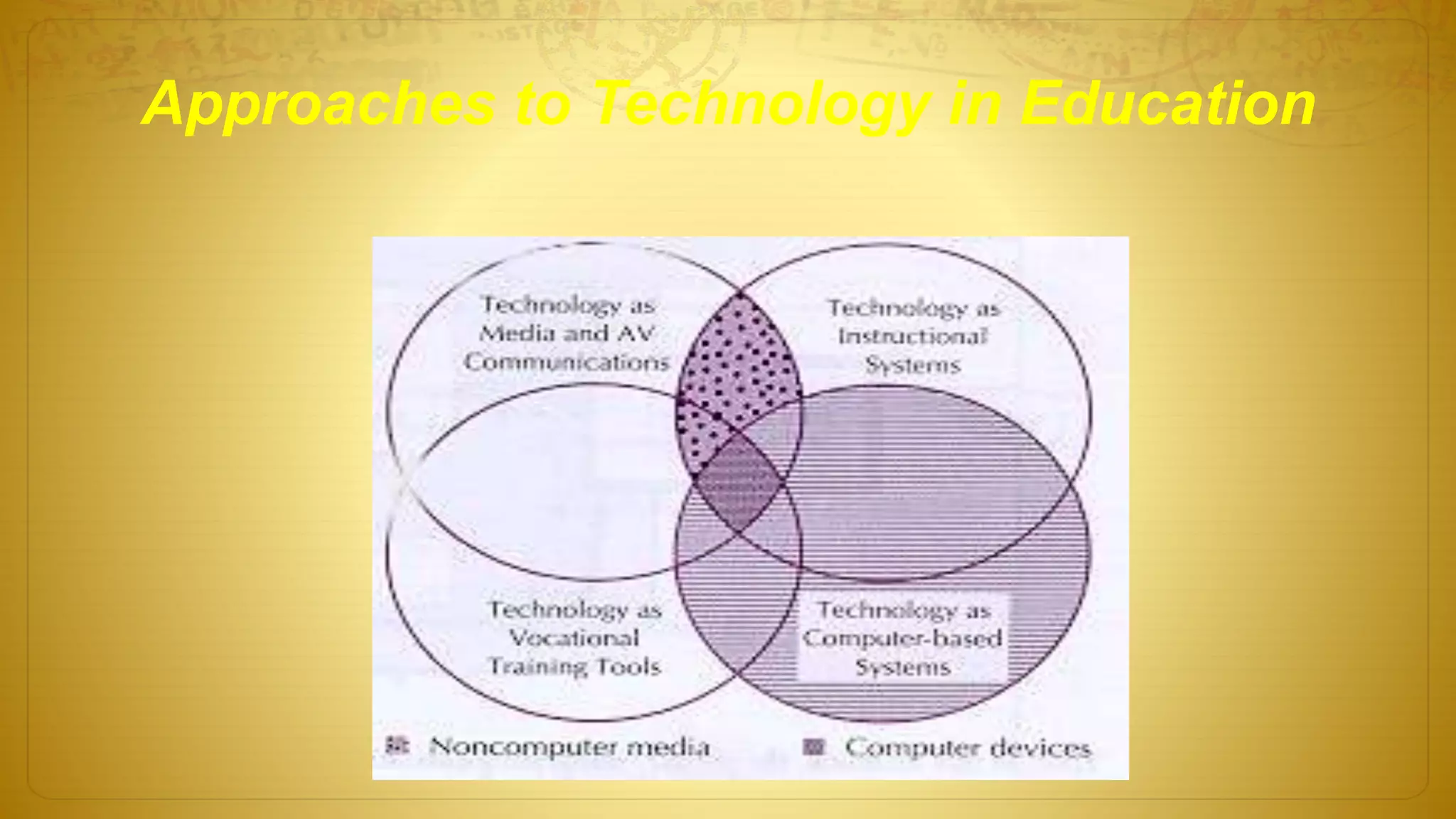
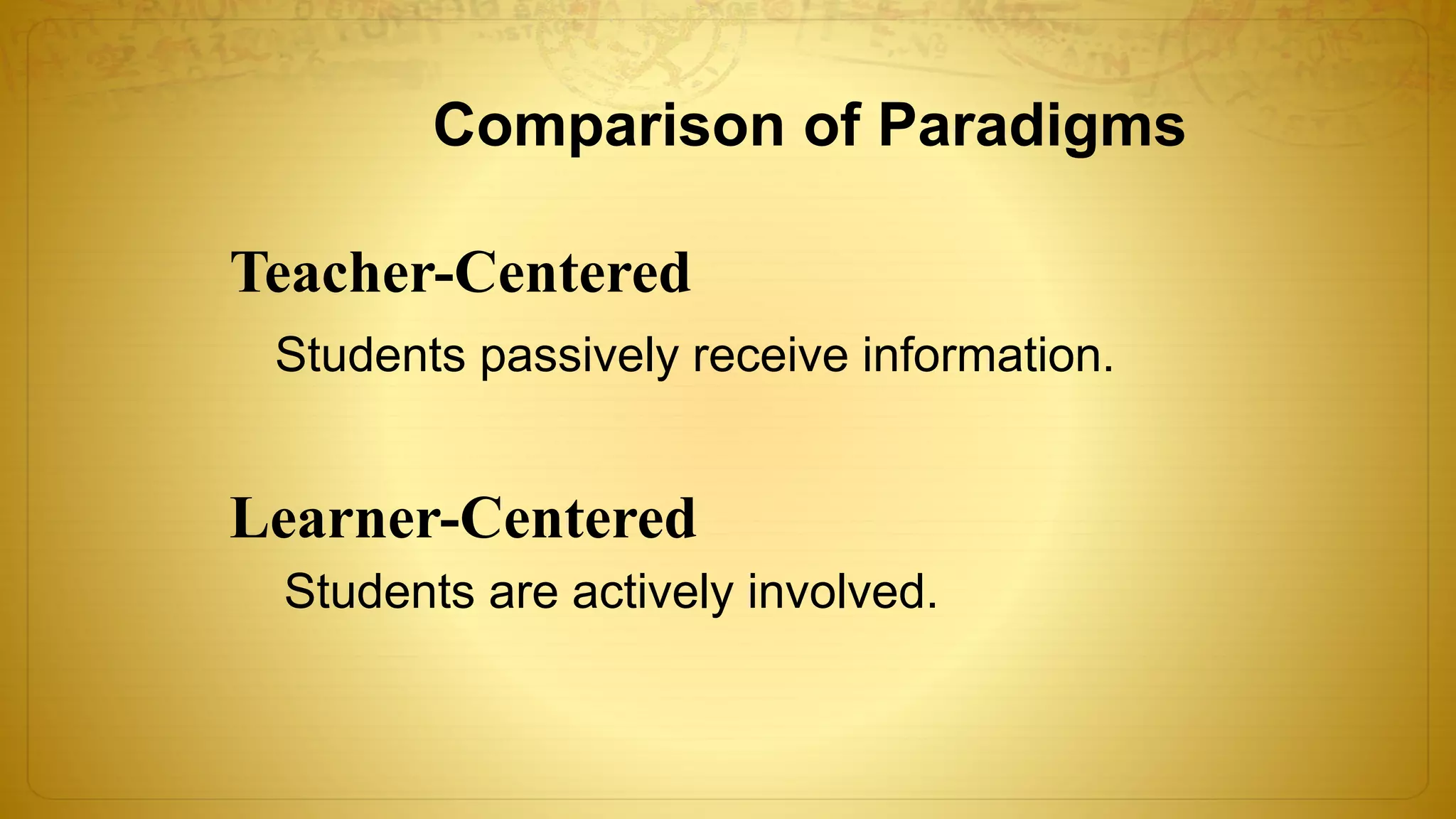
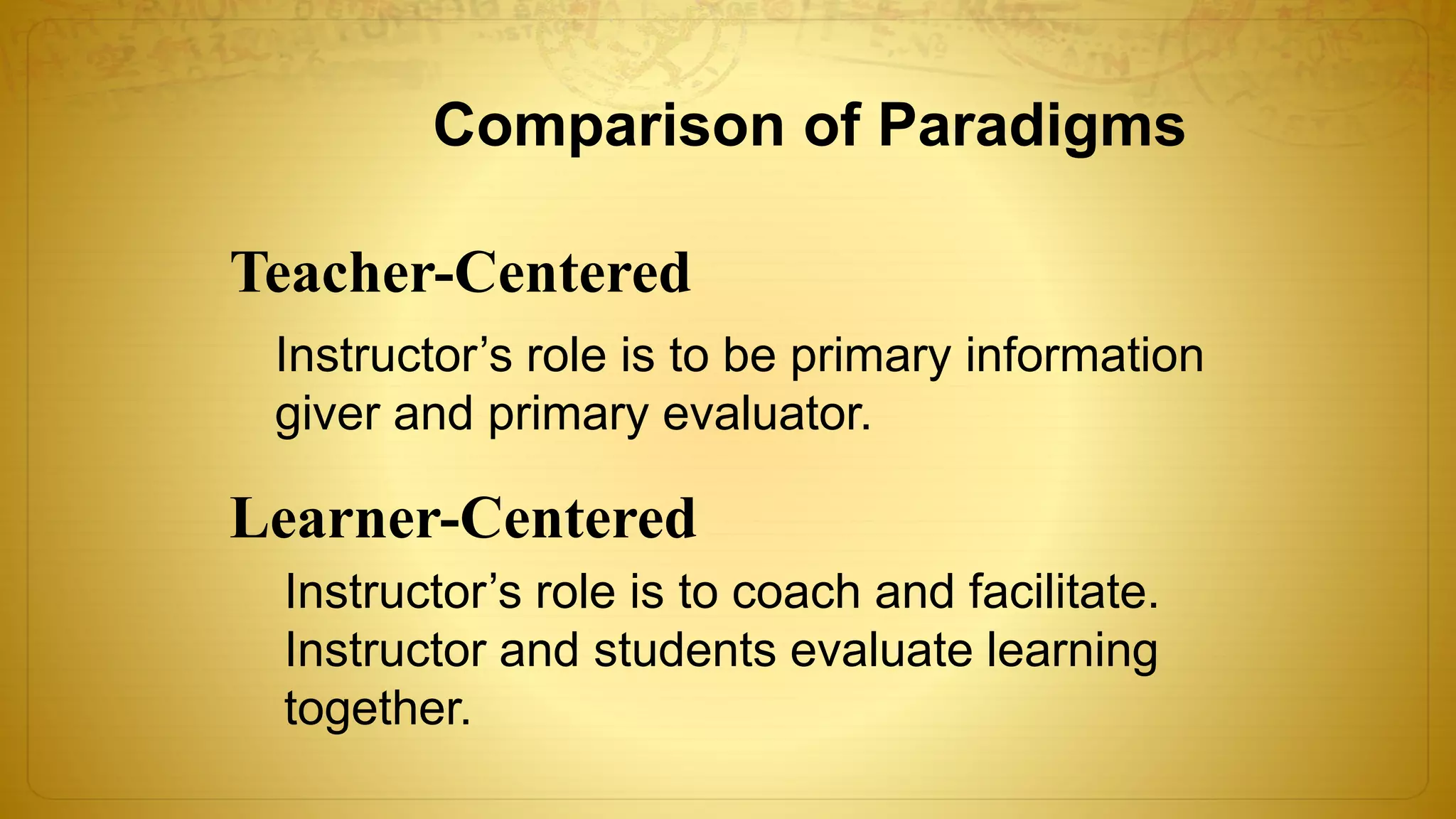
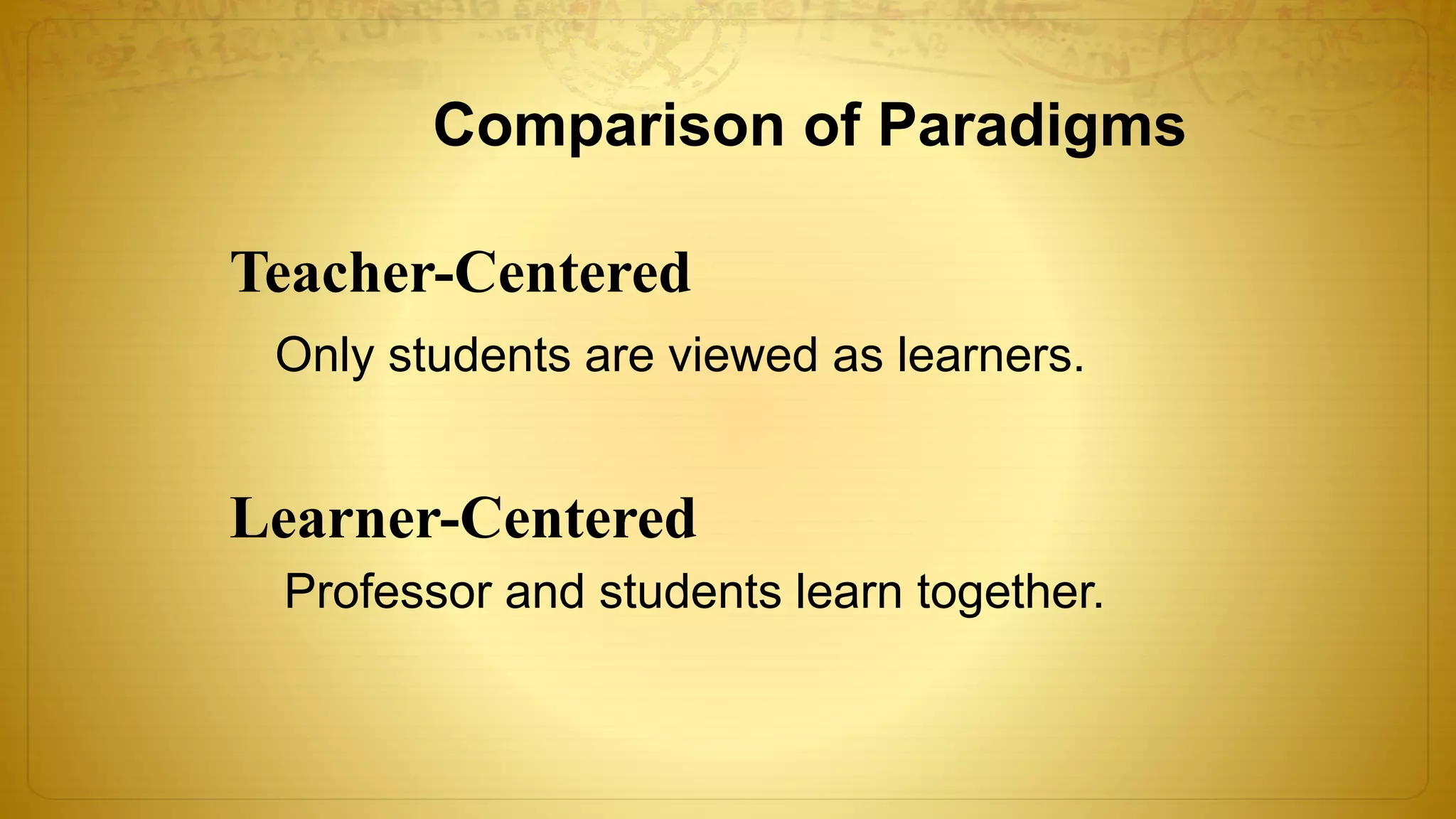
