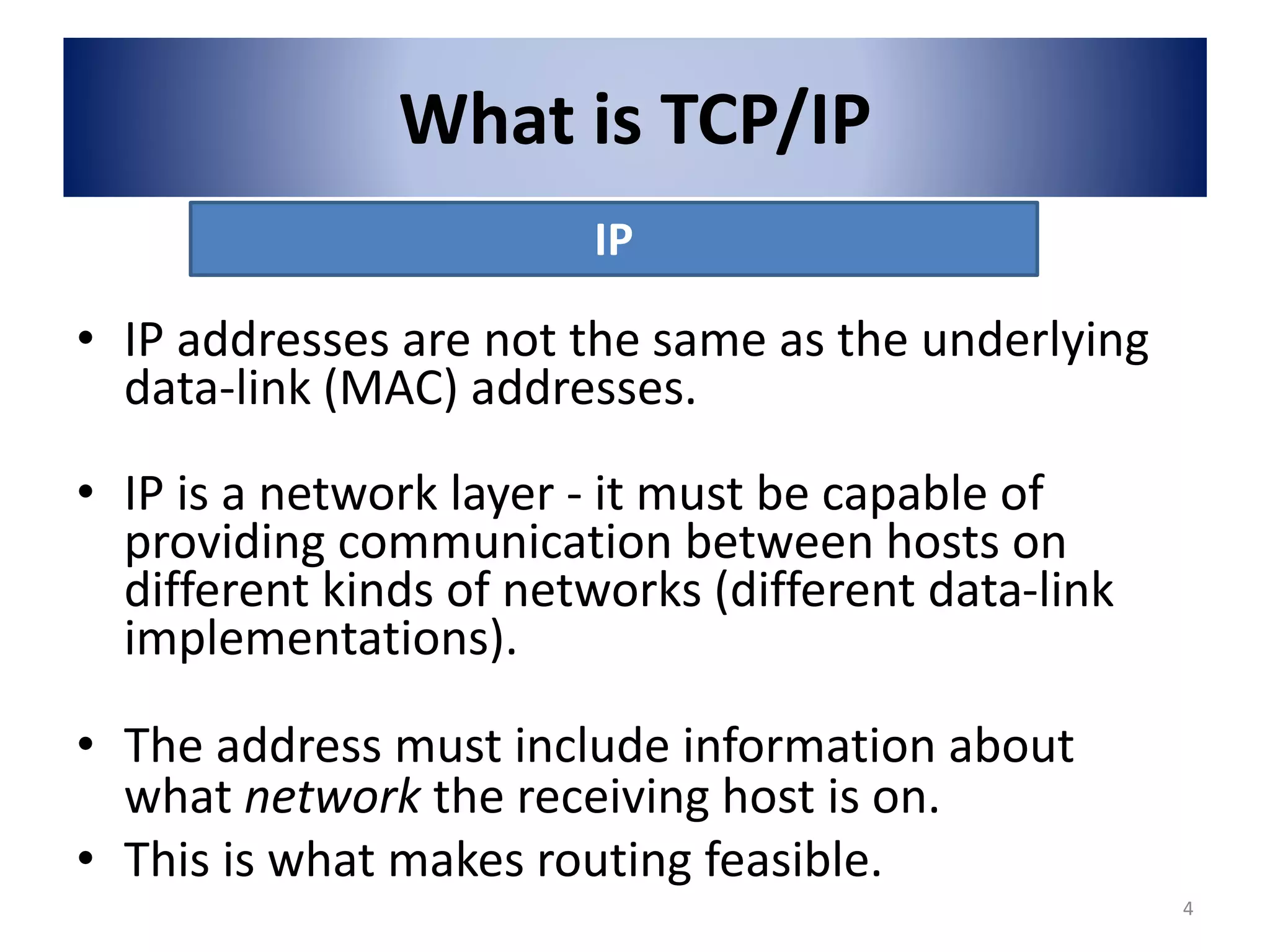
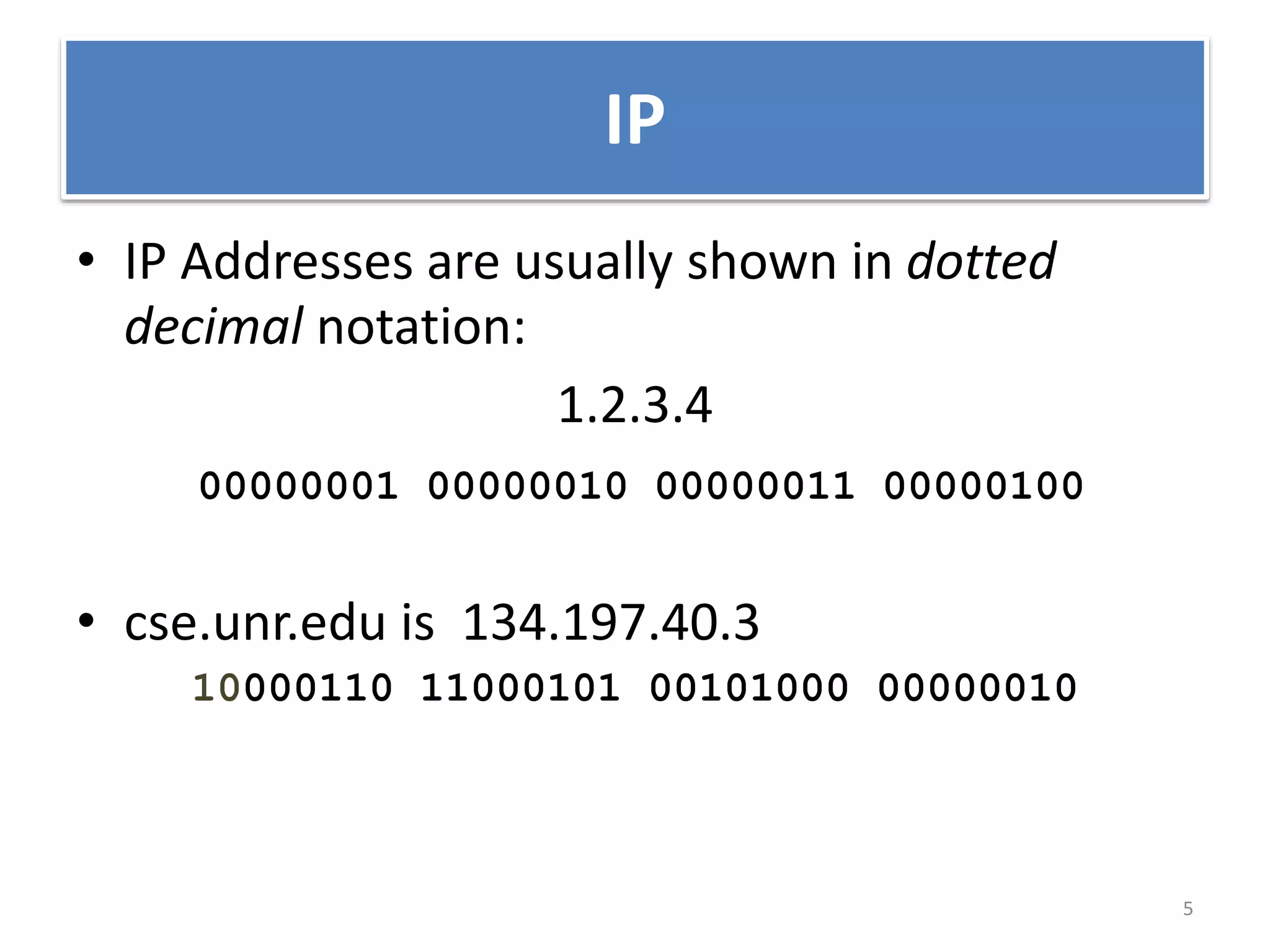
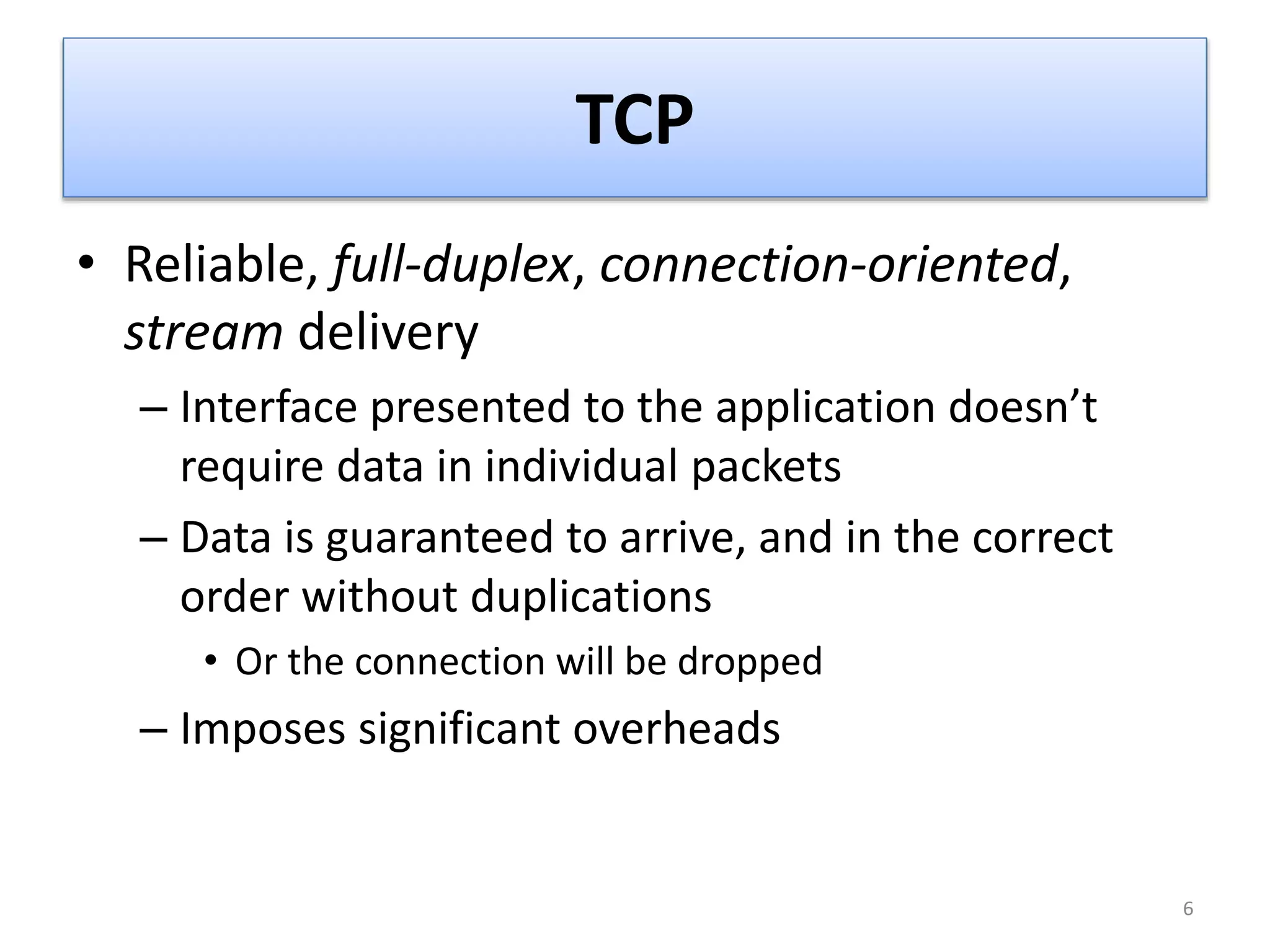
The document provides an overview of the TCP/IP network model. It discusses the four layers of the TCP/IP model: application layer, transport layer, internet layer, and network access layer. The application layer contains protocols like HTTP and FTP that allow applications to access networked services. The transport layer uses TCP and UDP to deliver data and provide reliability. The internet layer handles routing and uses IP. The network access layer deals with physical network components like cables and network interface cards.