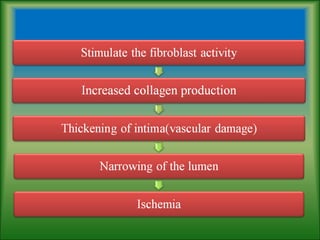
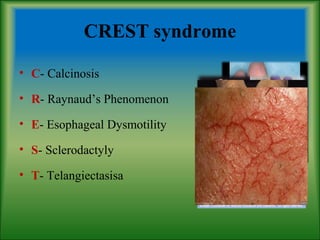
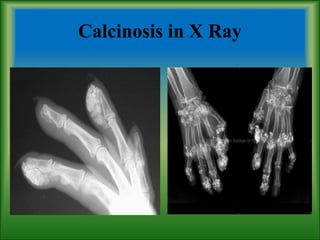
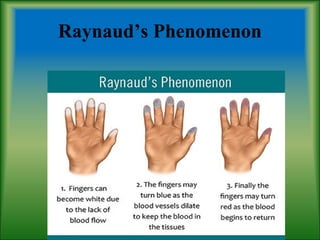
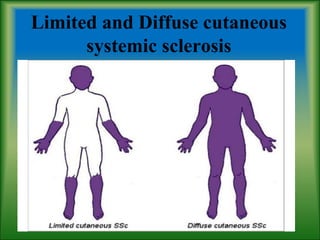
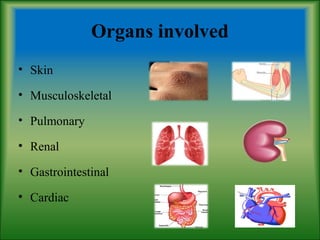
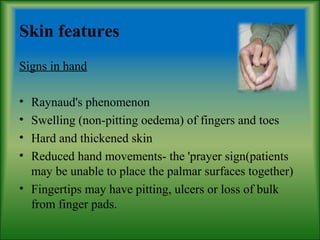
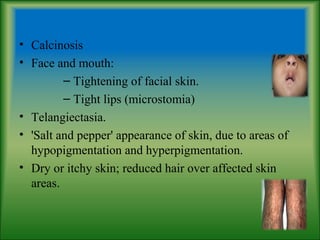
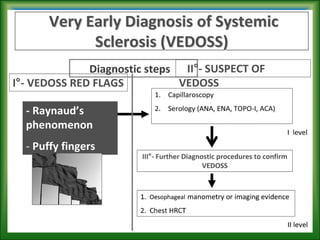
This document summarizes information about systemic sclerosis (SSc), including its definition, classification, epidemiology, etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic criteria, management, and treatment. SSc is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by fibrosis of the skin and internal organs. It can be classified as limited or diffuse cutaneous SSc depending on the extent of skin involvement. Common clinical features include Raynaud's phenomenon, skin thickening, joint/muscle involvement, and interstitial lung disease. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, preventing complications, suppressing the immune system, and detecting/treating organ involvement early. New treatments targeting the fibrotic process are showing promise.