Systemd is a new init system for Linux that is replacing sysvinit. It aims to address issues with sysvinit like synchronous startup and slow shell scripts. While systemd provides benefits like asynchronous startup of services and use of configuration files, it is also controversial due to concerns about feature creep and being Linux-specific. Many major Linux distributions have adopted systemd as the default init system.














![[Unit] Description=PostgreSQL database serverAfter=network.target[Service] Type=forkingUser=postgresGroup=postgresEnvironment=PGPORT=5432Environment=PGDATA=/var/lib/pgsql/dataOOMScoreAdjust=-1000ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/postgresql-check-db-dir ${PGDATA} ExecStart=/usr/bin/pg_ctl start -D ${PGDATA} -s -o "-p ${PGPORT}" -w -t 300ExecStop=/usr/bin/pg_ctl stop -D ${PGDATA} -s -m fastExecReload=/usr/bin/pg_ctl reload -D ${PGDATA} -sTimeoutSec=300[Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/systemd-mlug-20140614-140924014822-phpapp01/75/Systemd-mlug-20140614-18-2048.jpg)










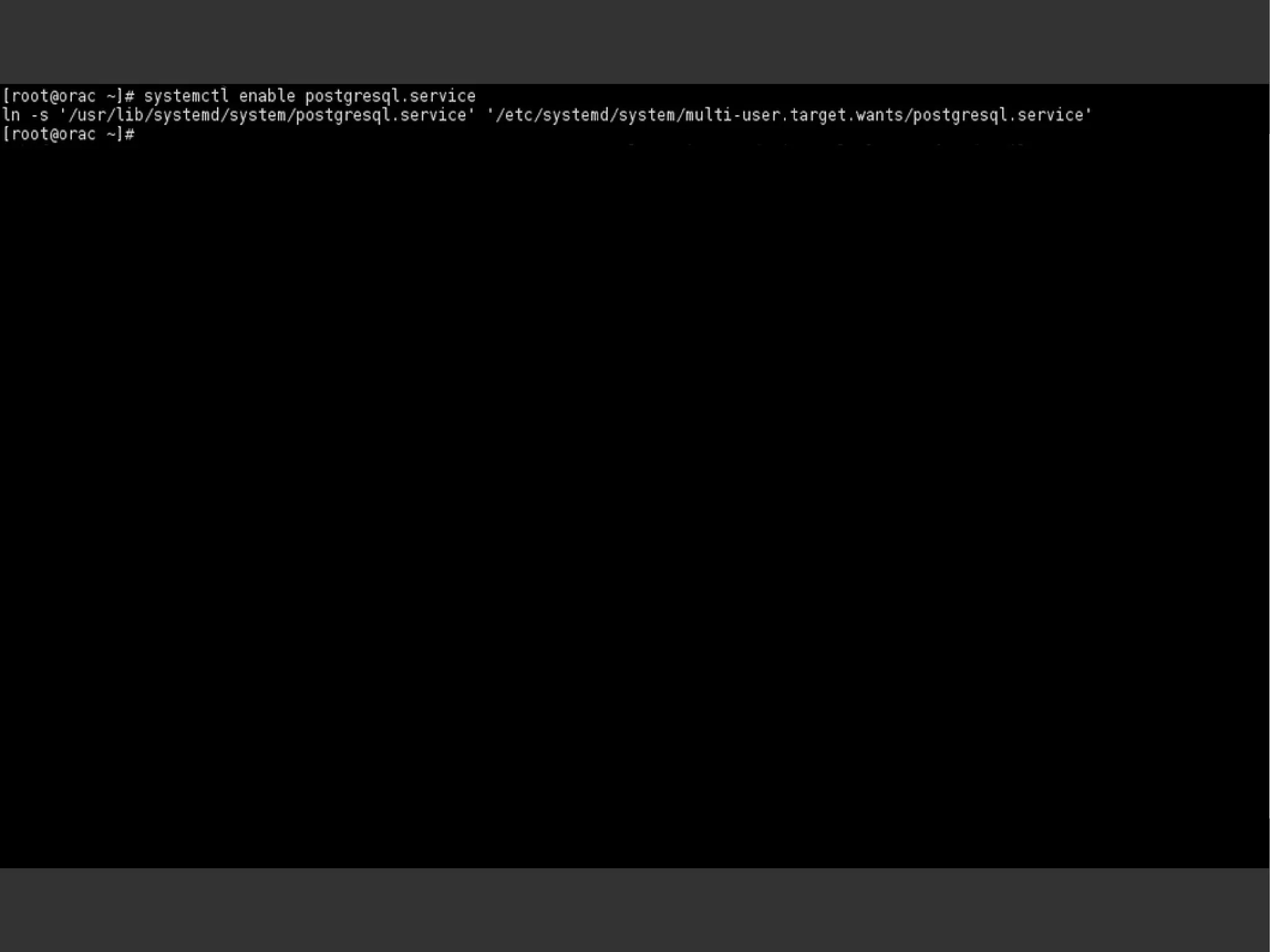
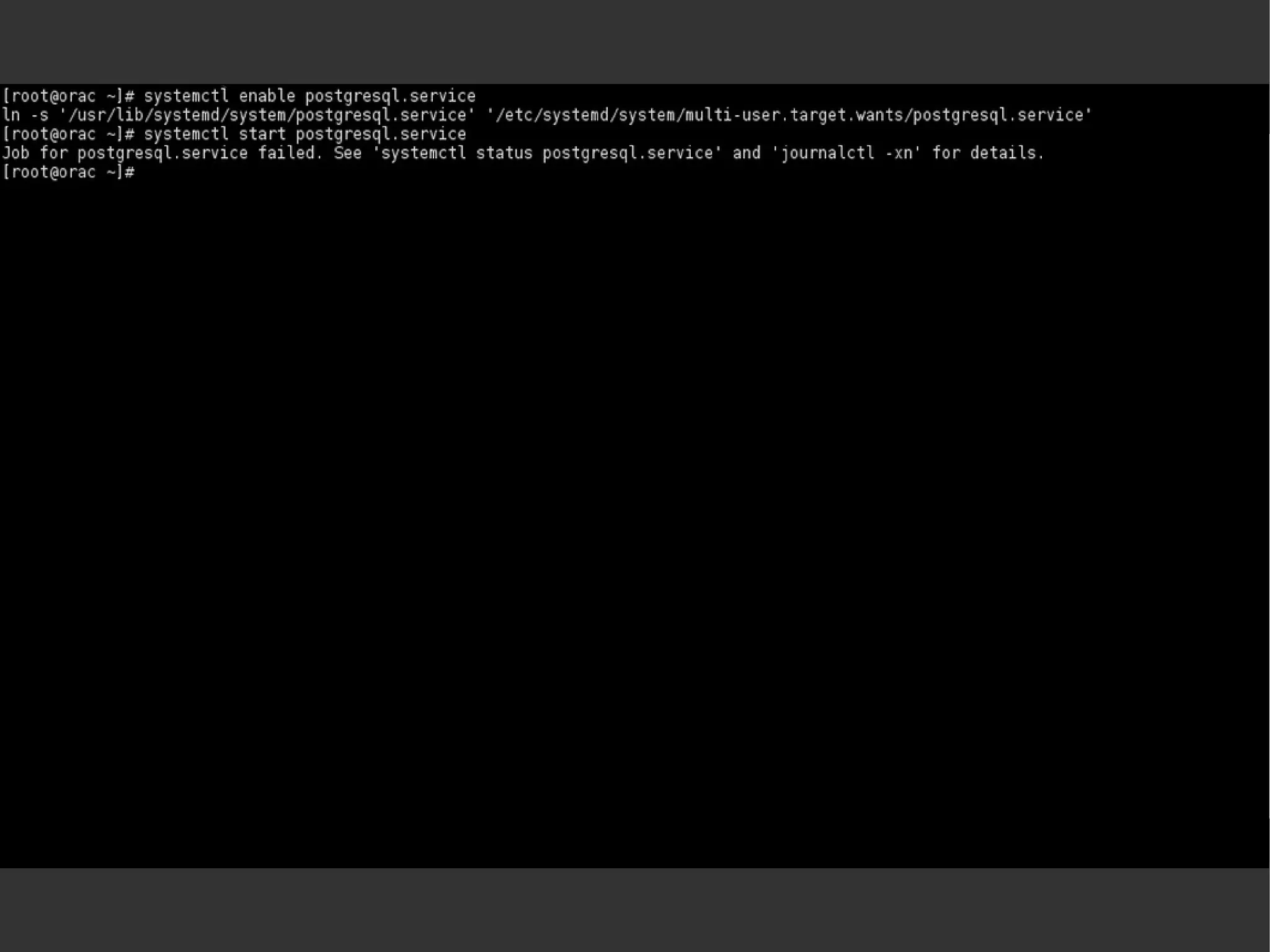
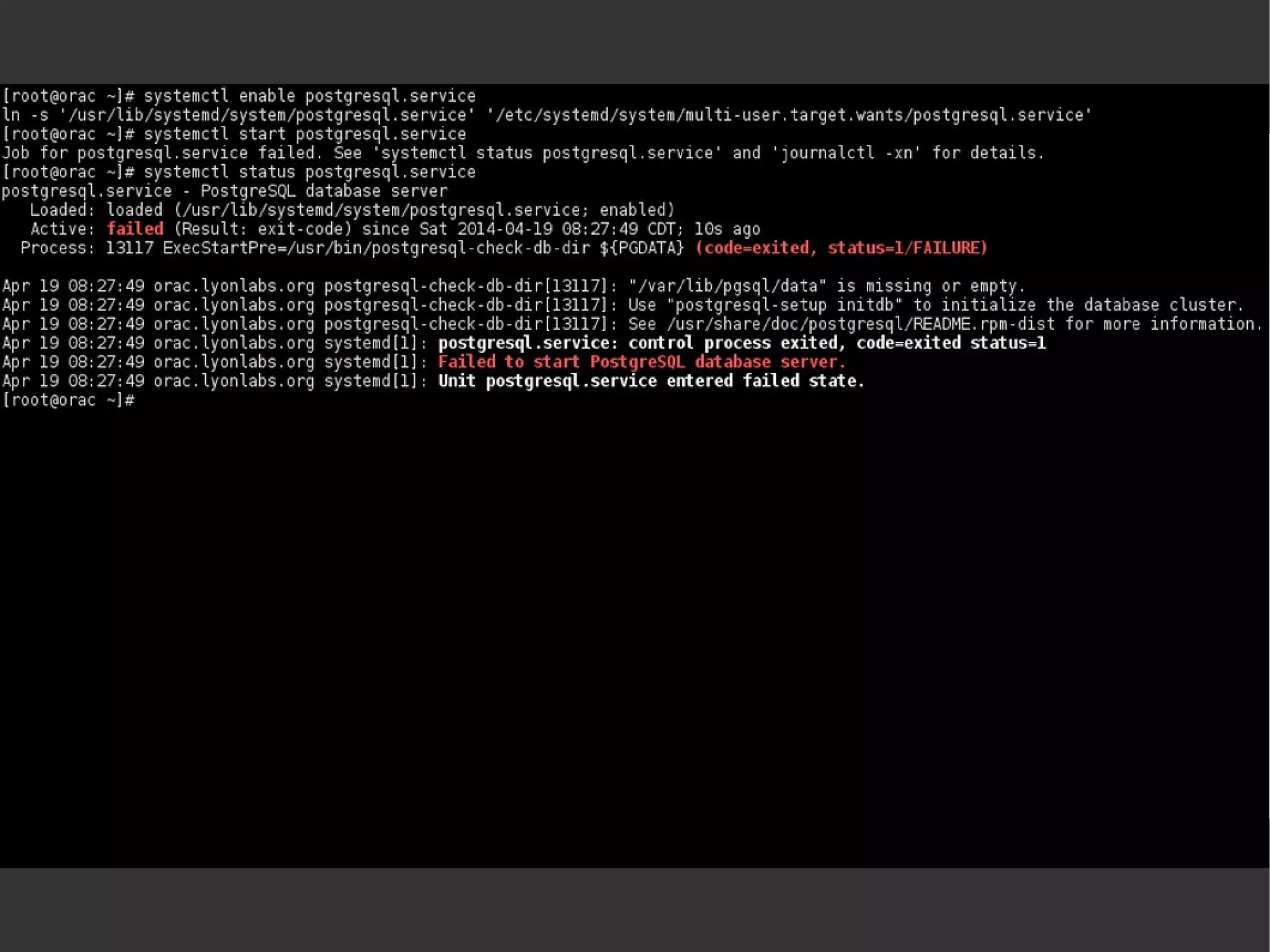
