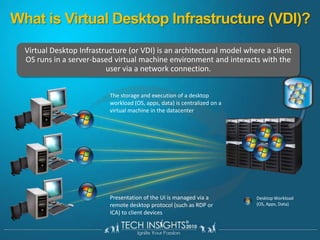
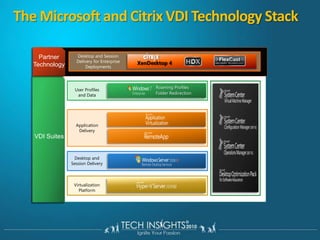
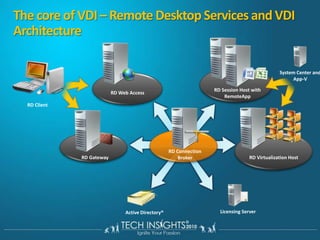
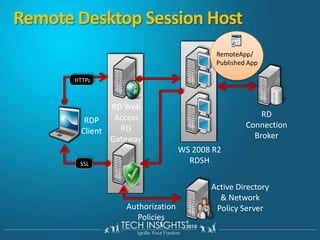
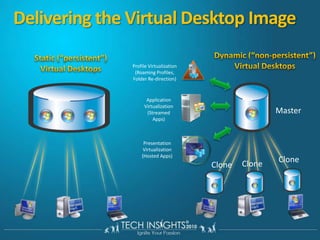
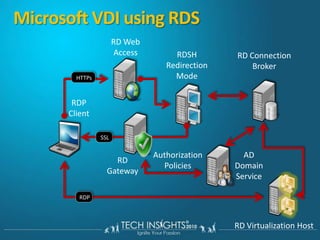
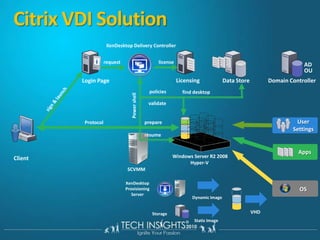
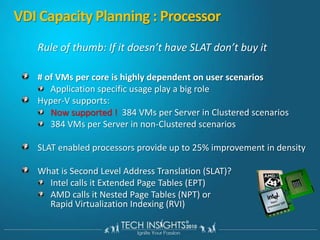
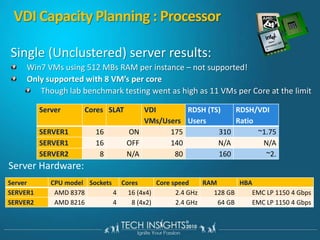
This document discusses virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) and provides demonstrations of VDI solutions using Microsoft Remote Desktop Services and Citrix. It begins with an introduction to VDI and how it works. It then demonstrates Remote Desktop Services for remote desktops and application publishing. Next, it demonstrates a VDI solution using Remote Desktop Services and Citrix with the Microsoft platform. It concludes with a discussion of VDI capacity planning considerations around processors, memory, disk I/O, and network performance.