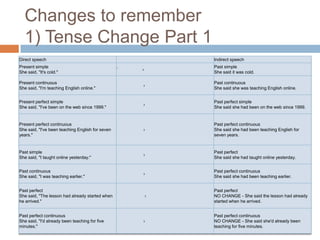
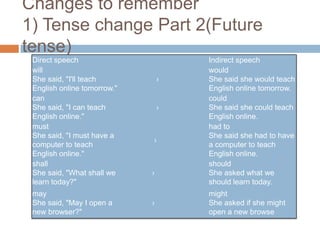
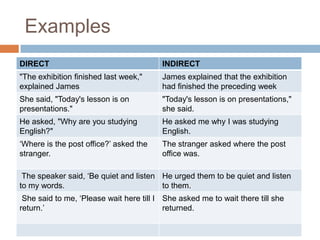
This document discusses direct and indirect speech. Direct speech uses quotation marks to report the exact words spoken, while indirect speech does not use quotation marks and changes pronouns and tense as needed. The document provides rules for changing direct speech to indirect speech, such as changing present to past tense and changing pronouns. It also discusses changes to time references like "now" becoming "then." Examples are given to illustrate the rules. Finally, the document briefly mentions rules for changing indirect speech to direct speech.