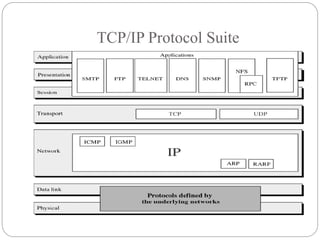
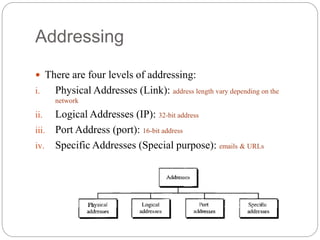
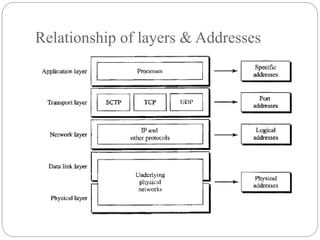
The document discusses the TCP/IP protocol suite, which is composed of four layers: physical/data link layer, network layer, transport layer, and application layer. The network layer uses IP and four supporting protocols to enable internetworking. The transport layer uses UDP for non-reliable delivery and TCP for reliable, connection-oriented delivery. TCP/IP addressing includes physical, IP, port, and special purpose addresses.