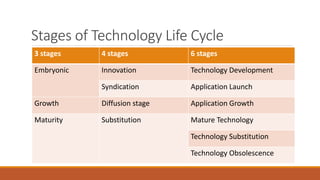
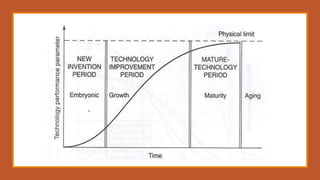
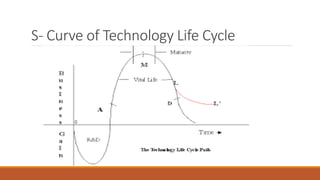
The document discusses the advantages of advanced technology in domestic and global markets. It outlines how technological advancement leads to economic growth and a wealthier nation by making organizations more efficient, competitive, and profitable. It also describes technology life cycles and strategies, including scanning the environment, strategic planning, forecasting, and analyzing strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The technology policy aims to promote scientific temper, skills, careers in science and research, infrastructure for R&D, private sector participation, and innovations that create wealth.