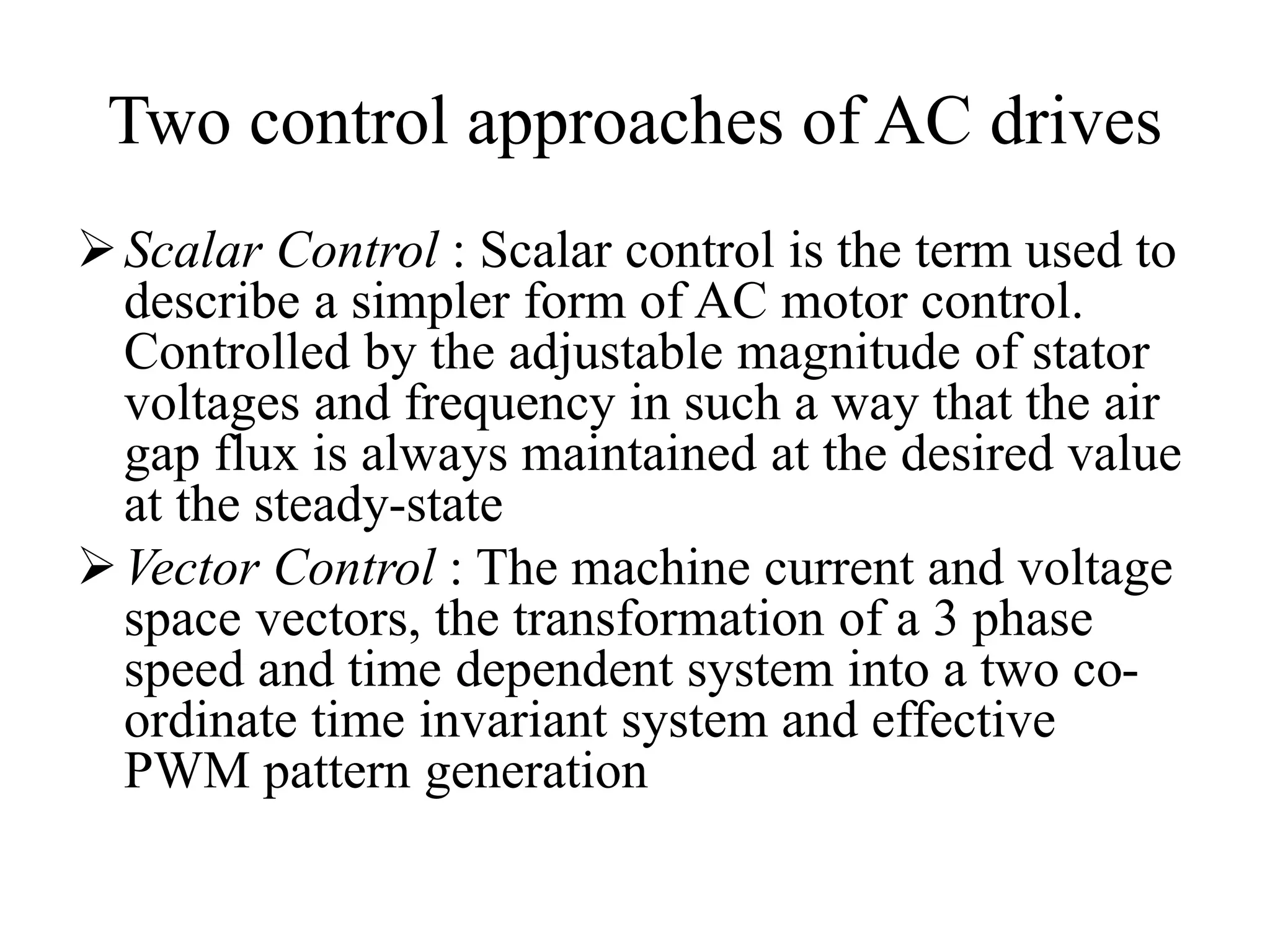
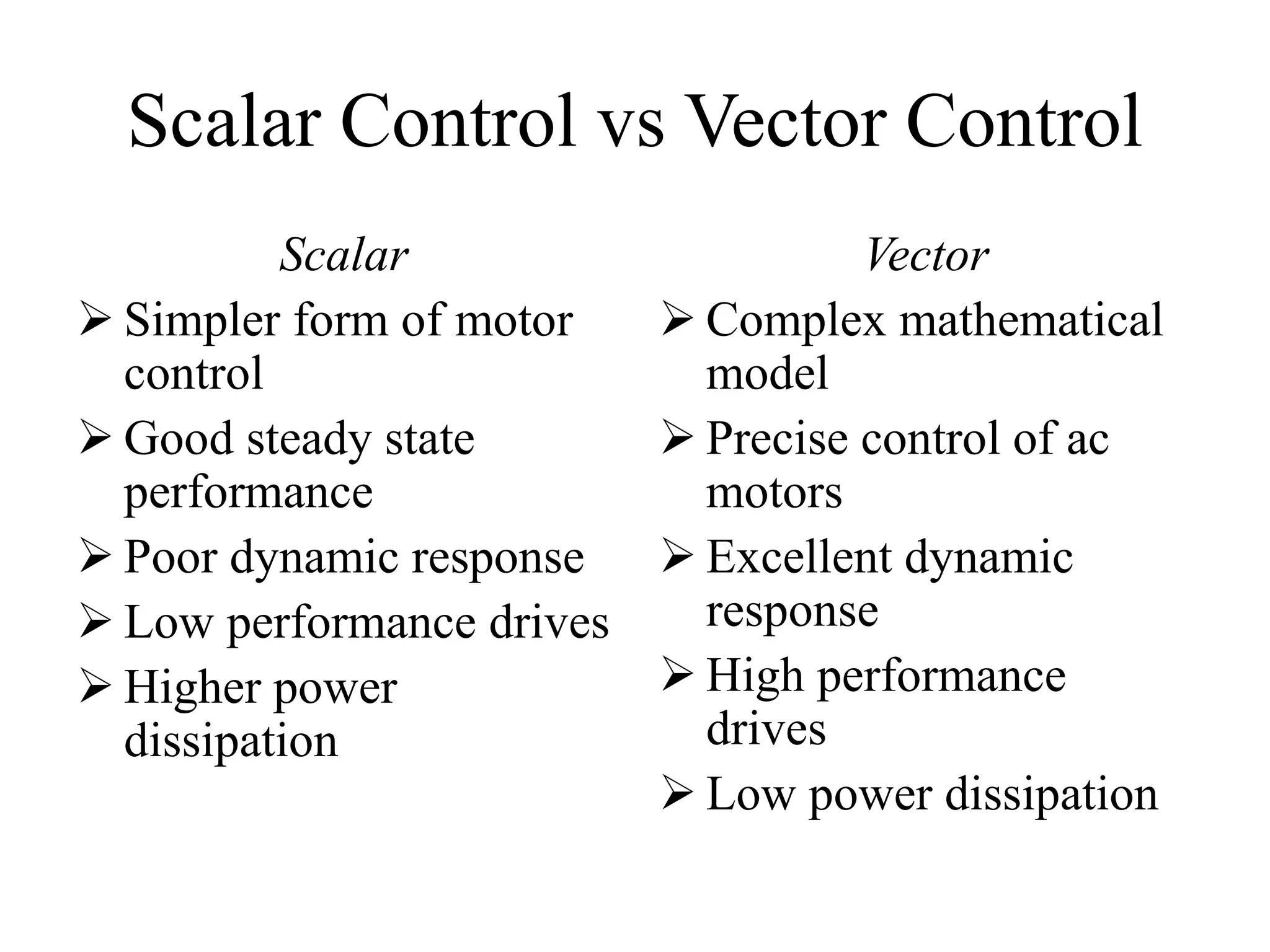
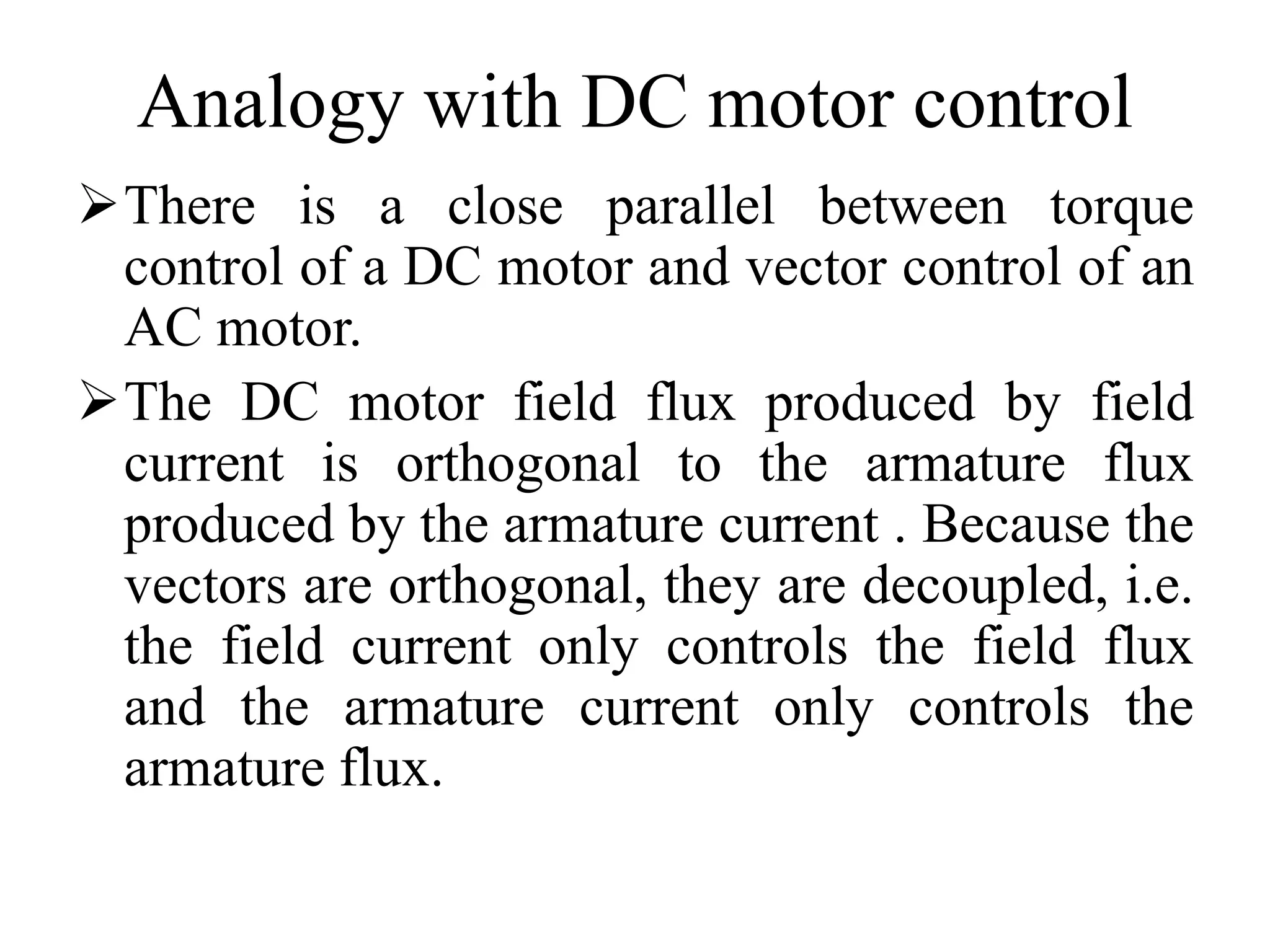
