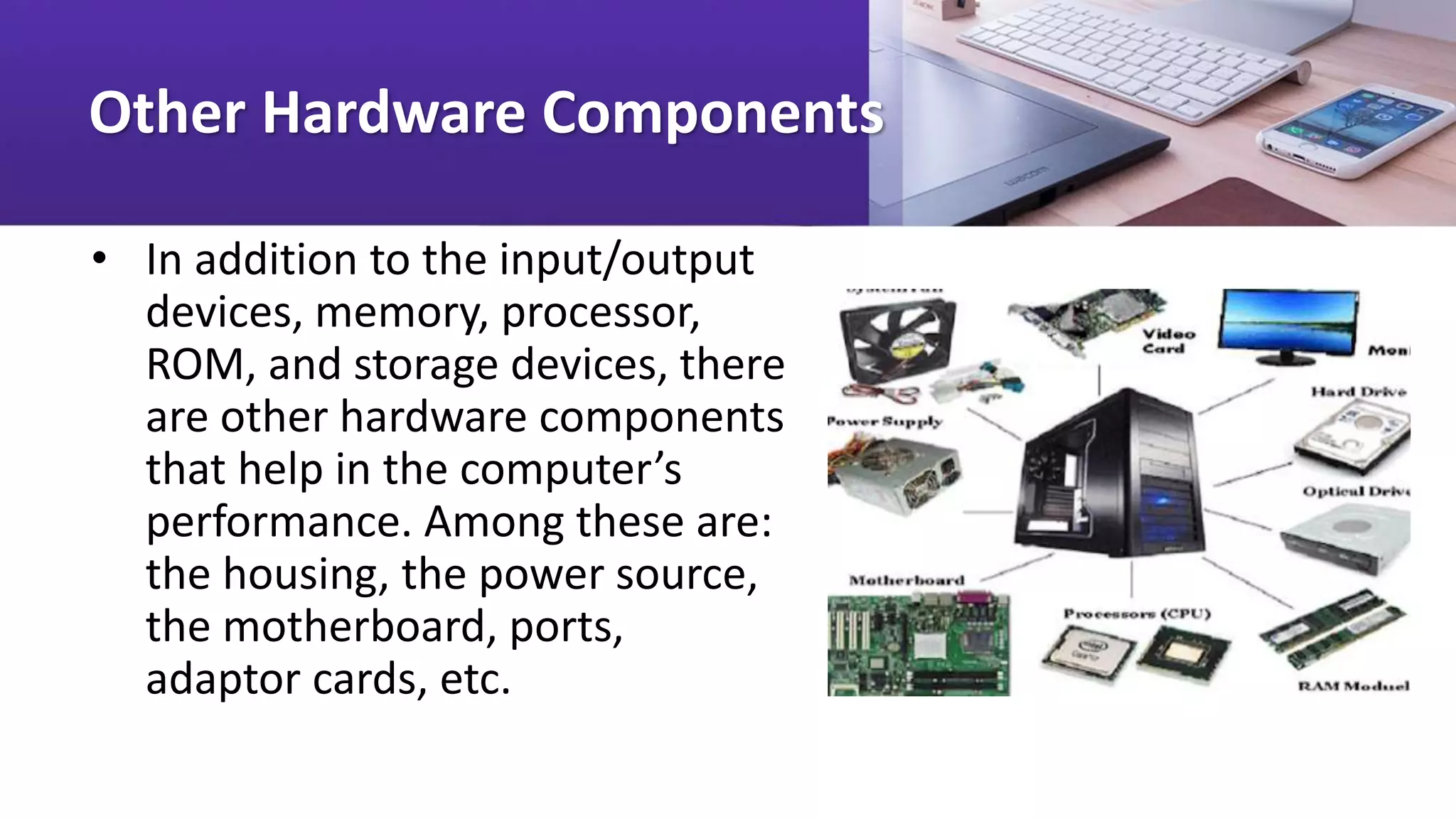
The document discusses the main hardware components of a computer system, categorizing them according to their functions of input, processing/memory, output, storage, and communications. It describes the basic components including processors like Intel and AMD CPUs, memory devices like RAM and ROM, input devices like keyboards and mice, output devices like monitors, and storage devices like hard disks, CDs, DVDs. It also mentions other components like motherboards, ports, and expansion cards that help connect and support the core hardware.