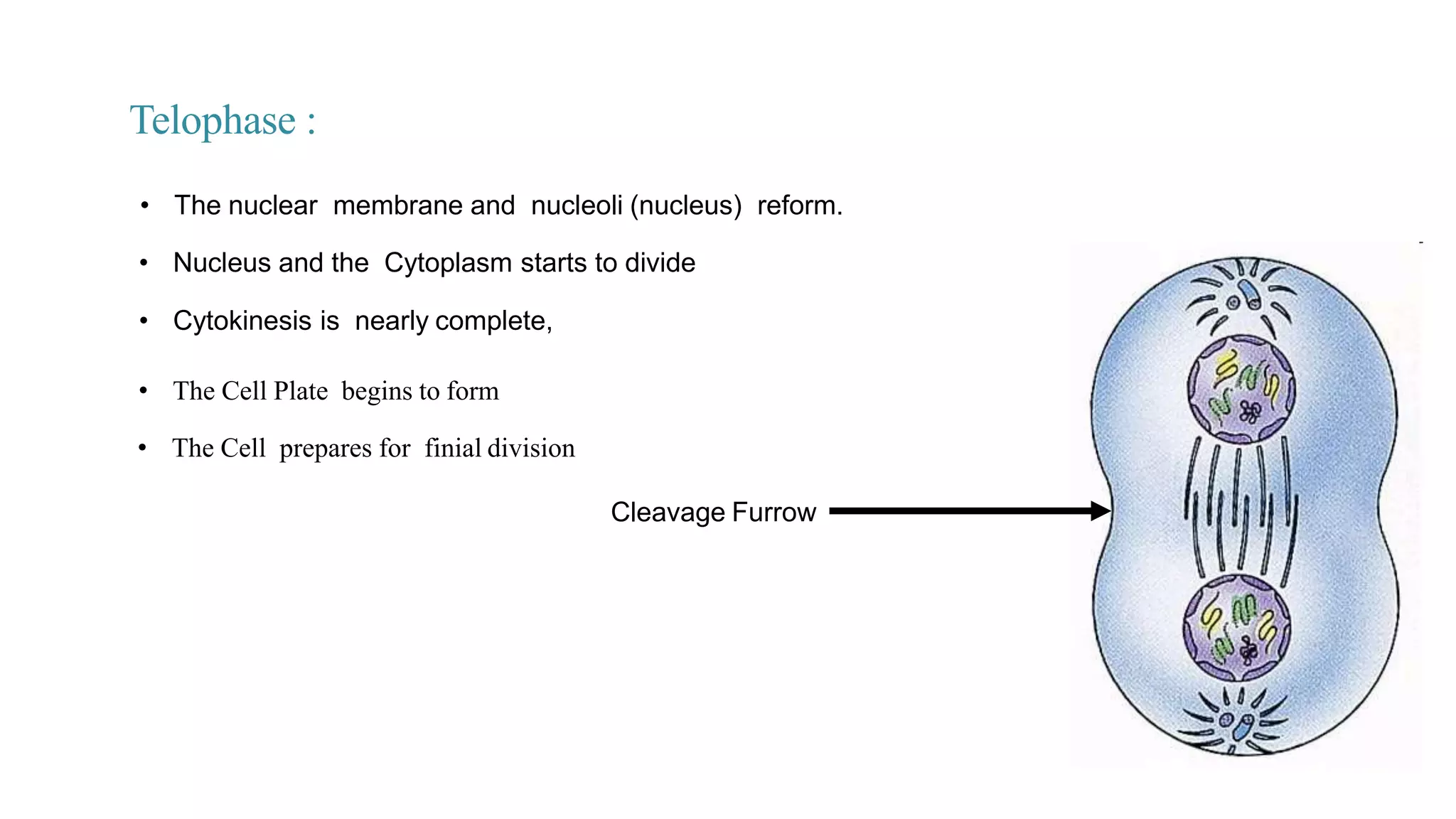
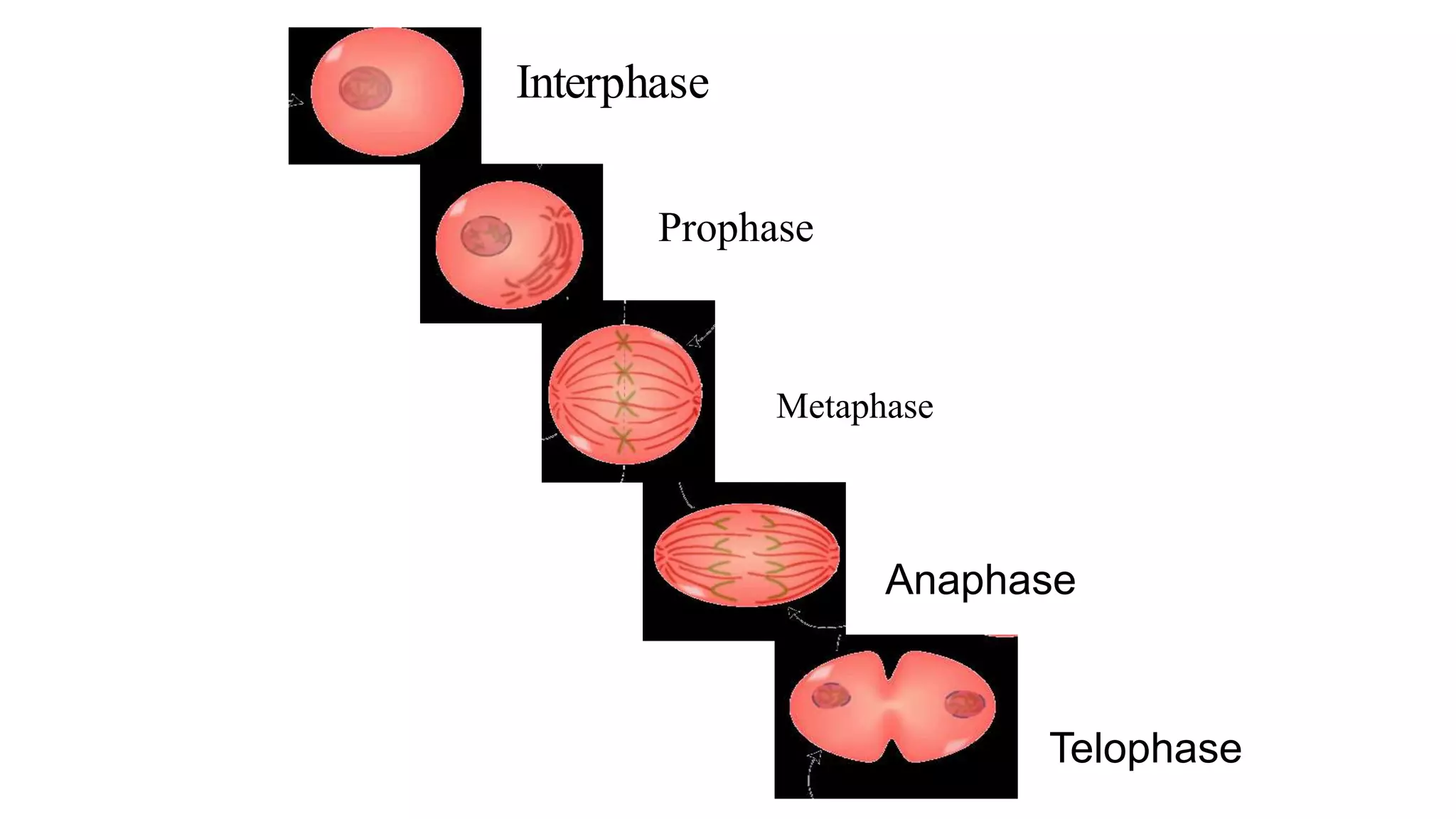
The document discusses the cell cycle and its key phases, detailing the structure and functions of various cell organelles and the crucial processes involved in cell growth, division, and apoptosis. It explains the checkpoints that regulate the cell cycle to prevent the propagation of damaged cells and the significance of each phase, particularly G1, S, G2, and M, in ensuring proper cell function and division. Furthermore, it touches upon mechanisms of growth regulation and the implications of uncontrolled cell division, such as cancer.