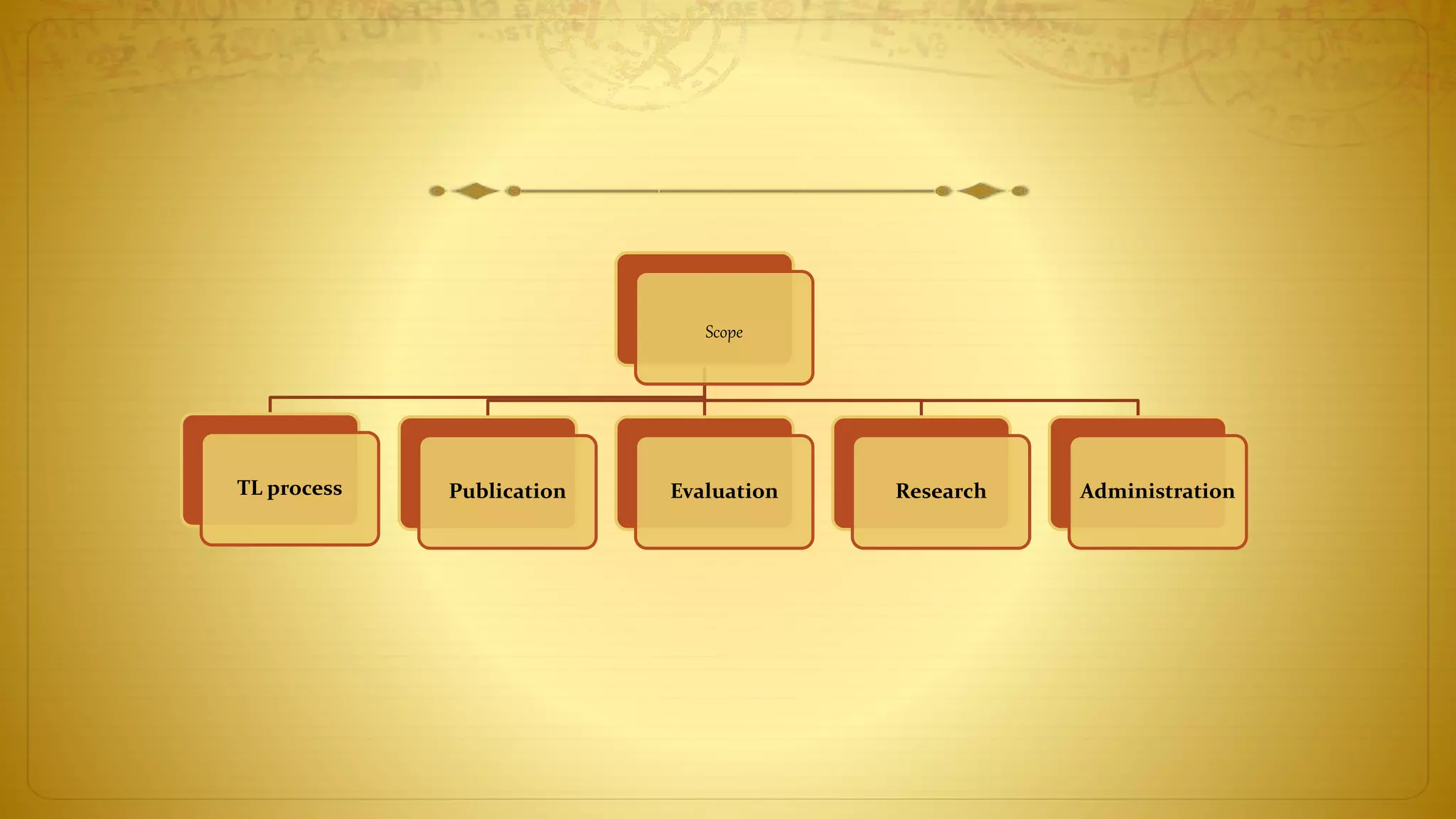
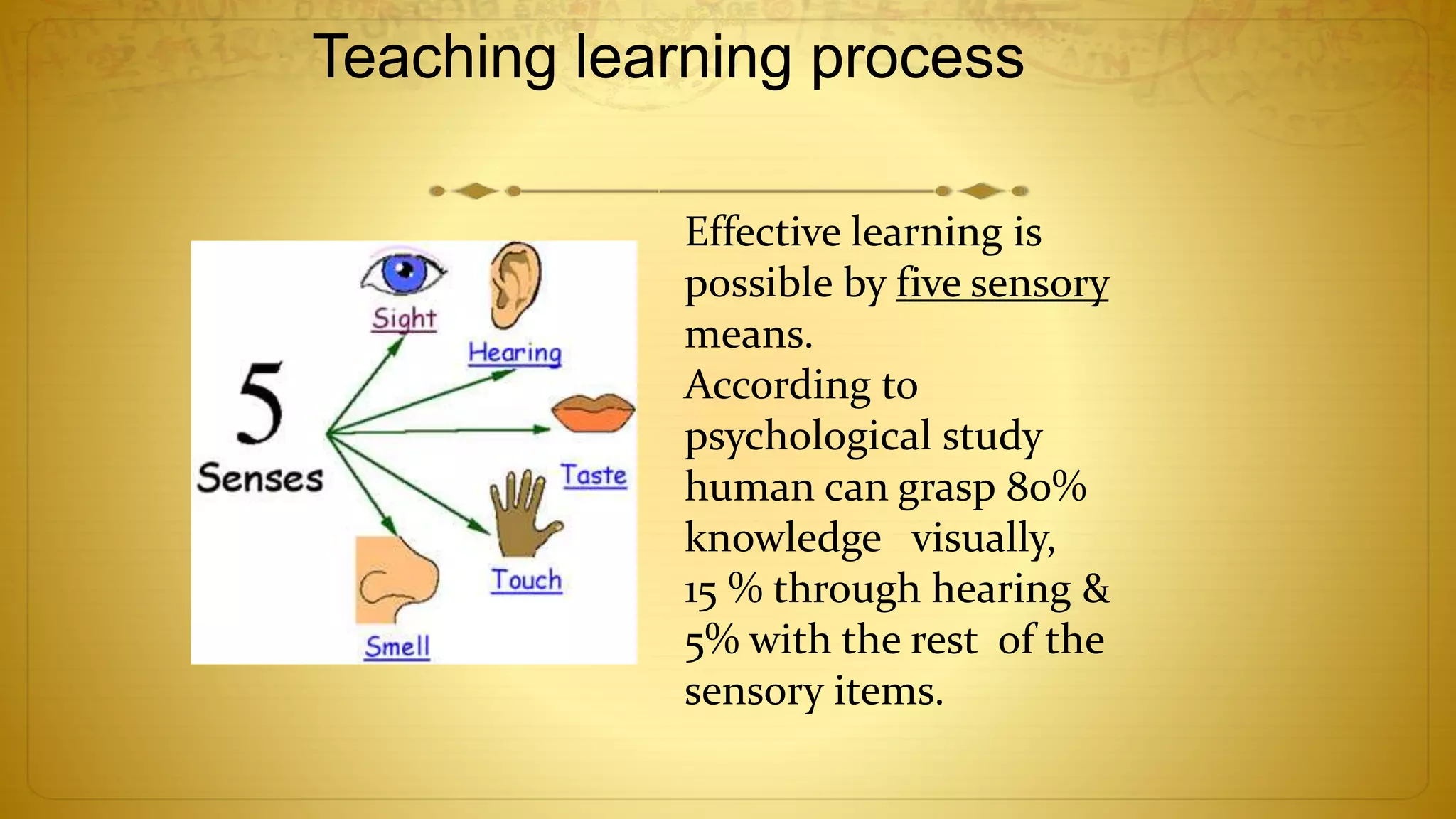
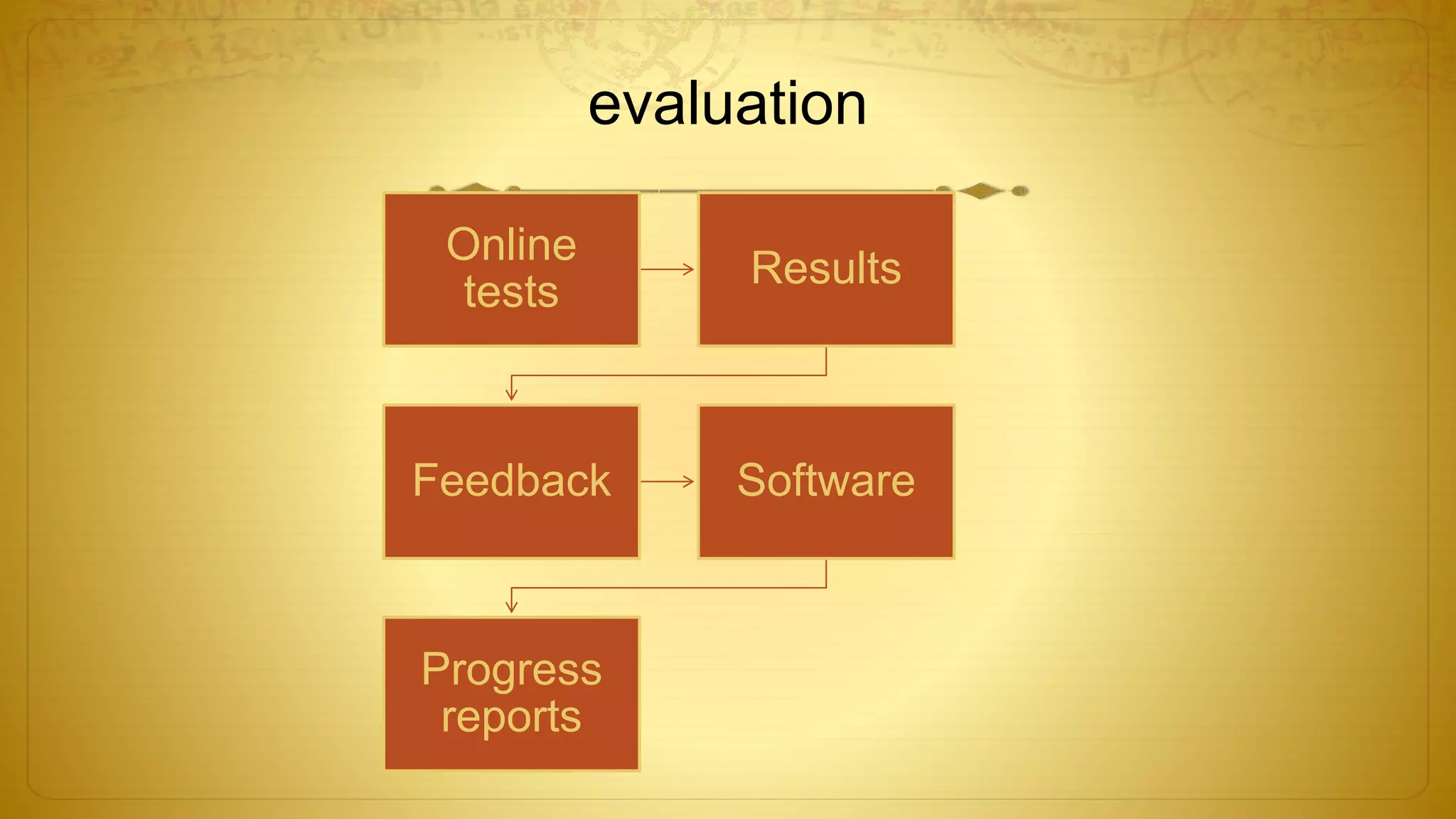
The document discusses the development of educational technology and the shift from teacher-centered to learner-centered approaches. It provides background on how educational technology has evolved from focusing on audiovisual tools, to instructional systems, vocational training, and computers/computer-based systems. It compares teacher-centered and learner-centered paradigms, highlighting how the latter focuses more on active student involvement, real-world applications, and collaborative/supportive learning environments. The document also covers definitions and scope of information and communication technology (ICT) in education, including its role in teaching/learning, publishing, evaluation, research, and administration.