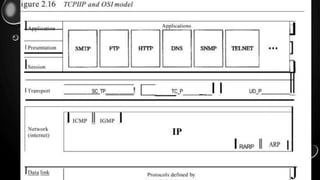
The document discusses the TCP/IP protocol suite. It provides a brief history, stating that TCP/IP was created by DARPA in the 1970s for ARPANET and was designed for UNIX. It describes the key protocols of TCP and IP and compares the TCP/IP model to the OSI model. The document outlines the layers of TCP/IP including the application, transport, network, and physical/data link layers. It notes advantages like being nonproprietary and compatible with all systems, and disadvantages including size and potential speed issues.