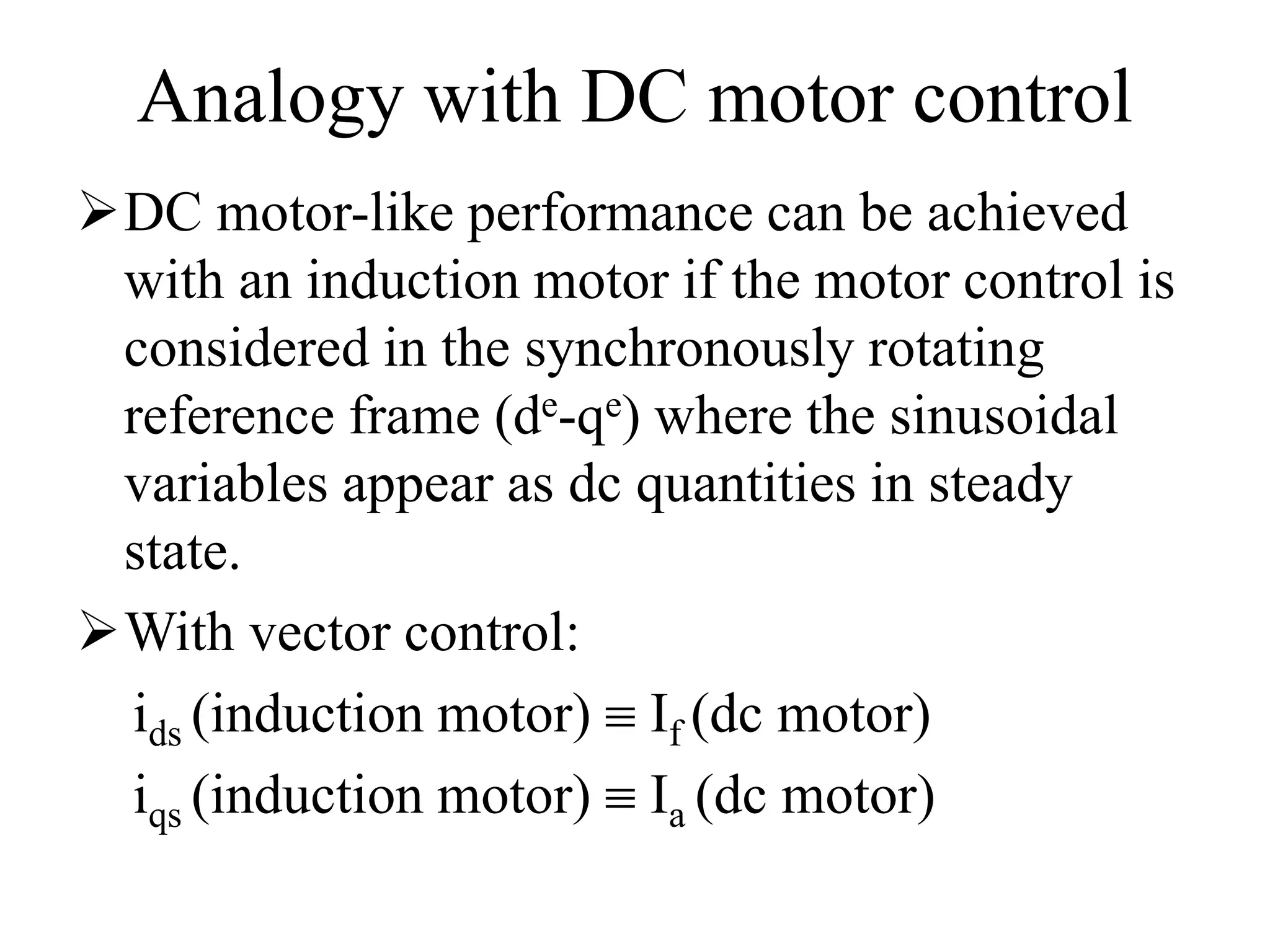
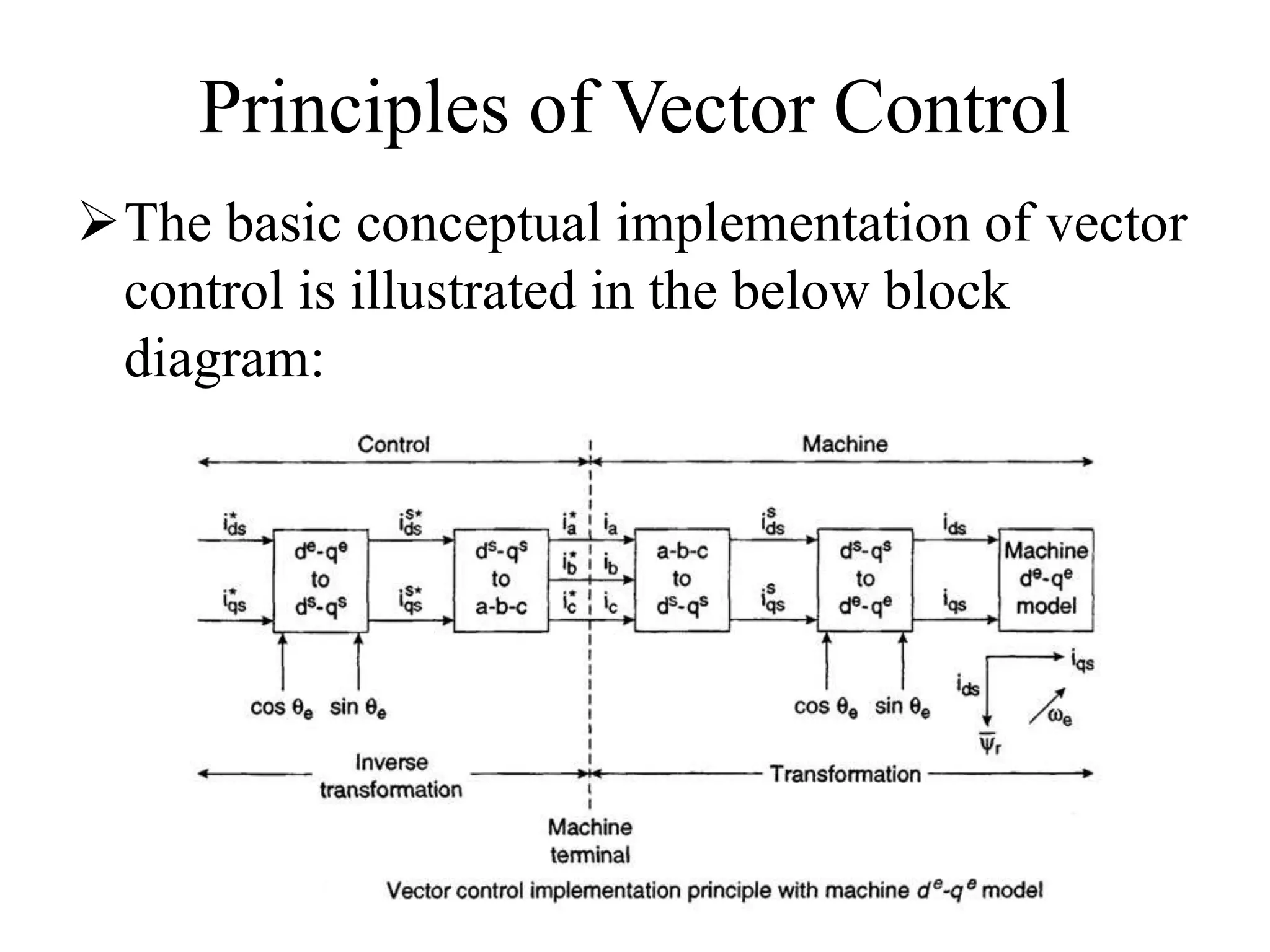
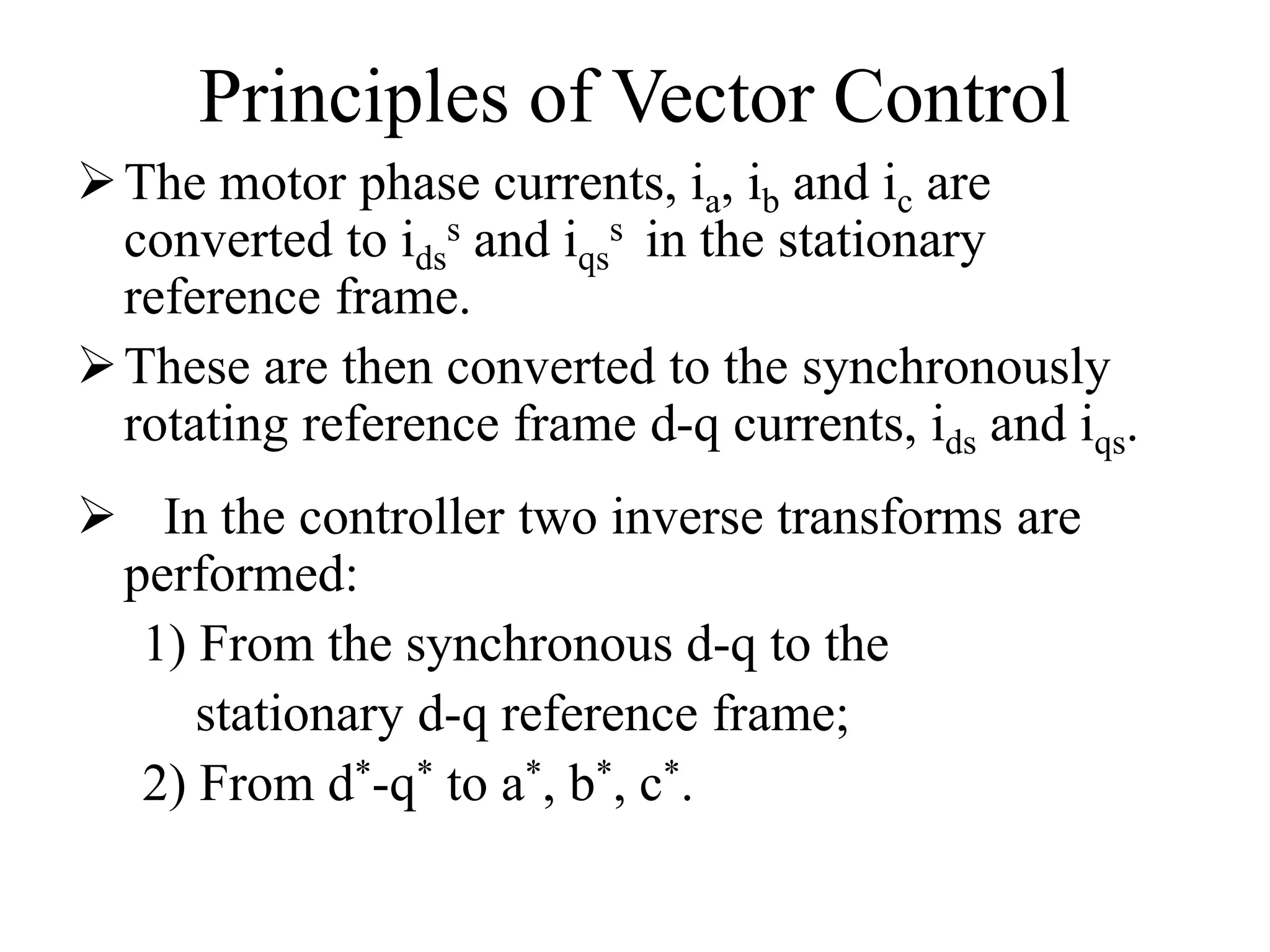
