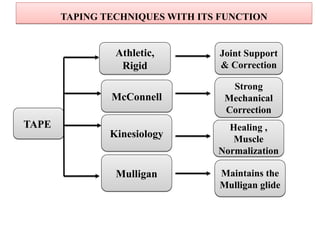
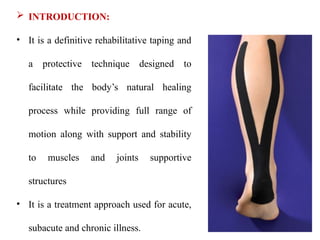
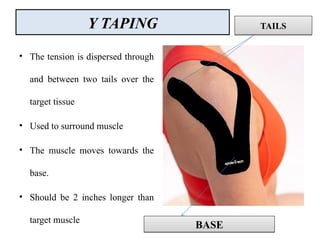
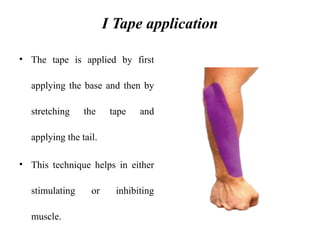
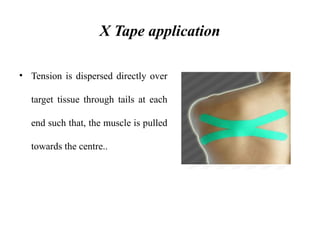
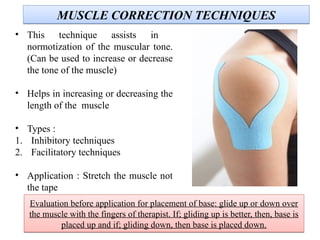
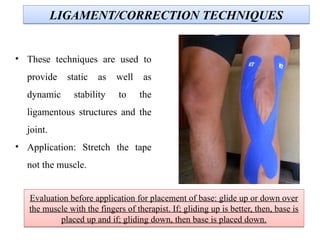
The document discusses various taping techniques, including kinesio-taping, mcconnell taping, and rigid taping, detailing their history, application methods, and physiological effects. Kinesio-taping is highlighted as a rehabilitative technique developed in 1979 by Dr. Kenzo Kase, focusing on supporting natural healing and enhancing range of motion. The document also outlines indications and contraindications for kinesio taping and describes various techniques for specific muscle and joint conditions.