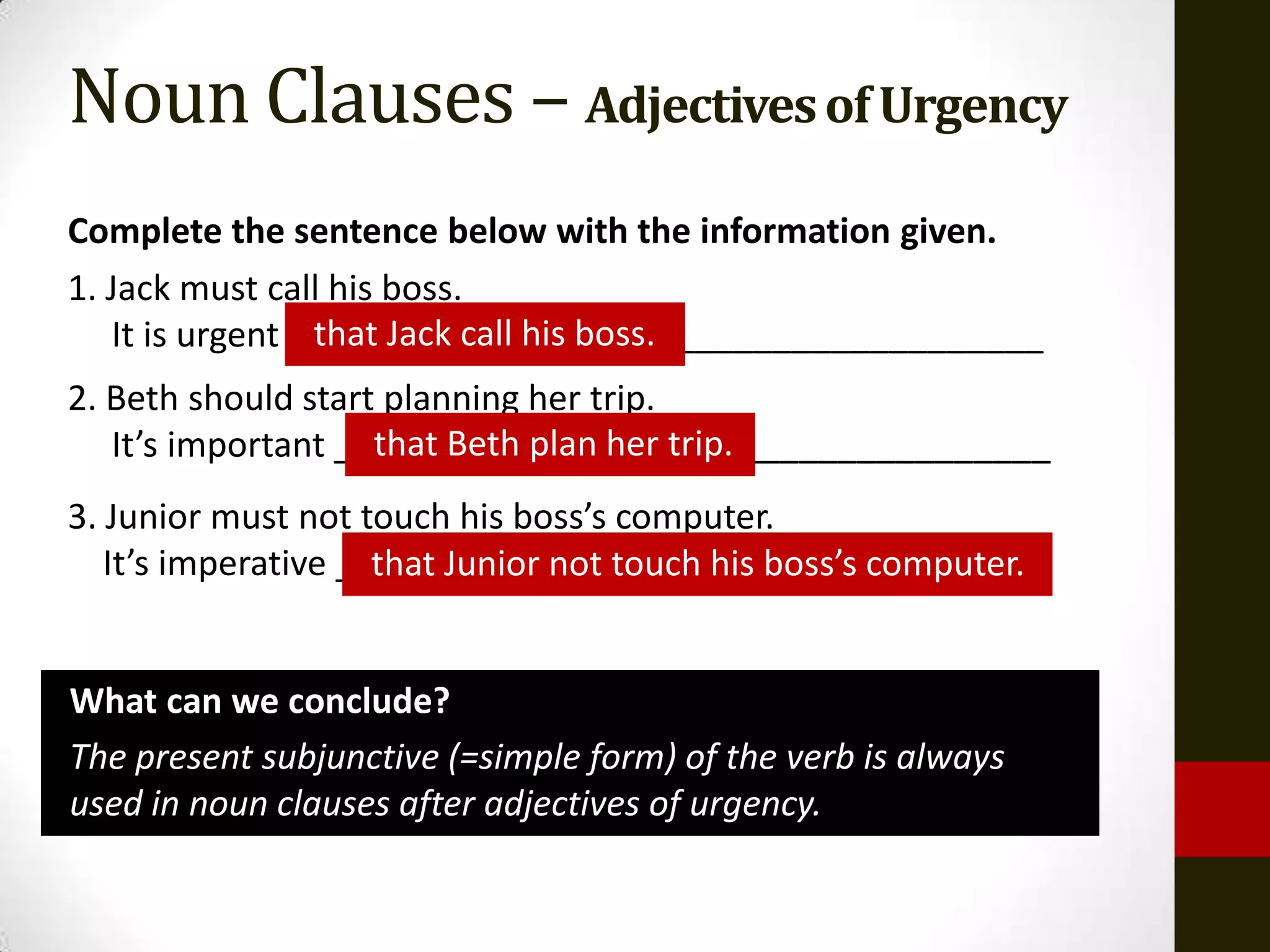
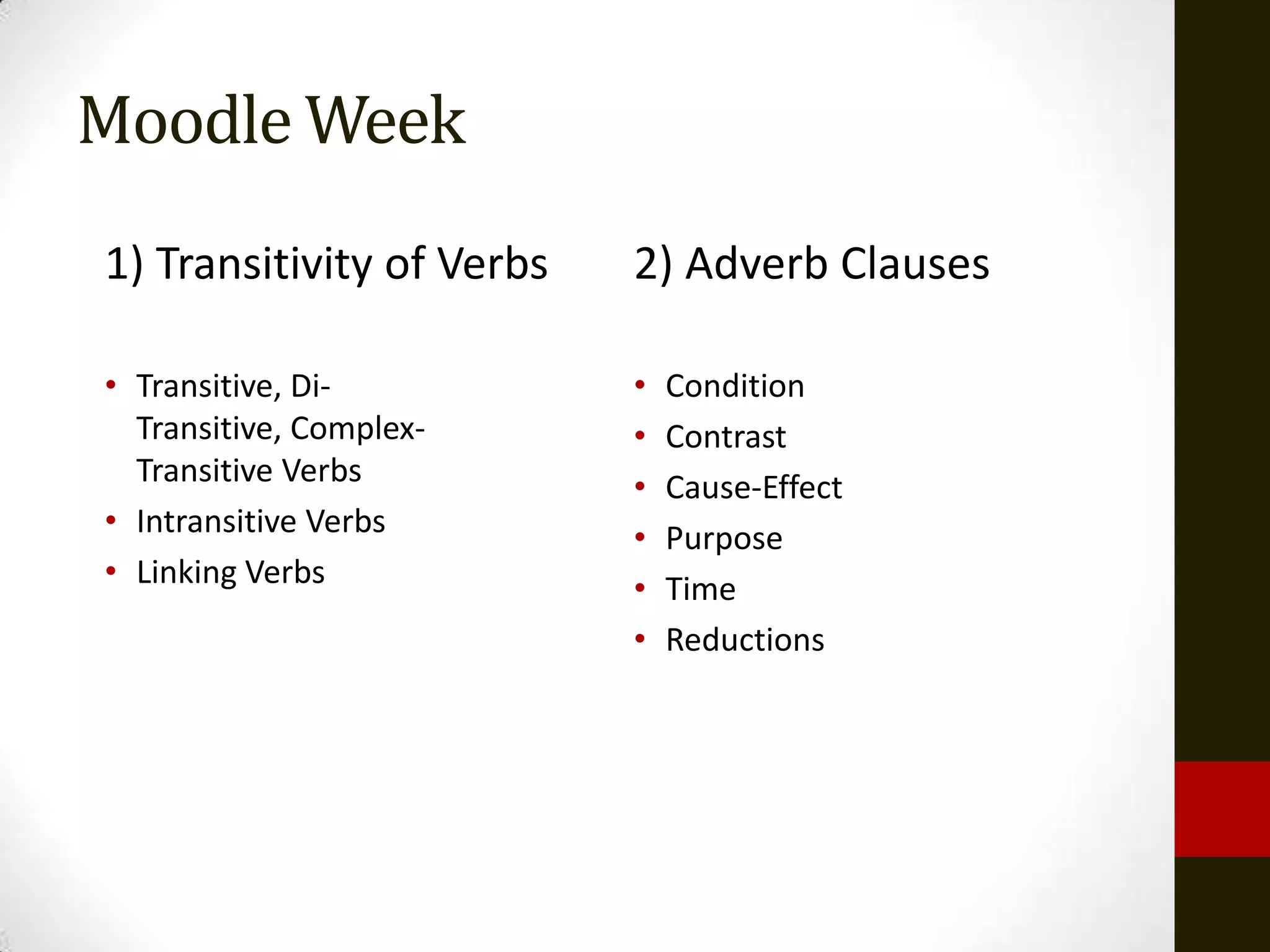
This document provides a review of grammatical structures for students including phrases, clauses, and sentence types. It discusses noun clauses in detail, including their functions in sentences, how they are introduced, indirect speech, verbs of urgency, and adjectives of urgency. Students are instructed to study these topics for an upcoming test. The review covers identifying and providing examples of structures, types of clauses and sentences, verb tenses, and transitivity. It also lists topics for the following week on the course website including adverb clauses.