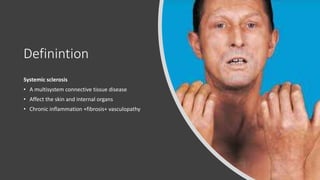
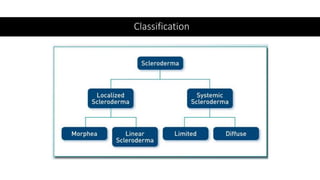
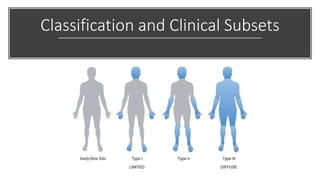
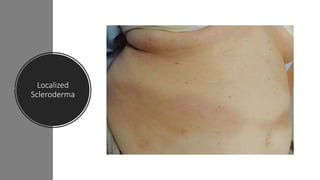
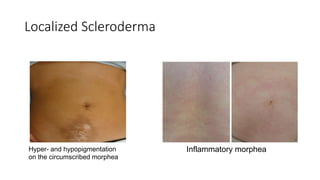
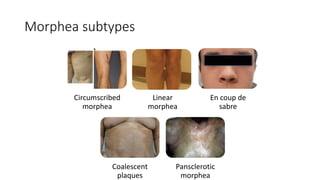
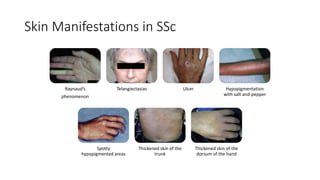
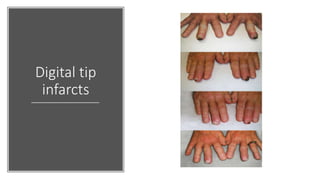
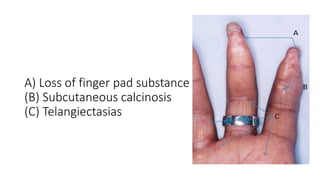
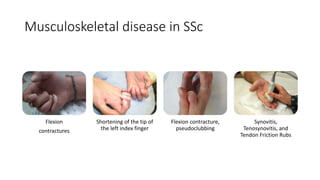
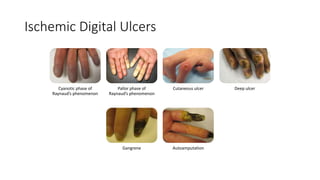
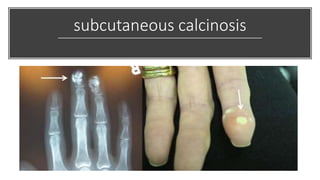
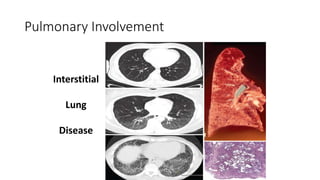
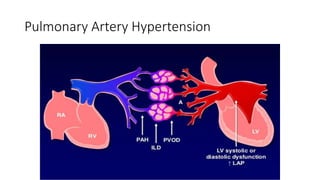
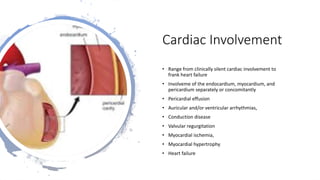
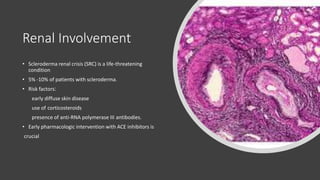
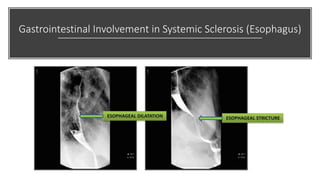
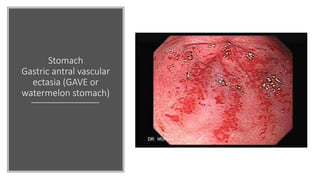
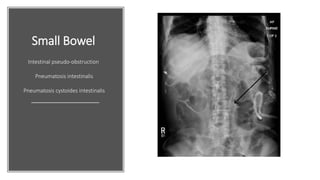
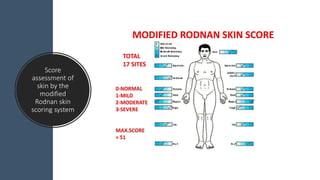
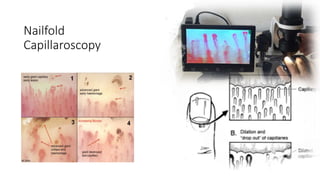
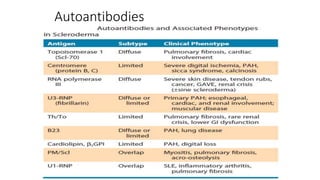
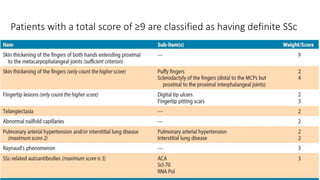
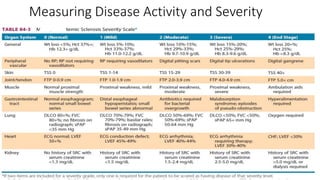
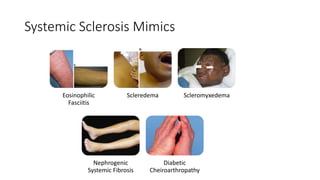
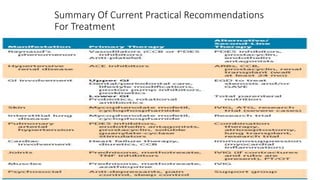
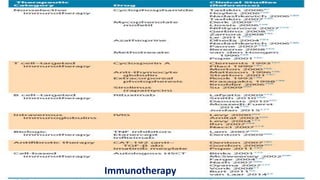
Systemic sclerosis is a rare multisystem connective tissue disease characterized by chronic inflammation, fibrosis, and vasculopathy, primarily affecting skin and internal organs, with a higher incidence in women aged 35-50. The disease presents with various symptoms including skin changes, musculoskeletal issues, organ involvement such as pulmonary and renal complications, and can be classified into localized and diffuse scleroderma. Treatment focuses on managing vascular complications and fibrosis, though no agents currently reverse the fibrotic process, with several novel therapies under investigation.