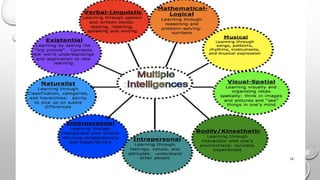
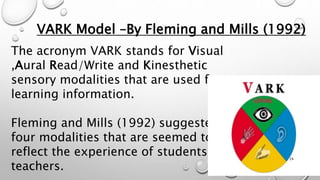
This document discusses learning styles and teaching strategies. It defines learning styles as a student's preferred way of thinking, processing, and understanding information. The document outlines several learning style models, including the VARK model which categorizes students as visual, auditory, reading/writing, or kinesthetic learners. It recommends that teachers incorporate strategies that appeal to all learning styles, such as using visual aids, role playing, and interactive activities. The document also discusses principles of effective teaching, including setting clear learning outcomes, presenting material clearly, engaging students actively, and displaying enthusiasm.