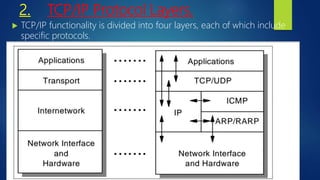
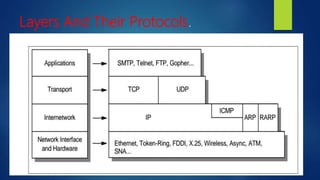
TCP/IP is a set of communication protocols used on the internet and networks. It is made up of the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP). TCP/IP functionality is divided into four layers - the application, transport, internet, and physical layers - with specific protocols at each layer defining how data is packetized, addressed, transmitted, routed and received. TCP/IP allows for connection between different computer types and organizations by operating independently of operating systems and supporting various routing protocols.