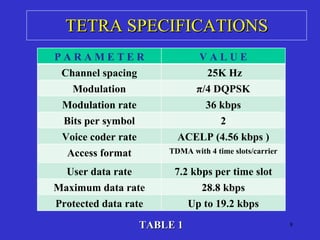
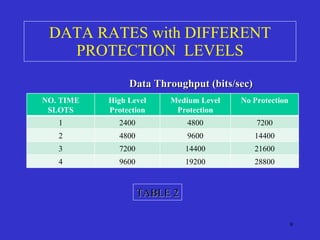
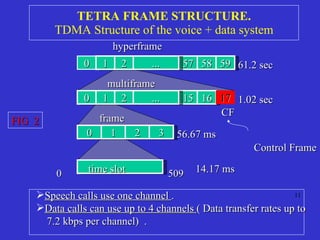
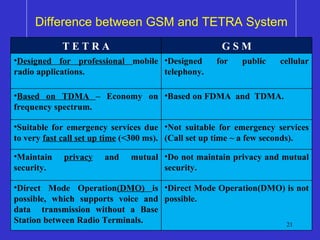
The document discusses TETRA (Terrestrial Trunked Radio), a digital mobile radio standard designed for professional applications, emphasizing its advantages over analog systems, such as reliability, flexibility, and faster call setup times. TETRA supports various communication types including private, group, and emergency calls while utilizing efficient trunking systems to manage limited frequency resources. The text also highlights its application in public safety and the necessity for integrated communication networks to enhance operational effectiveness in emergencies.