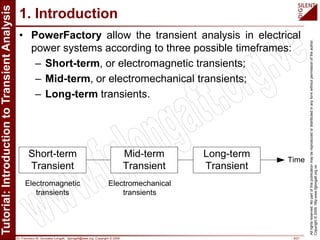
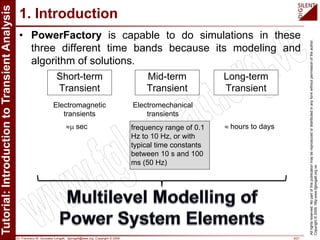
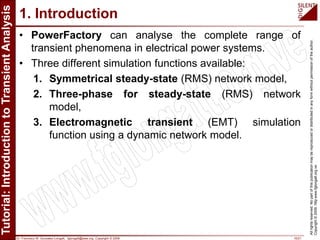
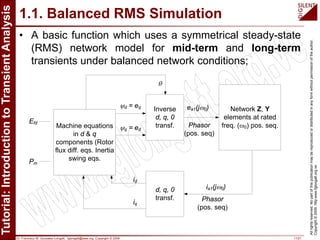
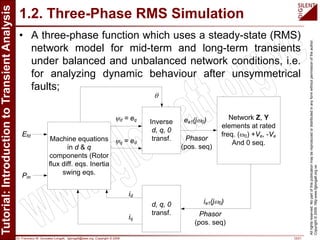
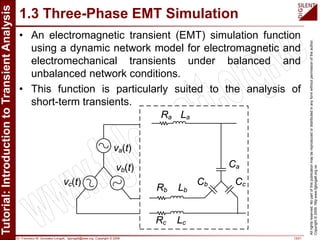
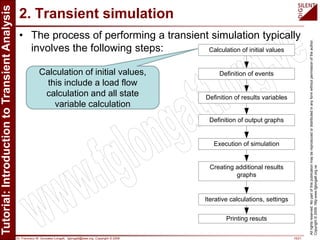
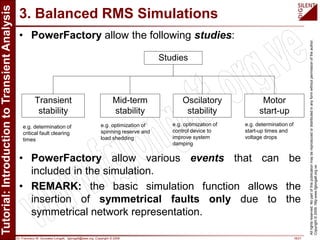
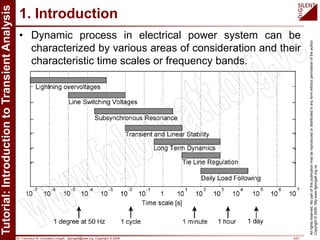
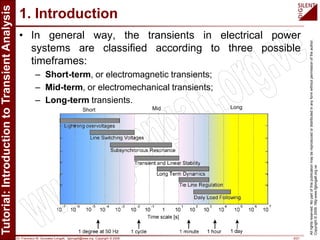
The document is a tutorial by Dr. Francisco M. Gonzalez-Longatt on transient analysis using PowerFactory, focusing on the modeling of transient phenomena in electrical power systems. It classifies transients into short-term, mid-term, and long-term categories and details the simulation capabilities of PowerFactory, including balanced RMS and EM transient simulations. Additionally, it outlines the steps involved in transient simulation and provides recommended readings for further understanding.



![Dr. Francisco M. Gonzalez-Longatt, fglongatt@ieee.org .Copyright © 2009 4/21
Allrightsreserved.Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedordistributedinanyformwithoutpermissionoftheauthor.
Copyright©2009.http:www.fglongatt.org.ve
1. Introduction
• Power system stability may be broadly defined as that
property of a power system that enables it to remain in a
state of operating equilibrium under normal operating
conditions ad to regain an acceptable state of equilibrium
after being subjected to a disturbance [1].
• The robustness of a system is defined by the ability of
the system to maintain stable operation under normal
and perturbed conditions [2].
[1] P. Kundur, Power System Stability and Control. New York:
McGraw- Hill, 1994.
[2] PowerFactory User’s Manual DIgSILENT PowerFactory Version
14.0. DIgSILENT GmbH, Gomaringen, Germany 2008](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tintrotran-150428081627-conversion-gate01/85/Tutorial-Introduction-to-Transient-Analysis-using-DIgSILENT-PowerFactory-4-320.jpg)
![Dr. Francisco M. Gonzalez-Longatt, fglongatt@ieee.org .Copyright © 2009 7/21
Allrightsreserved.Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedordistributedinanyformwithoutpermissionoftheauthor.
Copyright©2009.http:www.fglongatt.org.ve
1. Introduction
Classification of Power System Stability [1]
Power System Stability
Angle Stability Voltage Stability
Transient
Stability
Mid-term
Stability
Long-term
Stability
Large
Disturbance
Voltage
Stability
Small-Signal
Stability
Non-
oscillatory
Instability
Oscillatory
Instability
Small-
Disturbance
Voltage Stability
• Ability to remain in operating equilibrium
• Equilibrium between opposing forces
• Ability to maintain synchronism
• Torque balance of synchronous
machines
• Ability to maintain steady
acceptable voltage
• Reactive power balance
[1] P. Kundur, Power System Stability and Control. New York:
McGraw- Hill, 1994.
RECOMMENDED READ: P. Kundur, J. Paserba, V. Ajjarapu, G. Andersson, A. Bose, C. Canizares, N. Hatziargyriou, D. Hill, A.M.
Stanković, C. Taylor, T. Van Cutsem, V. Vittal, "Definition and classification of power system stability IEEE/CIGRE joint task force on
stability terms and definitions", IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, Vol. 19 , No. 3 , pp.1387 - 1401, Aug. 2004](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tintrotran-150428081627-conversion-gate01/85/Tutorial-Introduction-to-Transient-Analysis-using-DIgSILENT-PowerFactory-7-320.jpg)