Tetanus- Introduction and Its epidemiology in Nepal
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
1 like•1,826 views
Tetanus is a neurological disease caused by Clostridium tetani bacteria, characterized by painful muscle spasms. There are four main types: local, cephalic, generalized, and neonatal. Generalized tetanus is the most common form, with an incubation period of 2 days to weeks. Globally, tetanus causes 18 cases per 100,000 people annually, with higher rates in developing nations. In Nepal, tetanus was a major cause of death but vaccination programs have significantly reduced cases. Risk factors include agricultural work, unhygienic delivery practices, lack of healthcare, and puncture wounds introducing soil-containing bacteria into the body.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Review of RCH, RMNCH+A including other maternal health programmes.pptx

Review of RCH, RMNCH+A including other maternal health programmes.pptx
NTEP (National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme).pptx

NTEP (National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme).pptx
REVISED NATIONAL TUBERCULOSIS CONTROL PROGRAMME (RNTCP)

REVISED NATIONAL TUBERCULOSIS CONTROL PROGRAMME (RNTCP)
Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program- Dr. Atul MD, PGIMER

Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program- Dr. Atul MD, PGIMER
Similar to Tetanus- Introduction and Its epidemiology in Nepal
Similar to Tetanus- Introduction and Its epidemiology in Nepal (20)
TETANUS Department of Physiotherapy, SHUATS, Prayagraj

TETANUS Department of Physiotherapy, SHUATS, Prayagraj
More from Kapil Sharma Neupane
More from Kapil Sharma Neupane (13)
Community diagnosis project report presentation Group-B

Community diagnosis project report presentation Group-B
Pathogenesis And Morphological changes of Myocardial Infarction

Pathogenesis And Morphological changes of Myocardial Infarction
Recently uploaded
Presentació del doctor José Ferrer, metge d'Innovació i Projectes de Badalona Serveis Assistencials, al I Simposio Internacional de Realidad Inmersiva para Reanimación, celebrat a Múrcia el 24 i el 25 de maig de 2024.Presentació "Advancing Emergency Medicine Education through Virtual Reality"

Presentació "Advancing Emergency Medicine Education through Virtual Reality"Badalona Serveis Assistencials
Recently uploaded (20)
Surat @ℂall @Girls ꧁❤8527049040❤꧂@ℂall @Girls Service Vip Top Model Safe

Surat @ℂall @Girls ꧁❤8527049040❤꧂@ℂall @Girls Service Vip Top Model Safe
Scientificity and feasibility study of non-invasive central arterial pressure...

Scientificity and feasibility study of non-invasive central arterial pressure...
Aptopadesha Pramana / Pariksha: The Verbal Testimony

Aptopadesha Pramana / Pariksha: The Verbal Testimony
linearity concept of significance, standard deviation, chi square test, stude...

linearity concept of significance, standard deviation, chi square test, stude...
For Better Surat #ℂall #Girl Service ❤85270-49040❤ Surat #ℂall #Girls

For Better Surat #ℂall #Girl Service ❤85270-49040❤ Surat #ℂall #Girls
Impact of cancers therapies on the loss in cardiac function, myocardial fffic...

Impact of cancers therapies on the loss in cardiac function, myocardial fffic...
"Central Hypertension"‚ in China: Towards the nation-wide use of SphygmoCor t...

"Central Hypertension"‚ in China: Towards the nation-wide use of SphygmoCor t...
Presentació "Advancing Emergency Medicine Education through Virtual Reality"

Presentació "Advancing Emergency Medicine Education through Virtual Reality"
ANATOMY OF THE LOWER URINARY TRACT AND MALE [Autosaved] [Autosaved].pptx![ANATOMY OF THE LOWER URINARY TRACT AND MALE [Autosaved] [Autosaved].pptx](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![ANATOMY OF THE LOWER URINARY TRACT AND MALE [Autosaved] [Autosaved].pptx](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
ANATOMY OF THE LOWER URINARY TRACT AND MALE [Autosaved] [Autosaved].pptx
CURRENT HEALTH PROBLEMS AND ITS SOLUTION BY AYURVEDA.pptx

CURRENT HEALTH PROBLEMS AND ITS SOLUTION BY AYURVEDA.pptx
TEST BANK For Timby's Introductory Medical-Surgical Nursing, 13th American Ed...

TEST BANK For Timby's Introductory Medical-Surgical Nursing, 13th American Ed...
The POPPY STUDY (Preconception to post-partum cardiovascular function in prim...

