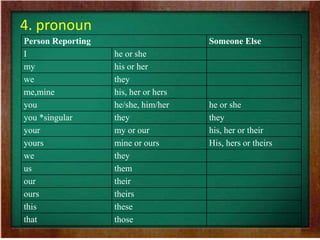
This document provides information about a learning activity that teaches the difference between direct and indirect/reported speech. The activity includes concept notes explaining the key differences, such as direct speech using quotation marks while indirect speech does not. It also lists the rules for changing direct speech to indirect speech, such as changing verb tenses and pronouns. Examples are provided to illustrate these changes. The activity also includes exercises for students to practice converting between direct and indirect speech.