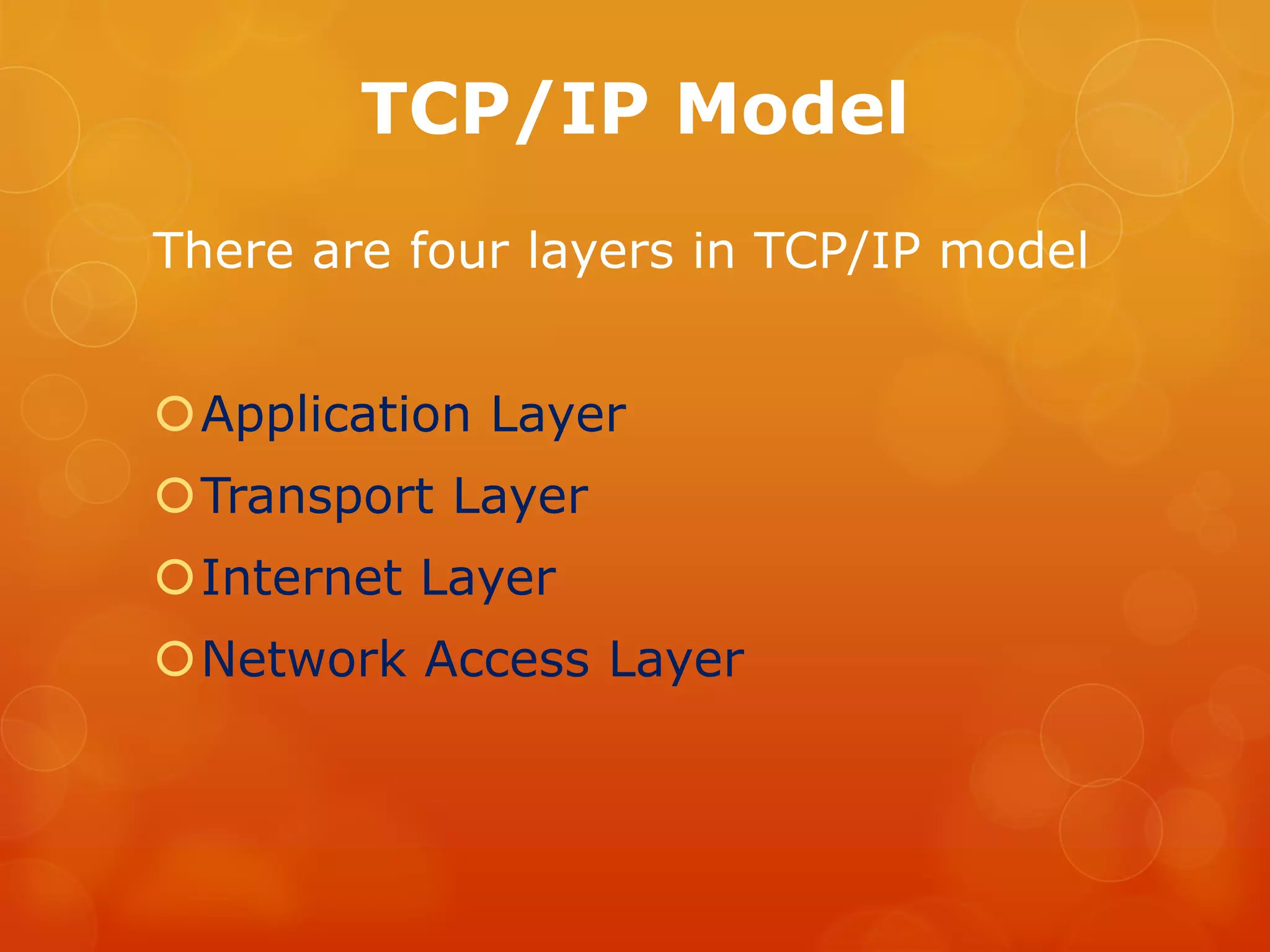
The TCP/IP model has four layers: Application layer, Transport layer, Internet layer, and Network Access layer. The Application layer contains protocols that provide services to users like web browsing, email, and file transfers. The Transport layer deals with manipulating data and preparing it for delivery through the network using protocols like TCP and UDP. The Internet layer determines routing and addresses using IP addressing and routing protocols. The Network Access layer is responsible for transmitting bits and bytes across physical network connections using devices like hubs, switches, and network interface cards.