The POPPY STUDY (Preconception to post-partum cardiovascular function in prim...
Compare home pulse pressure components collected directly from home

Compare home pulse pressure components collected directly from home
Tetanus- Introduction and Its epidemiology in Nepal
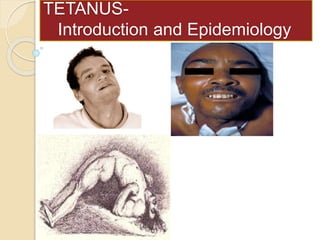
- 2. INTRODUCTION Tetanos (Gr.) =to stretch Tetanus is a neurological disease, characterized by an acute onset of hypertonia, painful muscular contractions and generalised muscle spasms without other apparent medical causes. Symptoms include trismus, resus sardoricus, opisthotonus, respiratory failure, dysphagia, ANS effects like hypertension, tachycardia, excessive sweeting, hyperpyrexia, peripheral vasoconstriction). Only VPD that is infectious but not contagious.
- 3. Causative agent: Clostridium tetani Spore- Drumstick/ Tennis racket appearance
- 4. TYPES OF TETANUS 1. LOCAL TETANUS: Contraction and spasm are only limited to site of injury. Usually lasts for a week and then subsides to milder and less threatening form. Proper treatment is required to avoid it’s development into generalised tetanus. 2. CEPHALIC TETANUS: Rarest form Associated with lesions of the head or face(otitis media) Incubation period:1 to 2 days Results in flaccid cranial nerve palsies rather than spasm. Spasm of the jaw muscles may also be present. Can progress to the generalized form.
- 5. 3. GENERALIZED TETANUS: Most common form of tetanus (80%) Descending pattern Spasms continues for 3-4 weeks and recovery can last for months. Incubation period: 2days- few weeks(8 days in average) 4. NEONATAL TETANUS Occurs in newly born children due to infection of unhealed umbilical stump, when it is cut with an unsterile instrument. Incubation period: 4-14 days
- 6. EPIDEMIOLOGY An important cause of death worldwide with high case fatality, in the developing world (comparatively less in developed countries- 43 cases per year in USA). Global incidence:18 cases per 1 lakh popn per year Case fatality: 20-50% Easily preventable by vaccination Ubiquitous distribution, but more in tropics, hot damp climates with soil highly rich in organic matters. Tetanus neonatarum: Due to lack of MCH care.
- 7. EPIDEMIOLOGY IN NEPAL Tetanus is the major cause of morbidity and mortality in Nepal. To control tetanus government of Nepal has introduced EPI in 1979 which significantly reduced the burden of VPDs including tetanus. Different programs like maternal and neonatal tetanus elimination program, safe motherhood program, tetanus toxoid (TT) campaign, training to birth attendants, health education etc are being conducted by GON. NT has been eliminated in Nepal since 2005. Now Nepal is aiming at controlling tetanus and sustaining NT elimination status.
- 8. In 1996, 6700 estimated deaths due to NT Mortality rate= 8.8 per 1000 live births. In 1997, 5800 estimated deaths Mortality rate=7 per 1000 live births. During the fiscal year 2003/2004, 63 cases of NT and 169 cases of non neonatal tetanus were reported. During the fiscal year 2006/2007, 42 cases of NT and 155 cases of non neonatal tetanus were reported.
- 9. Study conducted at BPKIHS Over 22 months period from 2004 to 2006, there were 19 cases of pediatric tetanus and 5 cases of NT. During the fiscal year 2006/2007, Morbidity at age 20-49= 43.2% of cases Pediatric tetanus= 26.3% cases
- 10. DETERMINANTS Agent factors: 1. Reservoir: Soil and intestine of mammals. 2. Toxins: Tetanospasmin and Tetanolysin (LD= 0.1 mg) 3. Period of communicability: None Host factors: 1. Age: Active age(5-40 years), new born baby, female during delivery and abortions. 2. Sex: Male> Female 3. Occupation: Agricultural workers 4. Distribution: Rural>urban
- 11. Environmental & social factors: 1. Unhygienic delivery practices 2. Traditional birth customs 3. Interest in immunization 4. Lack of PHC services Route of infections: 1. Pin prick & skin abrasion 2. Puncture wounds, burns 3. Unsterile surgery, IUDs and injections 4. Unsterile division of umbilical cord 5. Compound fractures, Otitis media 6. Chronic skin ulcers, Eye infections 7. Gangrenous limbs -NO WOUND, NO INFECTIONS
- 12. Tetanus prone wound: 1. >6 hours before surgery 2. Puncture type wound showing devitalised tissue, contaminated with soil.
- 13. Content Sources: Textbook of Preventive and Social Medicine-K. Park Anantanarayan and Paniker’s Textbook of Microbiology Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2009), Vol. 7, No. 3, Issue 27, 315- 322 WHO report (2018) Pictures Source:Internet
Editor's Notes
- lock jaw stiffness of neck difficulty in swallowing rigidity of abdominal and back muscles.