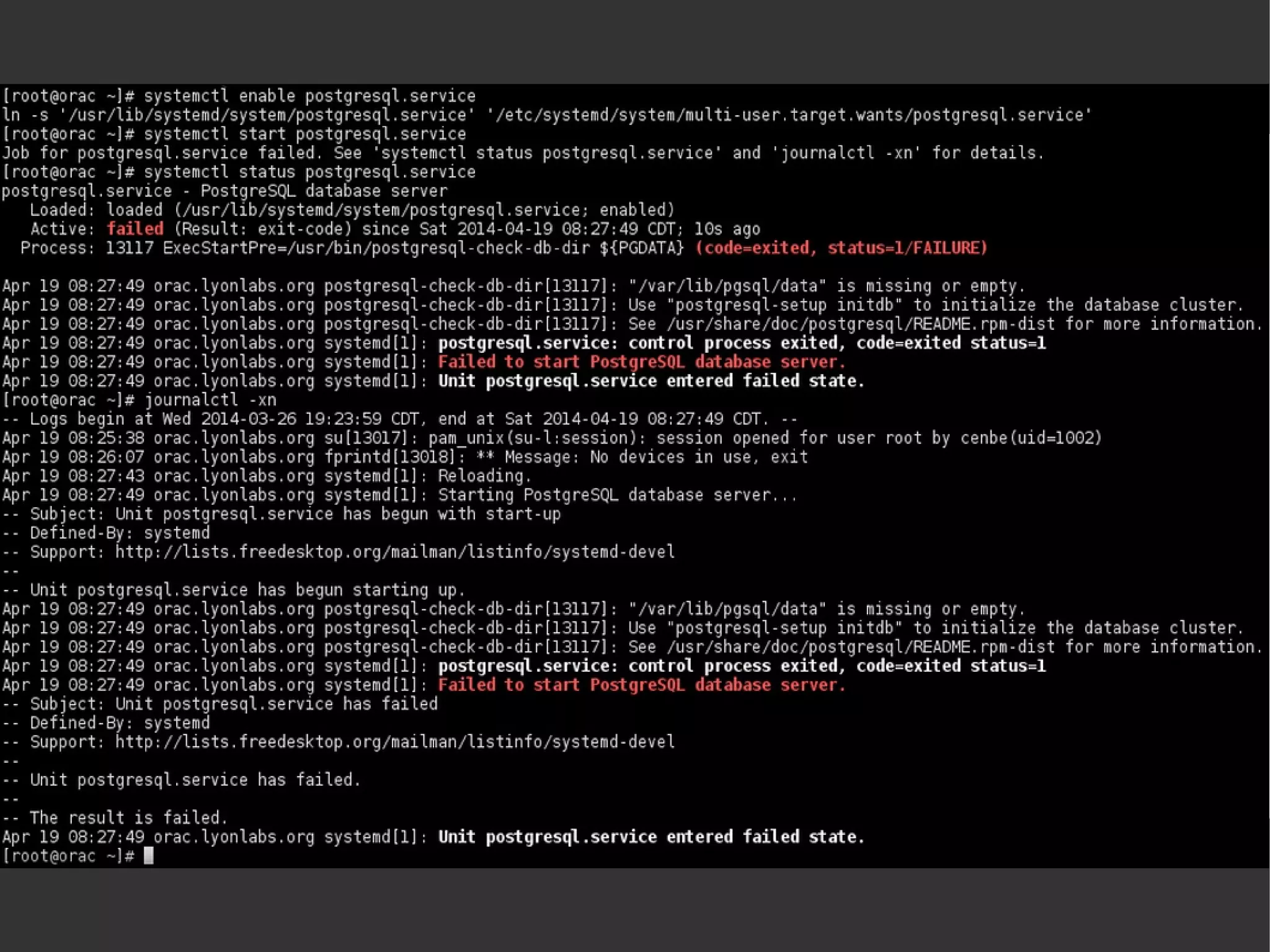
![systemctl [list-units] systemctl list-unit-filessystemctl -t servicesystemctl –-state failedsystemctl enable <servicename> systemctl start <servicename> systemctl status <servicename> systemctl daemon-reloadsystemctl halt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/systemd-mlug-20140614-140924014822-phpapp01/75/Systemd-mlug-20140614-29-2048.jpg)