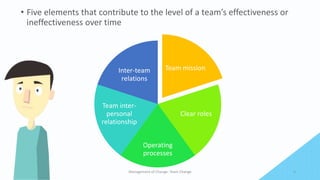
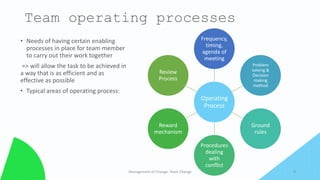
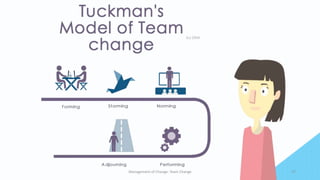
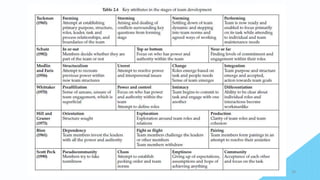
Team change involves going through distinct stages. Effective teams have clear missions and goals aligned with their purpose. They define roles and processes to work efficiently. Relationships and communication are important. When a team changes, it forms new structures and norms, potentially experiences internal conflict as roles are established (storming), then settles into ways of working together (norming) to perform its task. The final stage is completing the task and disbanding (adjourning).