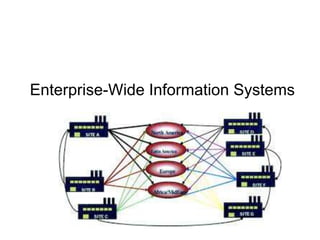
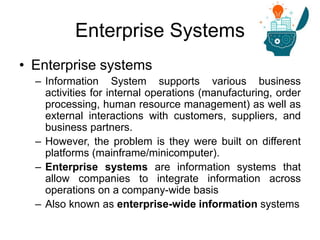
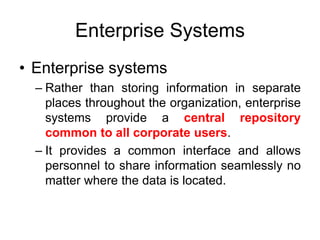
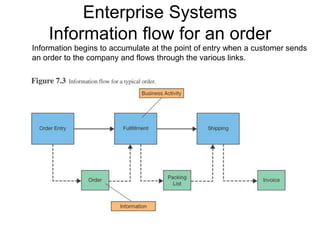
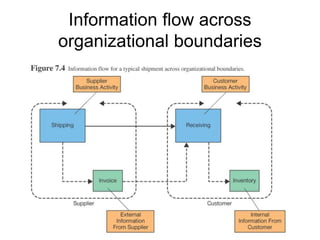
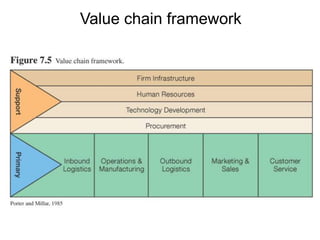
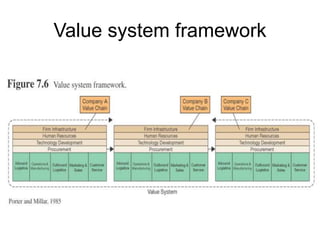
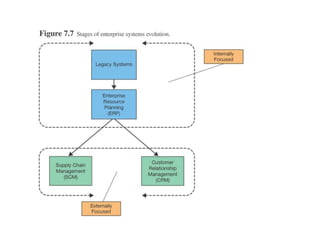
Enterprise systems integrate information across a company's operations on a company-wide basis. They provide a central repository for information that is common to all corporate users. These systems allow seamless sharing of information regardless of where the data is located. Interorganizational systems facilitate information flow between companies to streamline processes. Enterprise systems can be internally or externally focused to coordinate activities within a company or with external partners.