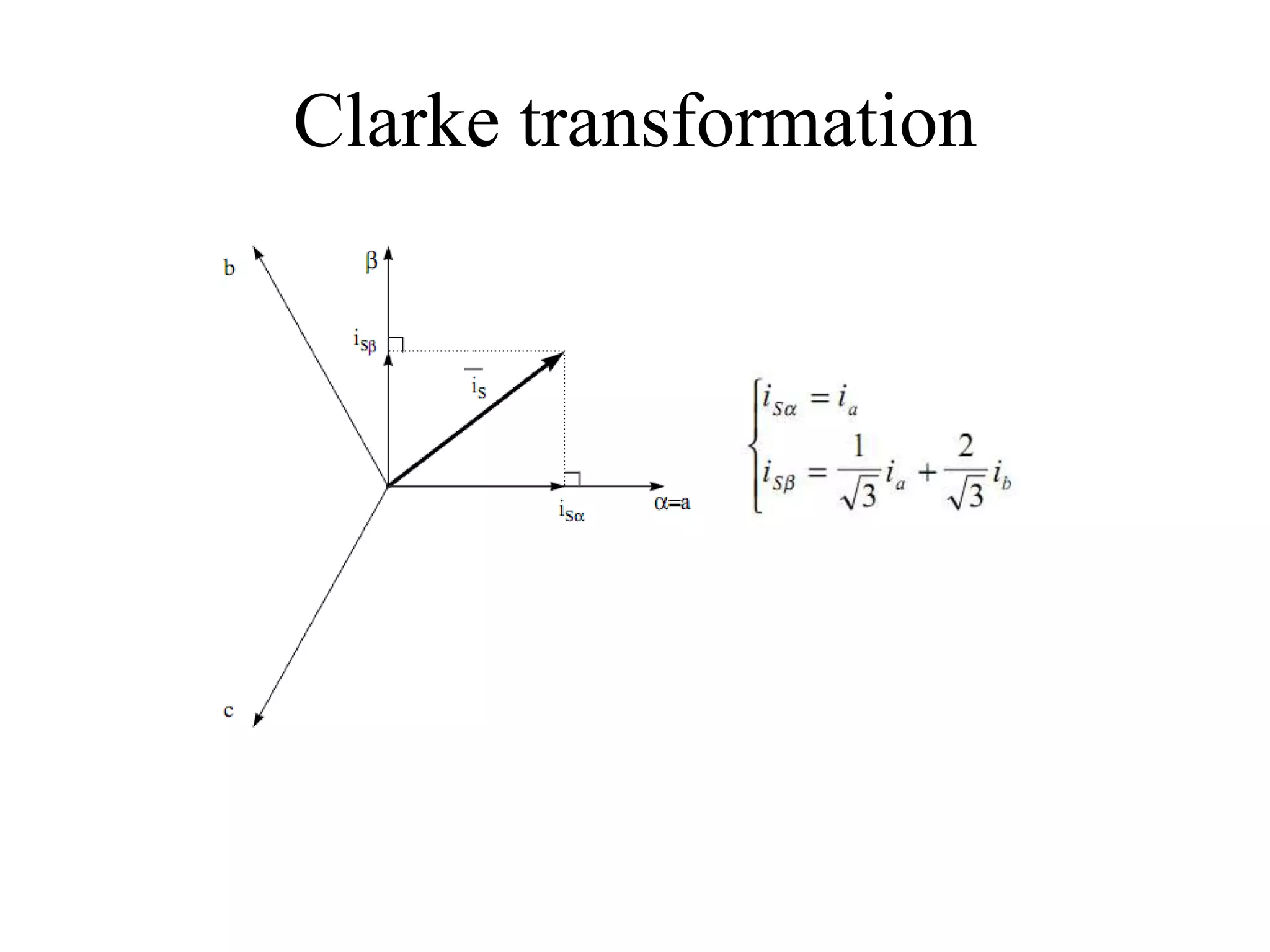
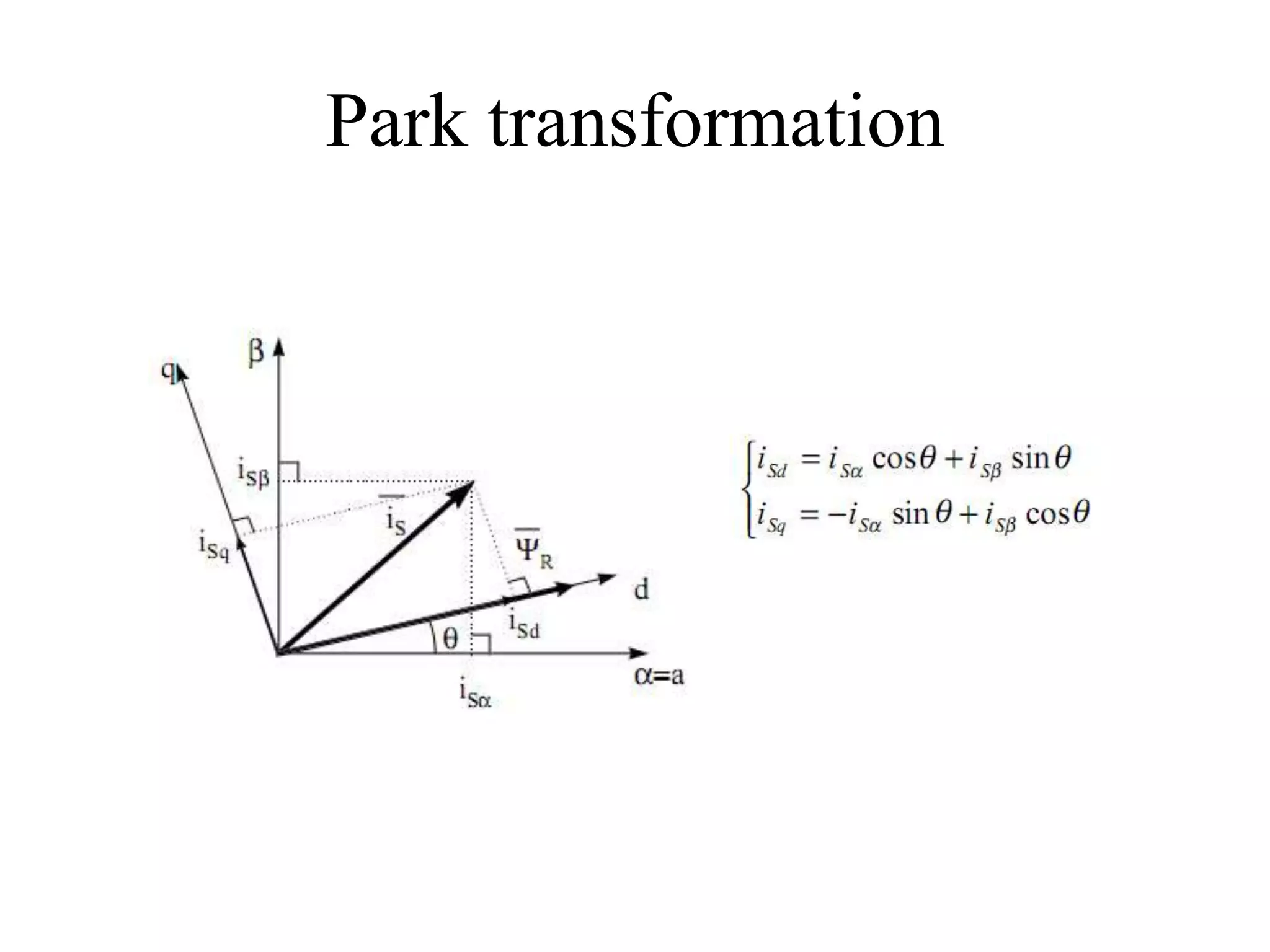
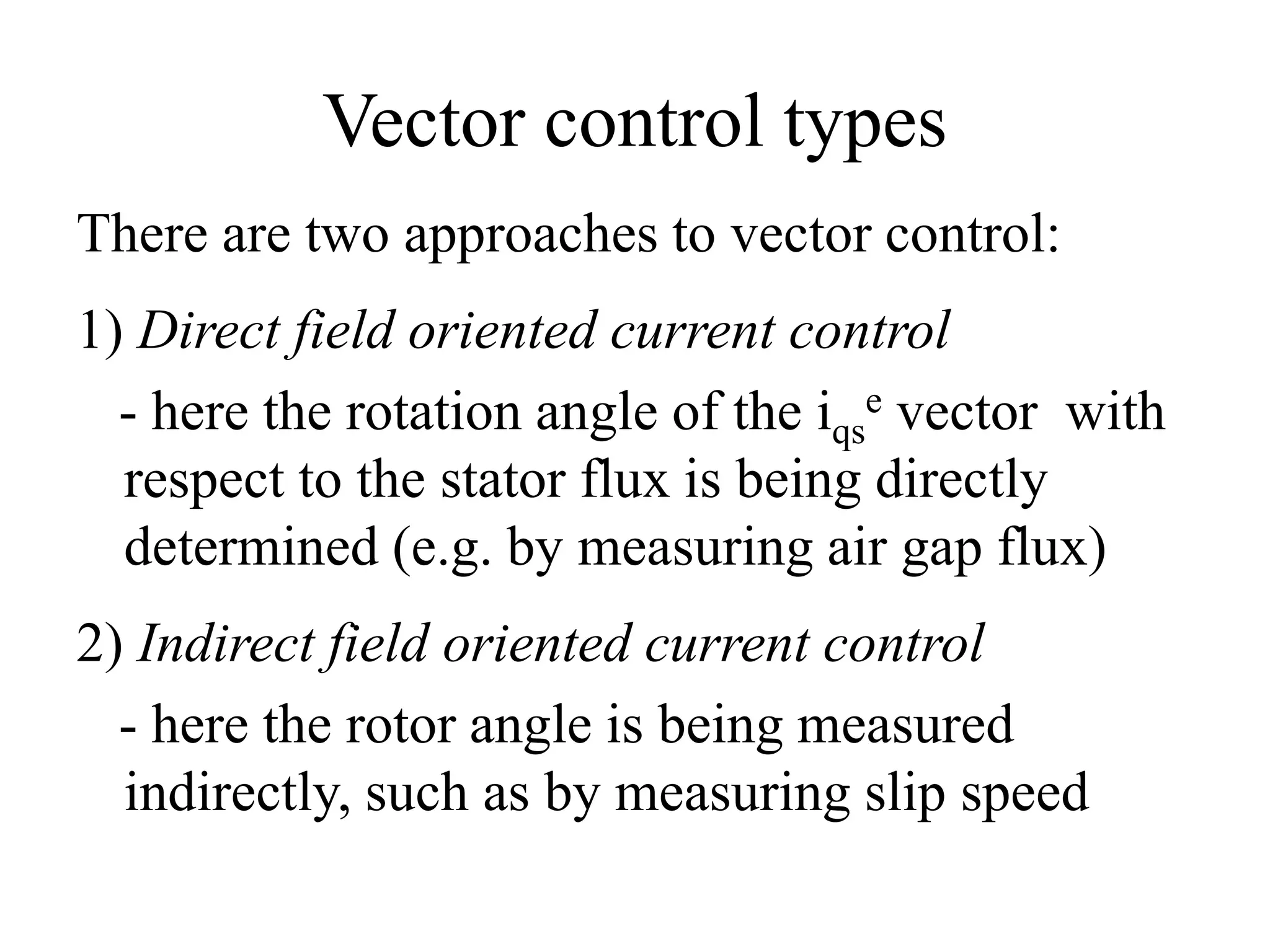
