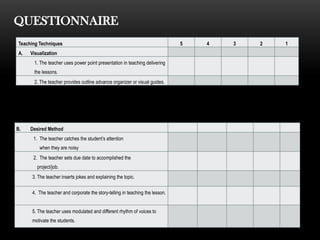
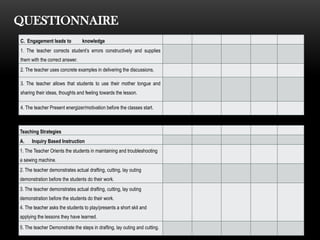
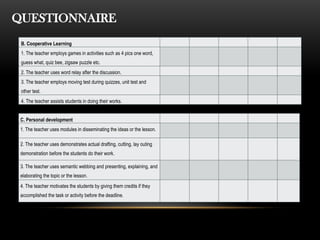
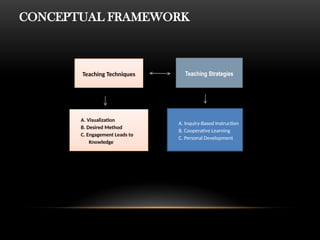
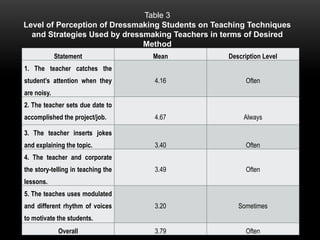
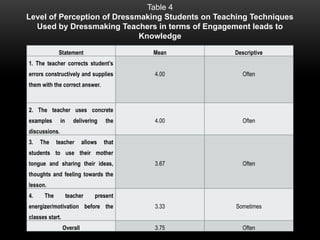
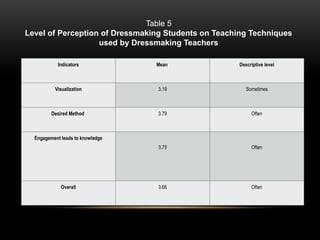
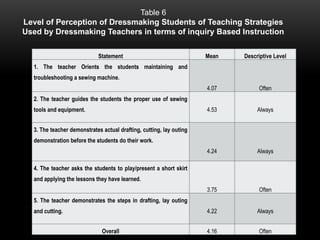
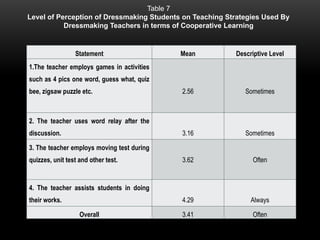
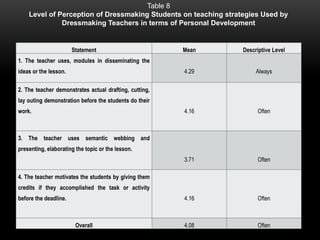
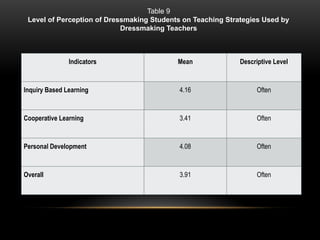
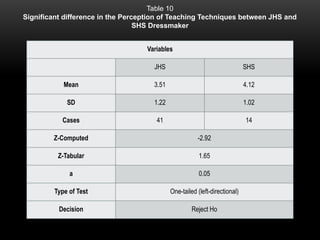
The document explores the perceptions of dressmaking students at Luzon National High School regarding teaching techniques and strategies employed by their instructors. It highlights concerns such as student failure and academic unpreparedness while posing research questions about the effectiveness of specific teaching methods and strategies. The study employs quantitative survey research to gather data from a sample of 55 students, analyzing their feedback on various teaching approaches and their overall educational engagement.