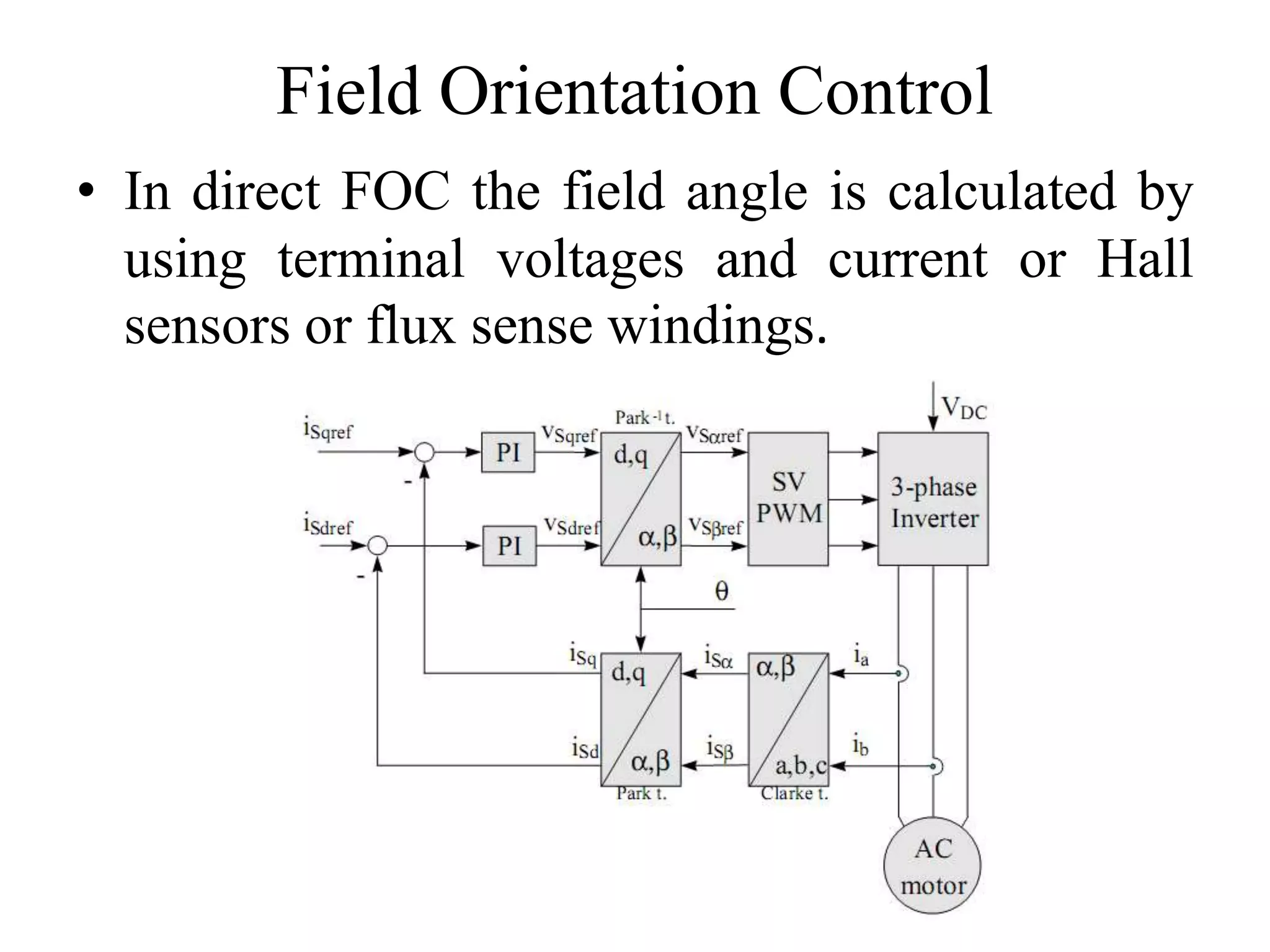
Vector control is a more advanced and precise method of controlling AC induction motors compared to scalar control. It involves transforming the motor currents and voltages into a rotating reference frame to obtain decoupled control similar to a DC motor. This allows for independent control of flux and torque for faster dynamic response and better performance than scalar control. The basic implementation of vector control uses Clarke and Park transformations to convert between stationary and rotating reference frames in the controller. It provides DC motor-like precision in speed and torque control of induction motors.